|
Visual Search
Visual search is a type of perception, perceptual task requiring attention that typically involves an active scan of the visual environment for a particular object or feature (the target) among other objects or features (the distractors). Visual search can take place with or without eye movements. The ability to consciously locate an object or target amongst a complex array of stimuli has been extensively studied over the past 40 years. Practical examples of using visual search can be seen in everyday life, such as when one is picking out a product on a supermarket shelf, when animals are searching for food among piles of leaves, when trying to find a friend in a large crowd of people, or simply when playing visual search games such as ''Where's Wally?'' Much previous literature on visual search used reaction time in order to measure the time it takes to detect the target amongst its distractors. An example of this could be a green square (the target) amongst a set of red circles ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system, which in turn result from physical or chemical stimulation of the sensory system.Goldstein (2009) pp. 5–7 Vision involves light striking the retina of the eye; smell is mediated by odor molecules; and hearing involves pressure waves. Perception is not only the passive receipt of these signals, but it is also shaped by the recipient's learning, memory, expectation, and attention. Gregory, Richard. "Perception" in Gregory, Zangwill (1987) pp. 598–601. Sensory input is a process that transforms this low-level information to higher-level information (e.g., extracts shapes for object recognition). The following process connects a person's concepts and expectations (or knowledge) with restorative and selective mechanisms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-attentive Processing
Pre-attentive processing is the subconscious accumulation of information from the environment.Atienza, M., Cantero, J. L., & Escera, C. (2001). Auditory information processing during human sleep as revealed by event-related brain potentials. Clinical Neurophysiology, 112(11), 2031-2045.Van der Heijden, A. H. C. (1996). Perception for selection, selection for action, and action for perception. Visual Cognition, 3(4), 357-361. All available information is pre-attentively processed. Then, the brain filters and processes what is important. Information that has the highest salience (a stimulus that stands out the most) or relevance to what a person is thinking about is selected for further and more complete analysis by conscious (attentive) processing. Understanding how pre-attentive processing works is useful in advertising, in education, and for prediction of cognitive ability. Pure-capture and contingent-capture The reasons are unclear as to why certain information proceeds from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
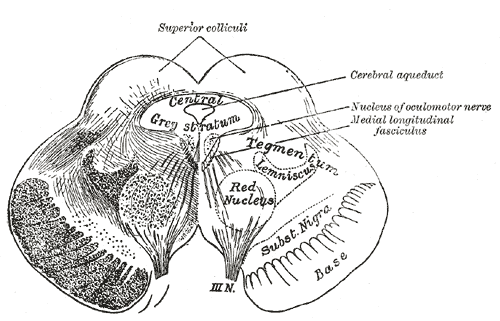
Superior Colliculus
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the tectum, roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the Homology (biology), homologous structure is known as the optic tectum or optic lobe. The adjective form ''tectum, tectal'' is commonly used for both structures. In mammals, the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain. It is a paired structure and together with the paired inferior colliculi forms the corpora quadrigemina. The superior colliculus is a layered structure, with a pattern that is similar in all mammals. The layers can be grouped into the superficial layers (retinal nerve fiber layer, stratum opticum and above) and the deeper remaining layers. Neurons in the superficial layers receive direct input from the retina and respond almost exclusively to visual stimuli. Many neurons in the deeper layers also respond to other modalities, and some respond to stimuli in multiple modalities. The deeper layers also conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vision Research
''Vision Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal specializing in the neuroscience and psychology of the visual system The visual system is the physiological basis of visual perception (the ability to perception, detect and process light). The system detects, phototransduction, transduces and interprets information concerning light within the visible range to ... of humans and other animals. The journal is abstracted and indexed in PubMed. The journal's impact factor for 2020 was 1.886 and its 5-year impact factor was 2.823. References External links * All articles {{neuroscience-journal-stub Vision Neuroscience journals Elsevier academic journals Academic journals established in 1961 Monthly journals English-language journals Perception journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Eye Field
The frontal eye fields (FEF) are a region located in the frontal cortex, more specifically in Brodmann area 8 or BA8, of the primate brain. In humans, it can be more accurately said to lie in a region around the intersection of the middle frontal gyrus with the precentral gyrus, consisting of a frontal and parietal portion. The FEF is responsible for saccadic eye movements for the purpose of visual field perception and awareness, as well as for voluntary eye movement. The FEF communicates with extraocular muscles indirectly via the paramedian pontine reticular formation. Destruction of the FEF causes deviation of the eyes to the ipsilateral side. Function The cortical area called the frontal eye field (FEF) plays an important role in the control of visual attention and eye movements. Electrical stimulation in the FEF elicits saccadic eye movements. The FEF have a topographic structure and represents saccade targets in retinotopic coordinates. The frontal eye field is reported t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body, such as: * Fluorodeoxyglucose ( 18F">sup>18FDG or FDG) is commonly used to detect cancer; * 18Fodium fluoride">sup>18Fodium fluoride (Na18F) is widely used for detecting bone formation; * Oxygen-15 (15O) is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common imaging technique, a medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical—a radioisotope attached to a drug—is injected into the body as a tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is emitted, and when the positron interacts with an ordinary electron, the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can Memory, hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, but some theorists consider the two forms of memory distinct, assuming that working memory allows for the manipulation of stored information, whereas short-term memory only refers to the short-term storage of information. Working memory is a theoretical concept central to cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and neuroscience. History The term "working memory" was coined by George Armitage Miller, Miller, Eugene Galanter, Galanter, and Karl H. Pribram, Pribram, and was used in the 1960s in the context of Computational theory of mind, theories that likened the mind to a computer. In 1968, Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model, Atkinson and Shiffrin used the term to describe their "short-term store". The term short-term store was the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive neurostimulation technique in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current in a targeted area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. A device called a stimulator generates electric pulses that are delivered to a magnetic coil placed against the scalp. The resulting magnetic field penetrates the skull and induces a secondary electric current in the underlying brain tissue, modulating neural activity. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a safe, effective, and FDA-approved treatment for major depressive disorder (approved in 2008), chronic pain (2013), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (2018). It has strong evidence for certain neurological and psychiatric conditions—especially depression (with a large effect size), neuropathic pain, and stroke recovery—and emerging advancements like iTBS and image-guided targeting may improve its efficacy and efficiency. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the 10–20 system (EEG), International 10–20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called Electrocorticography, "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG, quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier, bio amplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal Brain activity and meditation, brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying Huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases. The primary form of fMRI uses the blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast, discovered by Seiji Ogawa in 1990. This is a type of specialized brain and body scan used to map neuron, neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals by imaging the change in blood flow (hemodynamic response) related to energy use by brain cells. Since the early 1990s, fMRI has come to dominate brain mapping research because it does not involve the use of injections, surgery, the ingestion of substances, or exposure to ionizing radiation. This measure is frequently corrupted by noise from various sources; hence, statistical procedures are used to extract the underlying si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
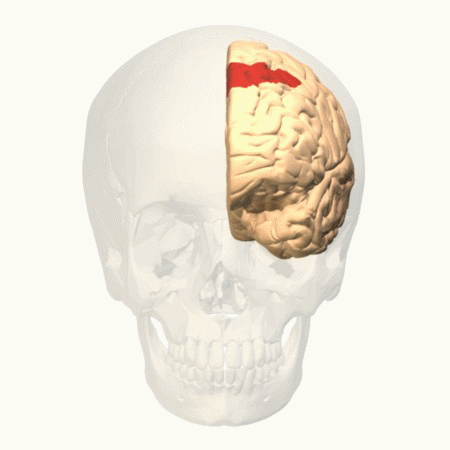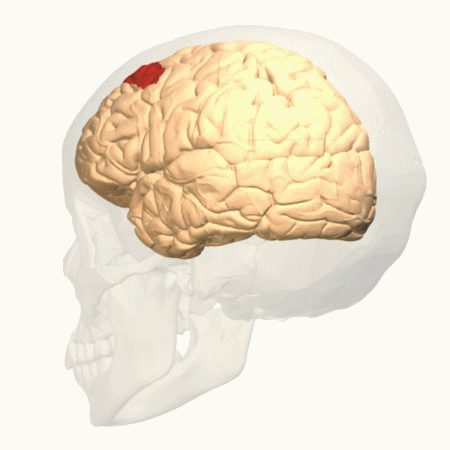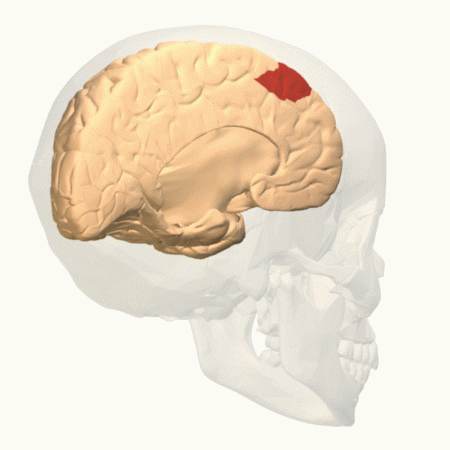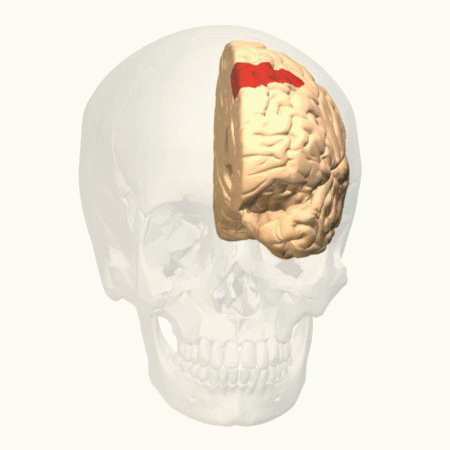
Parietal Cortex
The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus. The parietal lobe integrates sensory information among various modalities, including spatial sense and navigation (proprioception), the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch in the somatosensory cortex which is just posterior to the central sulcus in the postcentral gyrus, and the dorsal stream of the visual system. The major sensory inputs from the skin (touch, temperature, and pain receptors), relay through the thalamus to the parietal lobe. Several areas of the parietal lobe are important in language processing. The somatosensory cortex can be illustrated as a distorted figure – the cortical homunculus (Latin: "little man") in which the body parts are rendered according to how much of the somatosensory cortex is devoted to them. The superior parietal lobule an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |