|
Vernalisation
Vernalization (from Latin ''vernus'', "of the spring") is the induction of a plant's flowering process by exposure to the prolonged cold of winter, or by an artificial equivalent. After vernalization, plants have acquired the ability to flower, but they may require additional seasonal cues or weeks of growth before they will actually flower. The term is sometimes used to refer to the need of herbal (non-woody) plants for a period of cold dormancy in order to produce new shoots and leaves, but this usage is discouraged. Many plants grown in temperate climates require vernalization and must experience a period of low winter temperature to initiate or accelerate the flowering process. This ensures that reproductive development and seed production occurs in spring and winters, rather than in autumn. The needed cold is often expressed in chill hours. Typical vernalization temperatures are between 1 and 7 degrees Celsius (34 and 45 degrees Fahrenheit). For many perennial plants, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoscyamus Niger Hullukaali Bolmört C IMG 7657
''Hyoscyamus'' — known as the henbanes — is a small genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family, Solanaceae. It comprises 11 species, all of which are toxic. It, along with other genera in the same family, is a source of the drug hyoscyamine (daturine).Cruciferous type of stomata present in Hyoscyamus. ''Hyoscyamus'' means "hog-bean" in botanical Latin and was a name derogatorily applied to the plant by Dioscorides Pedanius Dioscorides ( grc-gre, Πεδάνιος Διοσκουρίδης, ; 40–90 AD), “the father of pharmacognosy”, was a Greek physician, pharmacologist, botanist, and author of ''De materia medica'' (, On Medical Material) —a 5-vol ....Gledhill D. 1996. ''The Names of Plants''. Cambridge University Press Selected species References External links {{Authority control Hyoscyameae Solanaceae genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hancock Klippart
John Hancock Klippart (1823–1878) was an American agriculturist and expert on wheat farming. Biography Klippart was born in Canton, Ohio on July 26, 1823. Klippart worked for the Ohio State Board of Agriculture and has been described as the most "informed individual" of his time on wheat culture. He published a large book in 1858 documenting information about wheat plants and farming. Klippart was an early evolutionary thinker to have mentioned the concept of natural selection. According to science historian Conway Zirkle "In 1858, Klippart showed how nature could displace one variety or species of wheat by another." He died at his home in Columbus, Ohio Columbus () is the state capital and the most populous city in the U.S. state of Ohio. With a 2020 census population of 905,748, it is the 14th-most populous city in the U.S., the second-most populous city in the Midwest, after Chicago, and t ... on October 24, 1878. Publications * ''An Essay on the Origin, Growth, Dise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Terminology
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After gathering wild grains beginning at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers began to plant them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. Industrial agriculture based on large-scale monoculture in the twentieth century came to dominate agricultural output, though about 2 billion people still depended on subsistence agriculture. The major agricultural products can be broadly grouped into foods, fibers, fuels, and raw materials (such as rubber). Food classes include cereals (grains), vegetables, fruits, cooking oils, meat, milk, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratification (seeds)
In horticulture, stratification is a process of treating seeds to simulate natural conditions that the seeds must experience before germination can occur. Many seed species have an embryonic dormancy phase, and generally will not sprout until this dormancy is broken. The term stratification can be traced back to at least 1664 in ''Sylva, or A Discourse of Forest-Trees and the Propagation of Timber'', where seeds were layered (stratified) between layers of moist soil and exposing these strata to winter conditions. Thus, stratification became the process by which seeds were artificially exposed to conditions to encourage subsequent germination. Cold stratification Cold stratification is the process of subjecting seeds to both cold and moist conditions. Seeds of many trees, shrubs and perennials require these conditions before germination will ensue. In the wild In the wild, seed dormancy is usually overcome by the seed spending time in the ground through a winter period and having ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
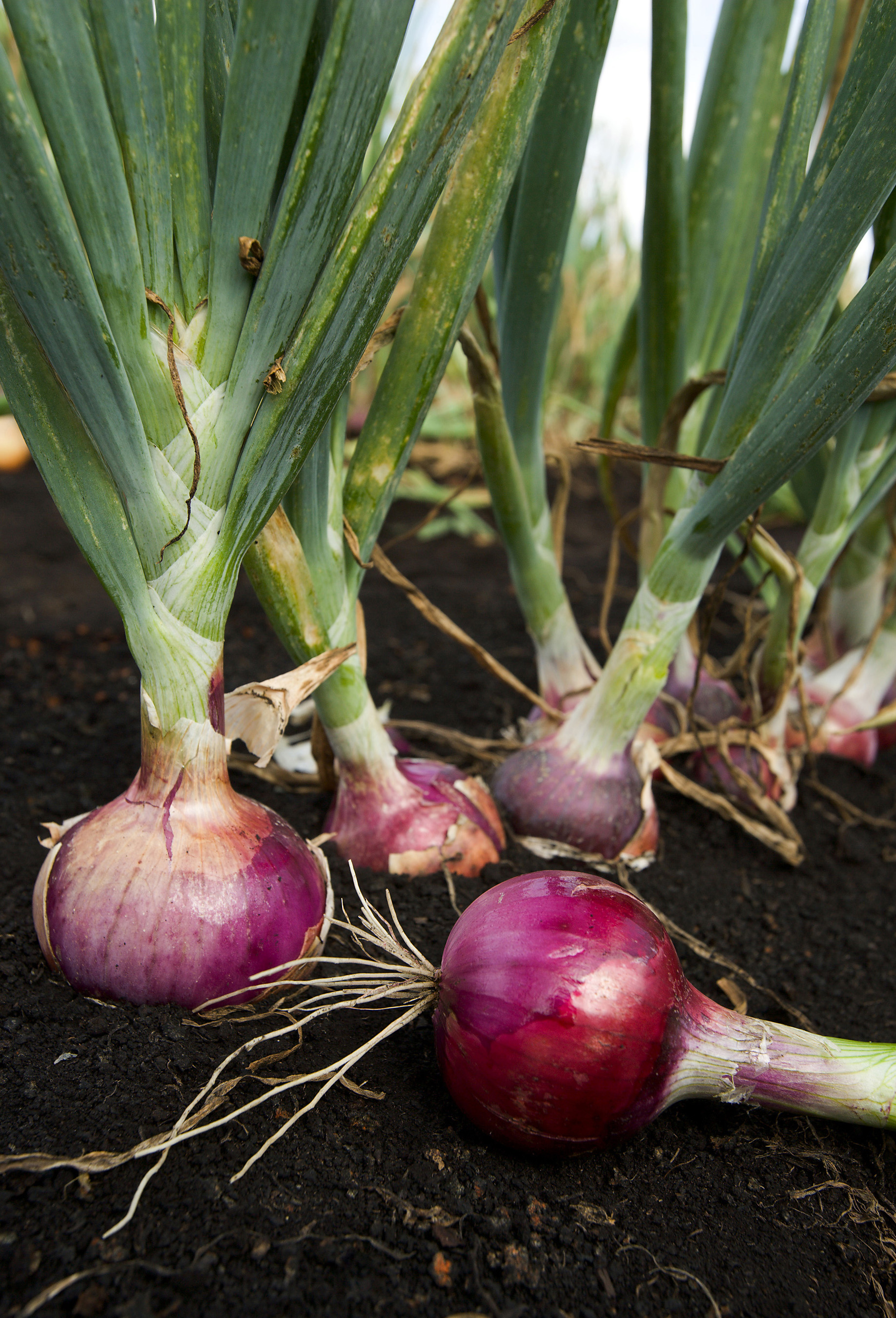
Onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus ''Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onion which was classified as a separate species until 2010. Its close relatives include garlic, scallion, leek, and chive. This genus also contains several other species variously referred to as onions and cultivated for food, such as the Japanese bunching onion (''Allium fistulosum''), the tree onion (''A.'' × ''proliferum''), and the Canada onion (''Allium canadense''). The name ''wild onion'' is applied to a number of ''Allium'' species, but ''A. cepa'' is exclusively known from cultivation. Its ancestral wild original form is not known, although escapes from cultivation have become established in some regions. The onion is most frequently a biennial or a perennial plant, but is usually treated as an annual and harvested in its f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
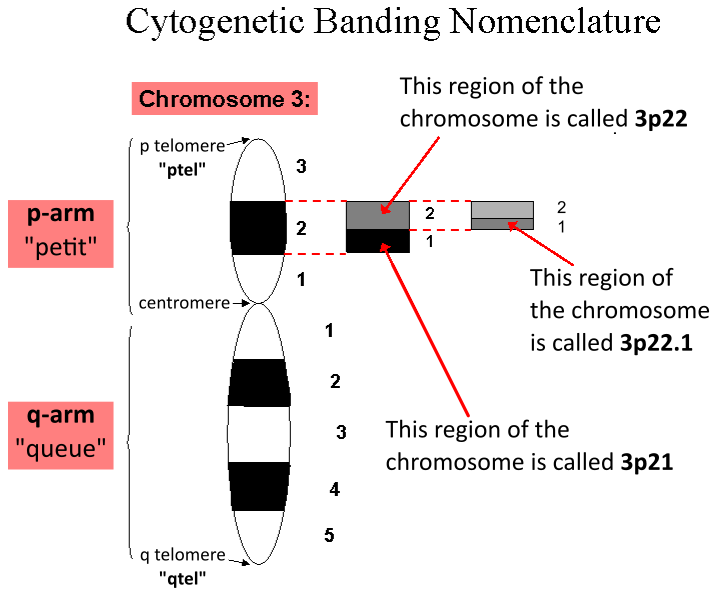
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meristem
The meristem is a type of tissue found in plants. It consists of undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells) capable of cell division. Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants. These cells continue to divide until a time when they get differentiated and then lose the ability to divide. Differentiated plant cells generally cannot divide or produce cells of a different type. Meristematic cells are undifferentiated or incompletely differentiated. They are totipotent and capable of continued cell division. Division of meristematic cells provides new cells for expansion and differentiation of tissues and the initiation of new organs, providing the basic structure of the plant body. The cells are small, with no or small vacuoles and protoplasm fills the cell completely. The plastids (chloroplasts or chromoplasts), are undifferentiated, but are present in rudimentary form (proplastids). Meristematic cells are packed closely together wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolting (horticulture)
Bolting is the production of a flowering stem (or stems) on agricultural and horticultural crops before the crop is harvested, in a natural attempt to produce seeds and reproduce. These flowering stems are usually vigorous extensions of existing leaf-bearing stems, and to produce them, a plant diverts resources from producing the edible parts such as leaves or roots, resulting in flavor and texture changes, withering, and in general, a poor quality harvest. Plants that have produced flowering stems in this way are said to have bolted. Crops inclined to bolt include lettuce, basil, beetroot, brassicas, spinach, celery, onion, and leek. Bolting is induced by plant hormones of the gibberellin family, and can occur as a result of several factors, including changes in day length, the prevalence of high temperatures at particular stages in a plant's growth cycle, and the existence of stresses such as insufficient water or minerals. These factors may interact in a complex way. Day length m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis Thaliana Rosette
''Arabidopsis'' (rockcress) is a genus in the family Brassicaceae. They are small flowering plants related to cabbage and mustard. This genus is of great interest since it contains thale cress (''Arabidopsis thaliana''), one of the model organisms used for studying plant biology and the first plant to have its entire genome sequenced. Changes in thale cress are easily observed, making it a very useful model. Status Currently, the genus ''Arabidopsis'' has nine species and a further eight subspecies recognised. This delimitation is quite recent and is based on morphological and molecular phylogenies by O'Kane and Al-Shehbaz and others. Their findings confirm the species formerly included in ''Arabidopsis'' made it polyphyletic. The most recent reclassification moves two species previously placed in ''Cardaminopsis'' and ''Hylandra'' and three species of ''Arabis'' into ''Arabidopsis'', but excludes 50 that have been moved into the new genera ''Beringia, Crucihimalaya, Ianhedgea, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigenetics
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in addition to" the traditional genetic basis for inheritance. Epigenetics most often involves changes that affect the regulation of gene expression, but the term can also be used to describe any heritable phenotypic change. Such effects on cellular and physiological phenotypic traits may result from external or environmental factors, or be part of normal development. The term also refers to the mechanism of changes: functionally relevant alterations to the genome that do not involve mutation of the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification, each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Gene expression c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Science
''Annals of Science'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering the history of science and technology. It is published by Taylor & Francis and was established in 1936. The founding editor-in-chief was the Canadian historian of science Harcourt Brown.R.E.W. MaddisonIndex to Volumes 1 to 25 (1936-1969). ''Annals of Science''. History The journal was established after Brown visited Britain for a year and discussed where he could publish work on the history of science with Henry Robinson of the library of the Royal Society of London. They decided that aside from the Belgian ''Isis'', there were few outlets for such work, and so founded the ''Annals of Science'' with Douglas McKie (University College London), who was the main editor. The aim was to publish faster than ''Isis'' and with a focus on the modern period. The editors chose to have a bright orange cover to make it stand out against the usual blue or grey of periodicals at the time. Around the time of World War II, only th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Physiology
Plant physiology is a subdiscipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology (structure of plants), plant ecology (interactions with the environment), phytochemistry (biochemistry of plants), cell biology, genetics, biophysics and molecular biology. Fundamental processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, plant nutrition, plant hormone functions, tropisms, nastic movements, photoperiodism, photomorphogenesis, circadian rhythms, environmental stress physiology, seed germination, dormancy and stomata function and transpiration, both parts of plant water relations, are studied by plant physiologists. Aims The field of plant physiology includes the study of all the internal activities of plants—those chemical and physical processes associated with life as they occur in plants. This includes study at many levels of scale of size and time. At the smallest scale are molecular interactions of photosynthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |