|
Value Network Analysis
Value network analysis (VNA) is a methodology for understanding, using, visualizing, optimizing internal and external value networks and complex economic ecosystems.Biem, Alain, and Nathan Caswell. "A Value Network Model for Strategic Analysis." ''HICSS. 2008.'' The methods include visualizing sets of relationships from a dynamic whole systems perspective. Robust network analysis approaches are used for understanding value conversion of financial and non-financial assets, such as intellectual capital, into other forms of value. Allee, Verna. "Value Network Analysis and Value Conversion of Tangible and Intangible Assets." Journal of Intellectual Capital. Publisher: Emerald Insights, Year: 2008, Volume: 9, Issue: 1, Page: 5 - 24, Digital Object Identifier: The value conversion question is critical in both social exchange theory that considers the cost/benefit returns of informal exchanges and more classical views of exchange value where there is concern with conversion of value into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value Network
A value network is a graphical illustration of social and technical resources within/between organizations and how they are utilized. The nodes in a value network represent people or, more abstractly, roles. The nodes are connected by interactions that represent deliverables. These deliverables can be objects, knowledge or money. Value networks record interdependence. They account for the worth of products and services. Companies have both internal and external value networks. Types External networks include customers/recipients, intermediaries, stakeholders, complementary, open innovation networks and suppliers. Internal networks focus on key activities, processes and relationships that cut across internal boundaries, such as order fulfillment, innovation, lead processing and customer support. Value is created through exchange and the relationships between roles. Definition Christensen defines value network as: "The collection of upstream suppliers, downstream channels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value Added
In business, total value added is calculated by tabulating the unit value added (measured by summing unit profit sale price and production cost">Price.html" ;"title="he difference between Price">sale price and production cost], unit depreciation cost, and unit Direct labor cost, labor cost) per each unit of product sold. Thus, total value added is equivalent to revenue minus intermediate consumption. Value added is a higher portion of revenue for integrated companies (e.g. manufacturing companies) and a lower portion of revenue for less integrated companies (e.g. retail companies); total value added is very closely approximated by compensation of employees, which represents a return to labor, plus earnings before taxes, representative of a return to capital. In economics, specifically macroeconomics, the term value added refers to the contribution of the factors of production (i.e. capital and labor) to raise the value of the product and increase the income of those who own the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value Shop
A value shop is an organization designed to solve customer or client problems, rather than creating value by producing output from an input of raw materials. The principles of value shops were first conceptualized by Thompson in 1967, and properly defined by Charles B. Stabell and Øystein D. Fjeldstad of the Norwegian School of Management in 1998, who also created the name. Compared to Michael Porter's concept of the value chain, there is no sequential fixed set of activities or resources utilized to create value. Each problem is treated uniquely and activities and resources are allocated specifically to cater to the problem in question. According to the research of Stabell and Fjeldstad, the value configuration analysis (1998), five main generic activities are carried out in the organization: * Problem Finding and acquisition * Problem Solving * Choice of problem solution * Execution of solution * Control and evaluation Value is created in the shop by several mechanisms allowi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value Network
A value network is a graphical illustration of social and technical resources within/between organizations and how they are utilized. The nodes in a value network represent people or, more abstractly, roles. The nodes are connected by interactions that represent deliverables. These deliverables can be objects, knowledge or money. Value networks record interdependence. They account for the worth of products and services. Companies have both internal and external value networks. Types External networks include customers/recipients, intermediaries, stakeholders, complementary, open innovation networks and suppliers. Internal networks focus on key activities, processes and relationships that cut across internal boundaries, such as order fulfillment, innovation, lead processing and customer support. Value is created through exchange and the relationships between roles. Definition Christensen defines value network as: "The collection of upstream suppliers, downstream channels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Dynamics
System dynamics (SD) is an approach to understanding the nonlinear behaviour of complex systems over time using stocks, flows, internal feedback loops, table functions and time delays. Overview System dynamics is a methodology and mathematical modeling technique to frame, understand, and discuss complex issues and problems. Originally developed in the 1950s to help corporate managers improve their understanding of industrial processes, SD is currently being used throughout the public and private sector for policy analysis and design. Convenient graphical user interface (GUI) system dynamics software developed into user friendly versions by the 1990s and have been applied to diverse systems. SD models solve the problem of simultaneity (mutual causation) by updating all variables in small time increments with positive and negative feedbacks and time delays structuring the interactions and control. The best known SD model is probably the 1972 '' The Limits to Growth''. This model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
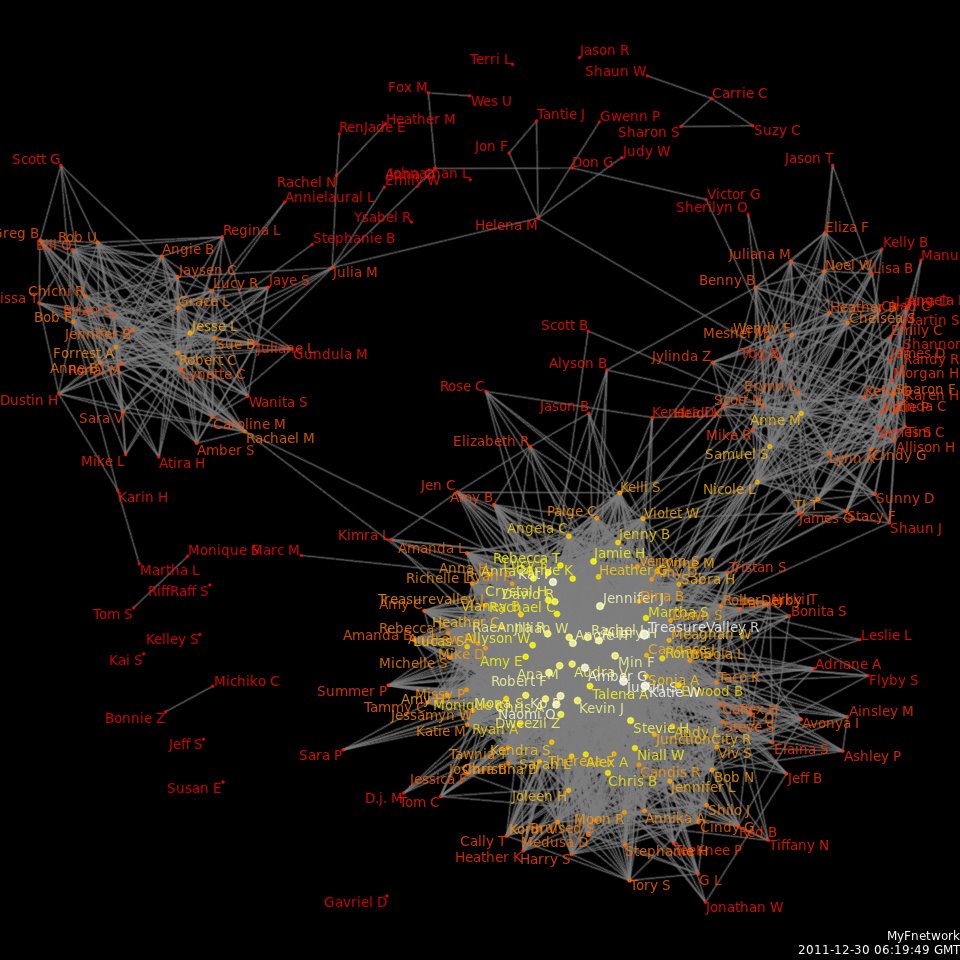
Social Network Analysis
Social network analysis (SNA) is the process of investigating social structures through the use of networks and graph theory. It characterizes networked structures in terms of ''nodes'' (individual actors, people, or things within the network) and the ''ties'', ''edges'', or ''links'' (relationships or interactions) that connect them. Examples of social structures commonly visualized through social network analysis include social media networks, memes spread, information circulation, friendship and acquaintance networks, business networks, knowledge networks, difficult working relationships, social networks, collaboration graphs, kinship, disease transmission, and sexual relationships. These networks are often visualized through '' sociograms'' in which nodes are represented as points and ties are represented as lines. These visualizations provide a means of qualitatively assessing networks by varying the visual representation of their nodes and edges to reflect attributes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Process Management
Business process management (BPM) is the discipline in which people use various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, optimize, and automate business processes. Any combination of methods used to manage a company's business processes is BPM. Processes can be structured and repeatable or unstructured and variable. Though not required, enabling technologies are often used with BPM. It can be differentiated from program management in that program management is concerned with managing a group of inter-dependent projects. From another viewpoint, process management includes program management. In project management, process management is the use of a repeatable process to improve the outcome of the project. Key distinctions between process management and project management are repeatability and predictability. If the structure and sequence of work is unique, then it is a project. In business process management, a sequence of work can vary from instance to instanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Process Reengineering
Business process re-engineering (BPR) is a business management strategy originally pioneered in the early 1990s, focusing on the analysis and design of workflows and business processes within an organization. BPR aims to help organizations fundamentally rethink how they do their work in order to improve customer service, cut operational costs, and become world-class competitors.Business Process Re-engineering Assessment Guide United States General Accounting Office, May 1997. BPR seeks to help companies radically restructure their organizations by focusing on the ground-up design of their business processes. According to early BPR proponent (1990), a bus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workflow
A workflow consists of an orchestrated and repeatable pattern of activity, enabled by the systematic organization of resources into processes that transform materials, provide services, or process information. It can be depicted as a sequence of operations, the work of a person or group, the work of an organization of staff, or one or more simple or complex mechanisms. From a more abstract or higher-level perspective, workflow may be considered a view or representation of real work. The flow being described may refer to a document, service, or product that is being transferred from one step to another. Workflows may be viewed as one fundamental building block to be combined with other parts of an organization's structure such as information technology, teams, projects and hierarchies. Historical development The development of the concept of a workflow occurred above a series of loosely defined, overlapping eras. Beginnings in manufacturing The modern history of workflow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is a production method aimed primarily at reducing times within the production system as well as response times from suppliers and to customers. It is closely related to another concept called just-in-time manufacturing (JIT manufacturing in short). Just-in-time manufacturing tries to match production to demand by only supplying goods which have been ordered and focuses on efficiency, productivity (with a commitment to continuous improvement) and reduction of "wastes" for the producer and supplier of goods. Lean manufacturing adopts the just-in-time approach and additionally focuses on reducing cycle, flow and throughput times by further eliminating activities which do not add any value for the customer. Lean manufacturing also involves people who work outside of the manufacturing process, such as in marketing and customer service. Lean manufacturing is particularly related to the operational model implemented in the post-war 1950s and 1960s by the J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value Chain
A value chain is a progression of activities that a firm operating in a specific industry performs in order to deliver a valuable product (i.e., good and/or service) to the end customer. The concept comes through business management and was first described by Michael Porter in his 1985 best-seller, ''Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance''. The concept of value chains as decision support tools, was added onto the competitive strategies paradigm developed by Porter as early as 1979. In Porter's value chains, Inbound Logistics, Operations, Outbound Logistics, Marketing and Sales, and Service are categorized as primary activities. Secondary activities include Procurement, Human Resource management, Technological Development and Infrastructure . According to the OECD Secretary-General the emergence of global value chains (GVCs) in the late 1990s provided a catalyst for accelerated change in the landscape of international investment and trade, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |