|
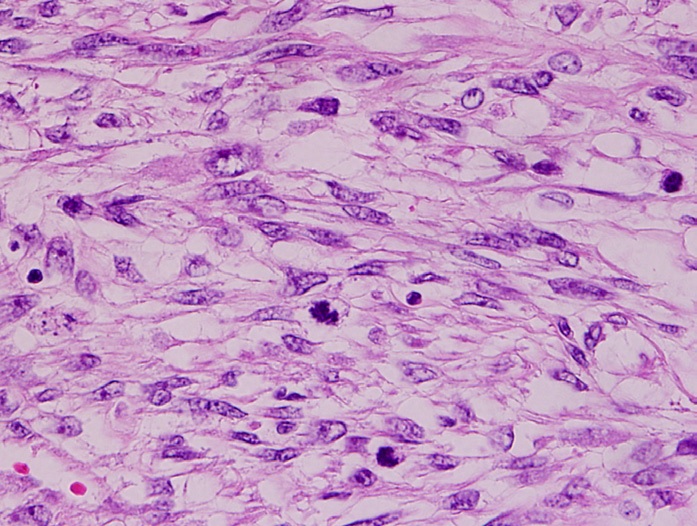
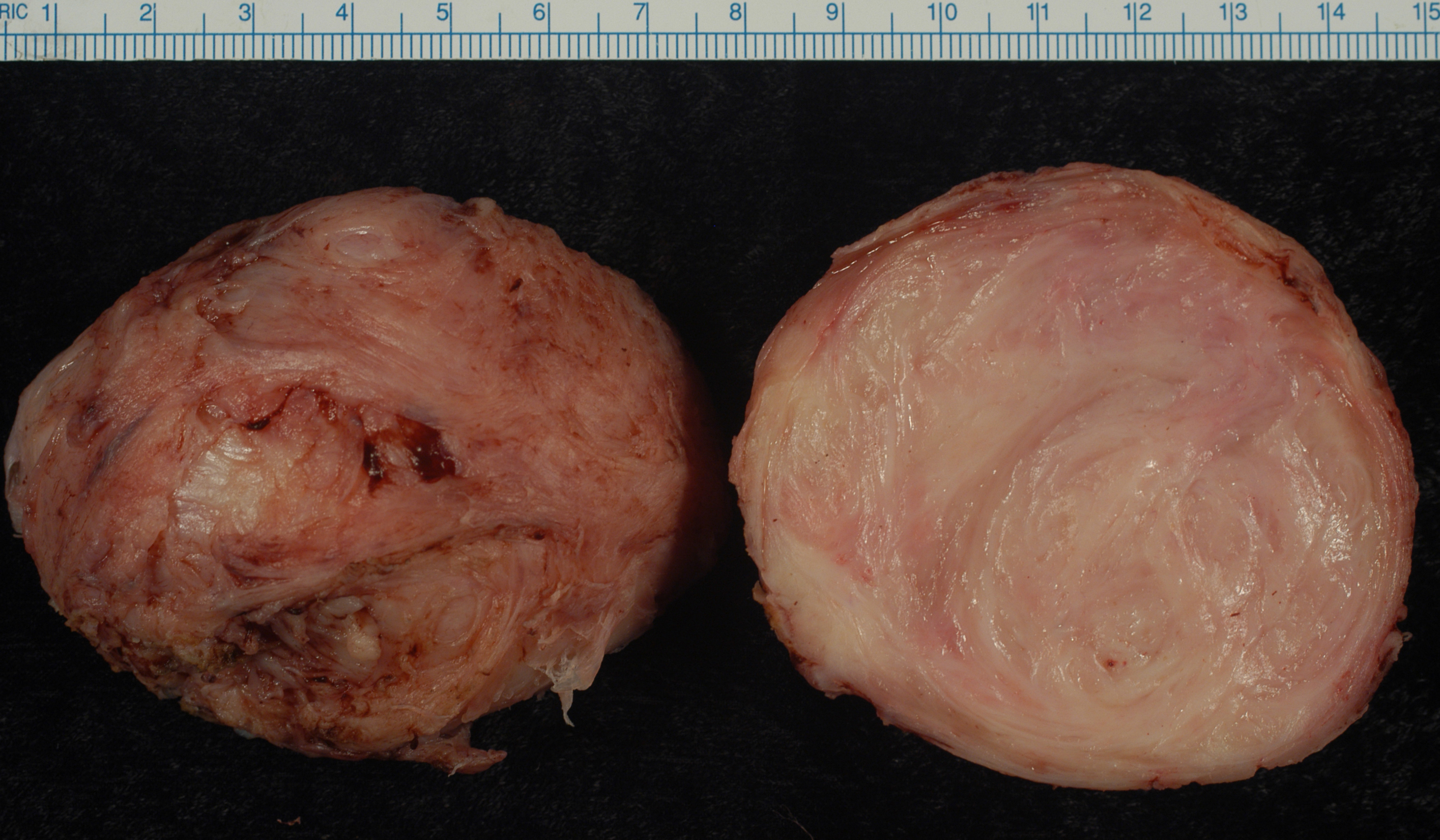
Uterine Sarcoma
The uterine sarcomas form a group of malignant tumors that arises from the smooth muscle or connective tissue of the uterus. Signs and symptoms Clinically, uterine sarcomas and leiomyomas (fibroids) both have similar symptoms such as increased uterine size, abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding so it can be difficult to tell them apart. Unusual or postmenopausal bleeding may be a sign of uterine sarcoma and needs to be investigated. Other signs include pelvic pain, pressure, and unusual discharge. A nonpregnant uterus that enlarges quickly is suspicious. However, none of the signs are specific. Specific screening test have not been developed; a Pap smear is a screening test for cervical cancer and not designed to detect uterine sarcoma. Histology Tumoral entities include leiomyosarcomas, endometrial stromal sarcomas, carcinosarcomas and "other" sarcomas. * If the lesion originates from the stroma of the uterine lining it is an endometrial stromal sarcoma. * If the uterine musc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry to measure X-ray attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979 Nob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
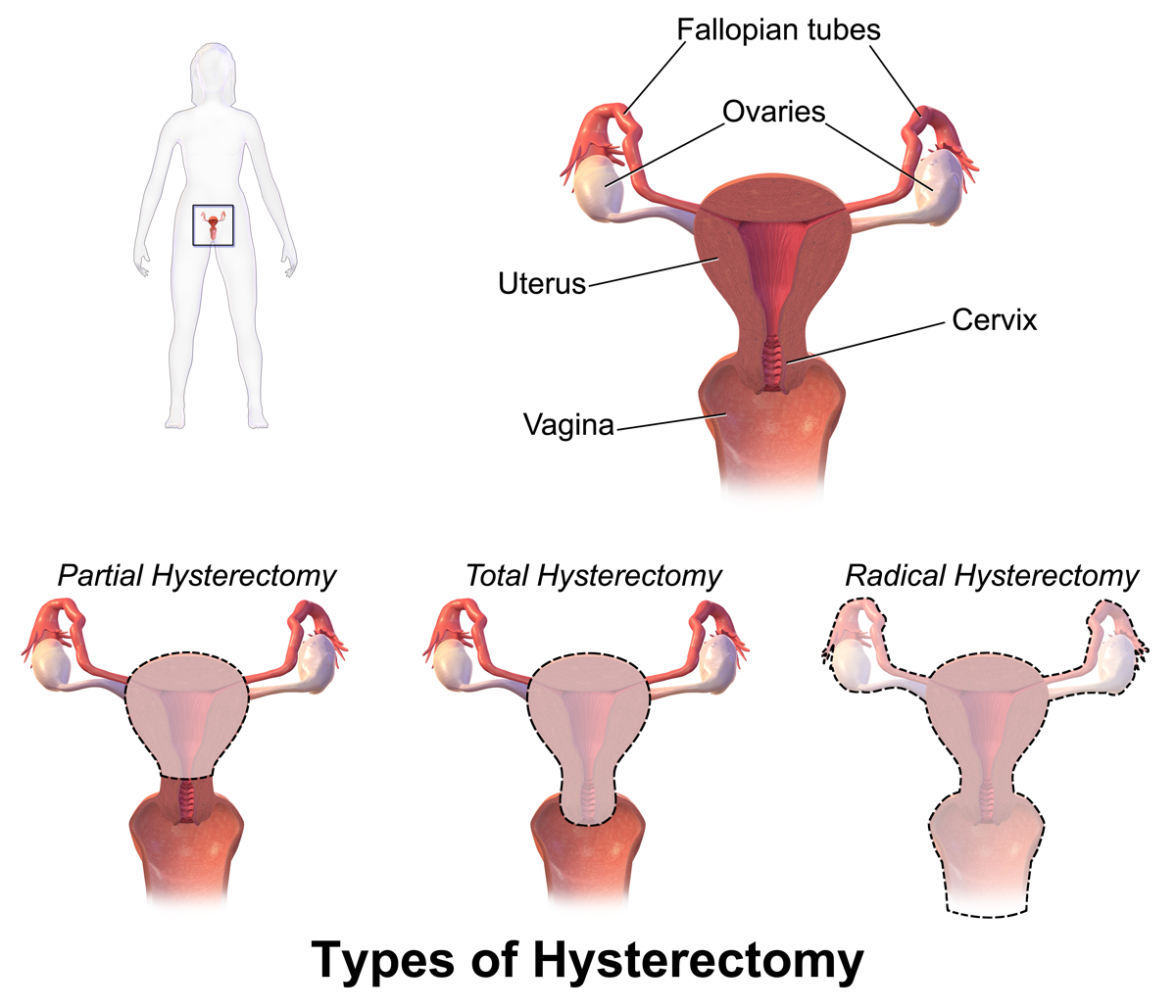
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus. It may also involve removal of the cervix, ovaries (oophorectomy), Fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and other surrounding structures. Usually performed by a gynecologist, a hysterectomy may be total (removing the body, fundus, and cervix of the uterus; often called "complete") or partial (removal of the uterine body while leaving the cervix intact; also called "supracervical"). Removal of the uterus renders the patient unable to bear children (as does removal of ovaries and fallopian tubes) and has surgical risks as well as long-term effects, so the surgery is normally recommended only when other treatment options are not available or have failed. It is the second most commonly performed gynecological surgical procedure, after cesarean section, in the United States. Nearly 68 percent were performed for conditions such as endometriosis, irregular bleeding, and uterine fibroids. It is expected that the frequency of hysterectom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraaortic Lymph Node
The periaortic lymph nodes (also known as lumbar) are a group of lymph nodes that lie in front of the lumbar vertebrae near the aorta. These lymph nodes receive drainage from the gastrointestinal tract and the abdominal organs. The periaortic lymph nodes are different from the paraaortic lymph nodes. The periaortic group is the general group, that is subdivided into: preaortic, paraaortic, and retroaortic groups. The paraaortic group is synonymous with the lateral aortic group. Divisions The periaortic lymph node group is divided into three subgroups: preaortic, paraaortic, and retroaortic: * The preaortic group drains the gastrointestinal viscera. They can be subdivided into three groups: the celiac nodes, the superior mesenteric nodes, and the inferior mesenteric nodes. *The paraaortic group (also known as lateral aortic group) drains the iliac nodes, the ovaries, the testes and other pelvic organs. The lateral group nodes are located adjacent to the aorta, anterior to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Müllerian Tumor
A malignant mixed Müllerian tumor, also known as malignant mixed mesodermal tumor (MMMT) is a cancer found in the uterus, the ovaries, the fallopian tubes and other parts of the body that contains both carcinomatous (epithelial tissue) and sarcomatous (connective tissue) components. It is divided into two types, homologous (in which the sarcomatous component is made of tissues found in the uterus such as endometrial, fibrous and/or smooth muscle tissues) and a heterologous type (made up of tissues not found in the uterus, such as cartilage, skeletal muscle and/or bone). MMMT account for between two and five percent of all tumors derived from the body of the uterus, and are found predominantly in postmenopausal women with an average age of 66 years. Risk factors are similar to those of adenocarcinomas and include obesity, exogenous estrogen therapies, and nulliparity. Less well-understood but potential risk factors include tamoxifen therapy and pelvic irradiation. Classificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
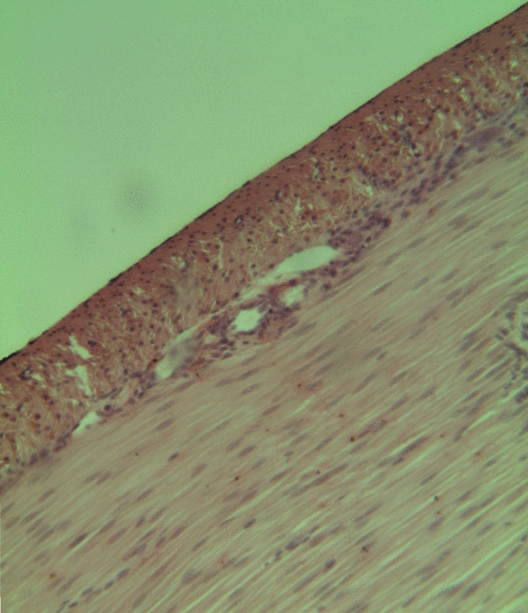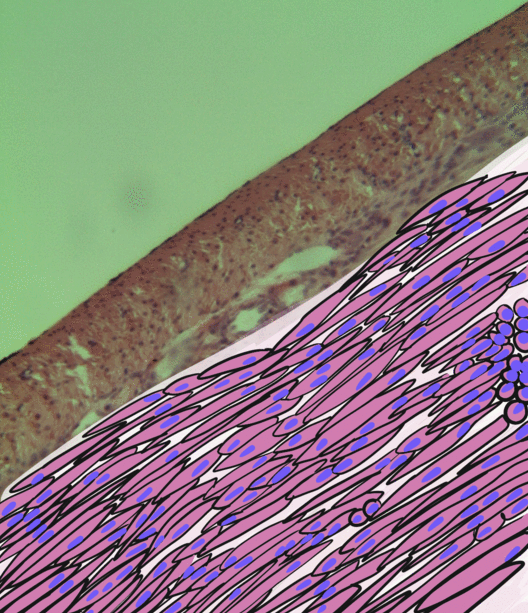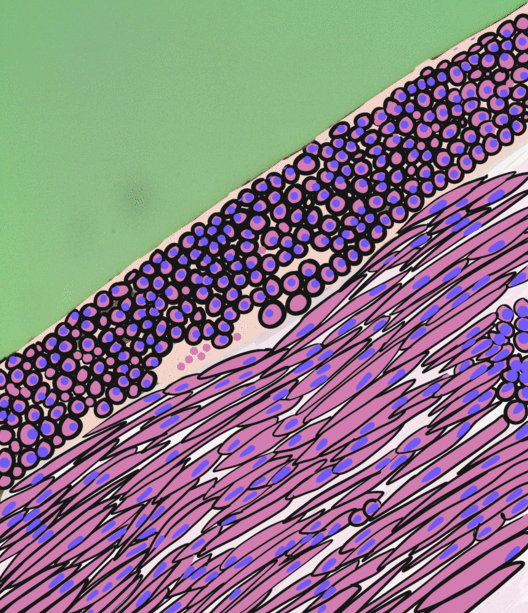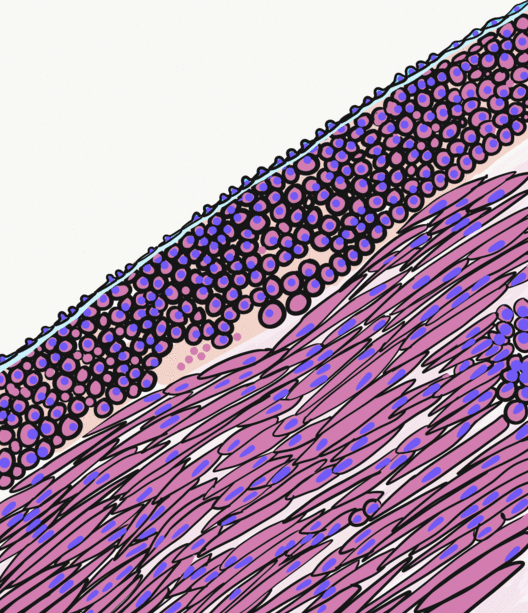
Uterine Adenosarcoma
Uterine adenosarcoma is an uncommon form of cancer that arises from mesenchymal tissue of the uterus and has a benign glandular component. Signs and symptoms The most common presentation is vaginal bleeding. Other presentations include pelvic mass and uterine polyp. Generally, the clinical findings are non-specific. Pathology Uterine adenosarcoma have, by definition, a malignant stroma and benign glandular elements. The World Health Organization (WHO) criteria have a mitotic rate cut point; however, this is often disregarded, as bland-appearing tumours with a low mitotic rate are known to metastasize occasionally. Image: Uterine adenosarcoma - low mag.jpg , Low mag. Image: Uterine adenosarcoma - add - intermed mag.jpg , Intermed. mag. Image: Uterine adenosarcoma - very high mag.jpg , Very high mag. Treatment Uterine adenosarcomas are typically treated with a total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingoophorectomy (TAH-BSO). Ovary-sparing surgery may be done in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma
Endometrial stromal sarcoma is a malignant subtype of endometrial stromal tumor arising from the stroma (connective tissue) of the endometrium rather than the glands. There are three grades for endometrial stromal tumors, as follows. It was previously known as ''endolymphatic stromal myosis'' because of diffuse infiltration of myometrial tissue or the invasion of lymphatic channels. Low-grade endometrial stromal sarcoma Low-grade endometrial stromal sarcoma consists of cells resembling normal proliferative phase endometrium, but with infiltration or vascular invasion. These behave less aggressively, sometimes metastasizing, with cancer stage the best predictor of survival. The cells express estrogen/progesterone-receptors. Undifferentiated uterine sarcoma Undifferentiated uterine sarcoma, or undifferentiated (high-grade) endometrial stromal sarcoma, does not resemble normal endometrial stroma and behaves much more aggressively, frequently metastasizing. The differential incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adnexa Of Uterus
The uterine appendages (or adnexa of uterus) are the structures most closely related structurally and functionally to the uterus. Terminology They can be defined in slightly different ways: * Some sources define the adnexa as the fallopian tubes and ovaries. * Others include the supporting tissues". * Another source defines the appendages as the "regions of the true pelvis posterior to the broad ligaments". * One dictionary includes the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and ligaments (without specifying precisely which ligaments are included). Clinical significance The term "adnexitis" is sometimes used to describe an inflammation of the uterine appendages (adnexa). In this context, it replaces the terms oophoritis and salpingitis. The term adnexal mass is sometimes used when the location of a uterine mass is not yet more precisely known. 63% of ectopic pregnancies present with an adnexal mass. Depending on the size of the mass, it could be a medical emergency. Term "Adnexectomy" in Gy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiomyosarcoma
Leiomyosarcoma is a malignant (cancerous) smooth muscle tumor. A benign tumor originating from the same tissue is termed leiomyoma. While leiomyosarcomas are not thought to arise from leiomyomas, some leiomyoma variants' classification is evolving. About one in 100,000 people are diagnosed with leiomyosarcoma (LMS) each year. LMS is one of the more common types of soft-tissue sarcoma, representing 10 to 20% of new cases. (Leiomyosarcoma of the bone is more rare.) Sarcoma is rare, consisting of only 1% of cancer cases in adults. Leiomyosarcomas can be very unpredictable; they can remain dormant for long periods of time and recur after years. It is a resistant cancer, meaning generally not very responsive to chemotherapy or radiation. The best outcomes occur when it can be removed surgically with wide margins early, while small and still ''in situ''. Mechanism Smooth muscle cells make up the involuntary muscles, which are found in most parts of the body, including the uterus, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Leiomyoma
Uterine fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas or fibroids, are benign smooth muscle tumors of the uterus. Most women with fibroids have no symptoms while others may have painful or heavy periods. If large enough, they may push on the bladder, causing a frequent need to urinate. They may also cause pain during penetrative sex or lower back pain. A woman can have one uterine fibroid or many. Occasionally, fibroids may make it difficult to become pregnant, although this is uncommon. The exact cause of uterine fibroids is unclear. However, fibroids run in families and appear to be partly determined by hormone levels. Risk factors include obesity and eating red meat. Diagnosis can be performed by pelvic examination or medical imaging. Treatment is typically not needed if there are no symptoms. NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, may help with pain and bleeding while paracetamol (acetaminophen) may help with pain. Iron supplements may be needed in those with heavy periods. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. In general, mitosis is preceded by S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant cells), prophase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)