|
Underconsumption
Underconsumption is a theory in economics that recessions and stagnation arise from an inadequate consumer demand, relative to the amount produced. In other words, there is a problem of overproduction and overinvestment during a demand crisis. The theory formed the basis for the development of Keynesian economics and the theory of aggregate demand after the 1930s. Underconsumption theory narrowly refers to heterodox economists in Britain in the 19th century, particularly from 1815 onwards, who advanced the theory of underconsumption and rejected classical economics in the form of Ricardian economics. The economists did not form a unified school, and their theories were rejected by mainstream economics of the time. Underconsumption is an old concept in economics that goes back to the 1598 French mercantilist text ''Les Trésors et richesses pour mettre l'Estat en Splendeur'' (''The Treasures and riches to put the State in Splendor'') by Barthélemy de Laffemas, if not earlie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisis Theory
Crisis theory, concerning the causes and consequences of the tendency for the rate of profit to fall in a capitalist system, is associated with Marxian critique of political economy, and was further popularised through Marxist economics. History Earlier analysis by Jean Charles Léonard de Sismondi provided the first suggestions of the systemic roots of Crisis. "The distinctive feature of Sismondi's analysis is that it is geared to an explicit dynamic model in the modern sense of this phrase ... Sismondi's great merit is that he used, systematically and explicitly, a schema of periods, that is, that he was the first to practice the particular method of dynamics that is called period analysis". Marx praised and built on Sismondi's theoretical insights. Rosa Luxemburg and Henryk Grossman both subsequently drew attention to both Sismondi's work on the nature of capitalism, and as a reference point for Karl Marx. Grossman in particular pointed out how Sismondi had contributed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overproduction
In economics, overproduction, oversupply, excess of supply or glut refers to excess of supply over demand of products being offered to the market. This leads to lower prices and/or unsold goods along with the possibility of unemployment. The demand side equivalent is underconsumption; some consider supply and demand two sides to the same coin – excess supply is only relative to a given demand, and insufficient demand is only relative to a given supply – and thus consider overproduction and underconsumption equivalent. Overproduction is often attributed as due to previous overinvestment – creation of excess productive capacity, which must then either lie idle (or under capacity), which is unprofitable, or produce an excess supply. Explanation Overproduction is the accumulation of unsalable inventories in the hands of businesses. Overproduction is a relative measure, referring to the excess of production over consumption. The tendency for an overproduction of commodities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keynesian Economics
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output and inflation. In the Keynesian view, aggregate demand does not necessarily equal the productive capacity of the economy. Instead, it is influenced by a host of factors – sometimes behaving erratically – affecting production, employment, and inflation. Keynesian economists generally argue that aggregate demand is volatile and unstable and that, consequently, a market economy often experiences inefficient macroeconomic outcomes – a recession, when demand is low, or inflation, when demand is high. Further, they argue that these economic fluctuations can be mitigated by economic policy responses coordinated between government and central bank. In particular, fiscal policy actions (taken by the government) and monetary policy actio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Over-investment
In economics, overproduction, oversupply, excess of supply or glut refers to excess of supply over demand of products being offered to the market. This leads to lower prices and/or unsold goods along with the possibility of unemployment. The demand side equivalent is underconsumption; some consider supply and demand two sides to the same coin – excess supply is only relative to a given demand, and insufficient demand is only relative to a given supply – and thus consider overproduction and underconsumption equivalent. Overproduction is often attributed as due to previous overinvestment – creation of excess productive capacity, which must then either lie idle (or under capacity), which is un profitable, or produce an excess supply. Explanation Overproduction is the accumulation of unsalable inventories in the hands of businesses. Overproduction is a relative measure, referring to the excess of production over consumption. The tendency for an overproduction of commoditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
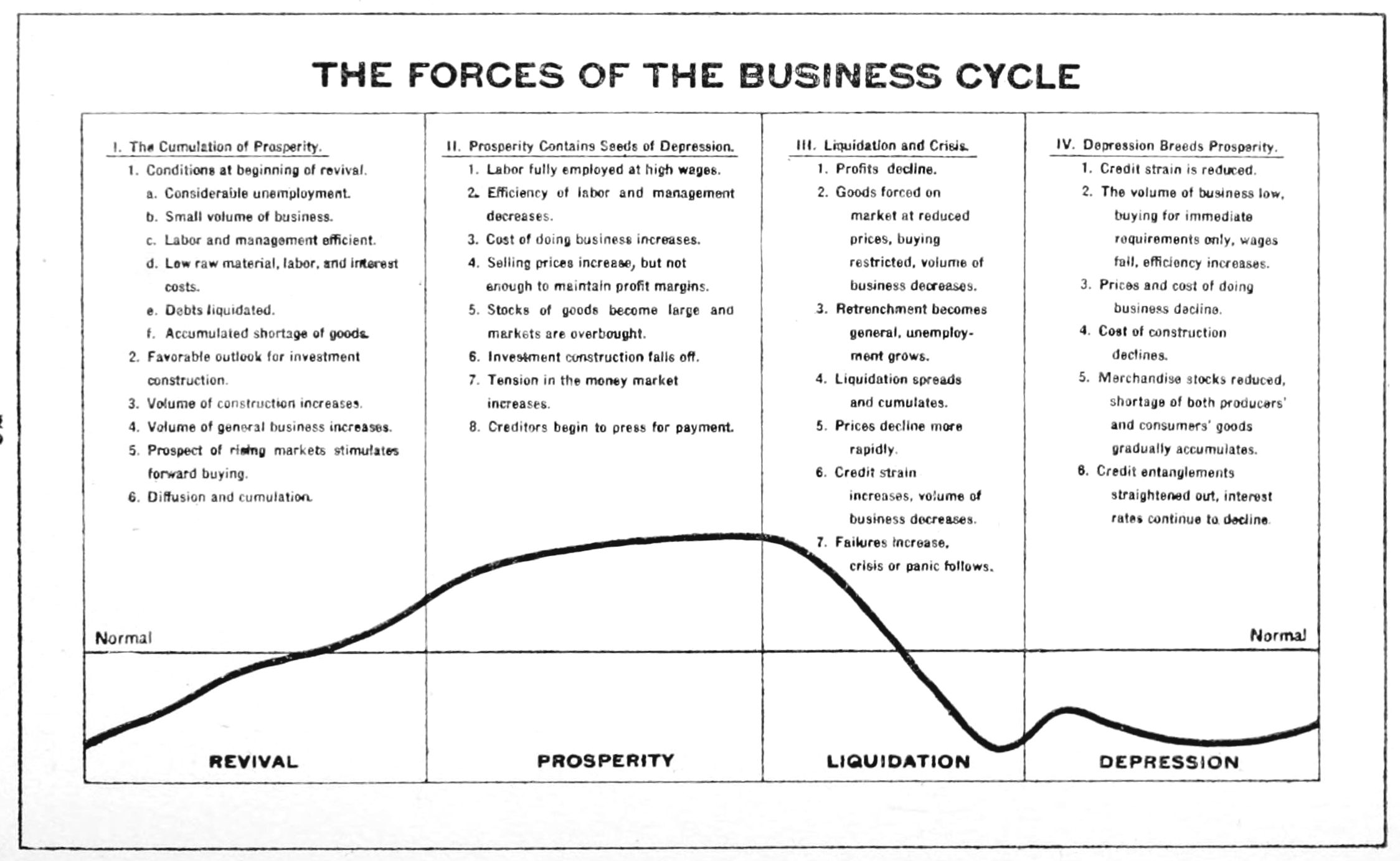
Business Cycles
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examining trends in a broad economic indicator such as Real Gross Domestic Production. Business cycle fluctuations are usually characterized by general upswings and downturns in a span of macroeconomic variables. The individual episodes of expansion/recession occur with changing duration and intensity over time. Typically their periodicity has a wide range from around 2 to 10 years (the technical phrase "stochastic cycle" is often used in statistics to describe this kind of process.) As in arvey, Trimbur, and van Dijk, 2007, ''Journal of Econometrics'' such flexible knowledge about the frequency of business cycles can actually be included in their mathematical study, using a Bayesian statistical paradigm. There are numerous sources of busines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainstream Economics
Mainstream economics is the body of knowledge, theories, and models of economics, as taught by universities worldwide, that are generally accepted by economists as a basis for discussion. Also known as orthodox economics, it can be contrasted to heterodox economics, which encompasses various schools or approaches that are only accepted by a minority of economists. The economics profession has traditionally been associated with neoclassical economics. This association has however been challenged by prominent historians of economic thought like David Collander. They argue the current economic mainstream theories, such as game theory, behavioral economics, industrial organization, information economics, and the like, share very little common ground with the initial axioms of neoclassical economics. History Economics has always featured multiple schools of economic thought, with different schools having different prominence across countries and over time. The current use of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Say's Law
In classical economics, Say's law, or the law of markets, is the claim that the production of a product creates demand for another product by providing something of value which can be exchanged for that other product. So, production is the source of demand. In his principal work, ''A Treatise on Political Economy'' (''Traité d'économie politique'', 1803), Jean-Baptiste Say wrote: "A product is no sooner created, than it, from that instant, affords a market for other products to the full extent of its own value." And also, "As each of us can only purchase the productions of others with his own productions – as the value we can buy is equal to the value we can produce, the more men can produce, the more they will purchase." Some maintain that Say further argued that this law of markets implies that a general glut (a widespread excess of supply over demand) cannot occur. If there is a surplus of one good, there must be unmet demand for another: "If certain goods remain unsold, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marxian Economics
Marxian economics, or the Marxian school of economics, is a heterodox school of political economic thought. Its foundations can be traced back to Karl Marx's critique of political economy. However, unlike critics of political economy, Marxian economists tend to accept the concept of the economy prima facie. Marxian economics comprises several different theories and includes multiple schools of thought, which are sometimes opposed to each other; in many cases Marxian analysis is used to complement, or to supplement, other economic approaches. Because one does not necessarily have to be politically Marxist to be economically Marxian, the two adjectives coexist in usage, rather than being synonymous: They share a semantic field, while also allowing both connotative and denotative differences. Marxian economics concerns itself variously with the analysis of crisis in capitalism, the role and distribution of the surplus product and surplus value in various types of economic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barthélemy De Laffemas
Bartholomew Laffemas was an economist, born in Beausemblant, France in 1545. He is officially recorded as dying in Paris in 1612. However, it is rumoured that he actually died on September 23, 1611, after falling from his horse. He is known as the first person to write about underconsumption Biography Beginnings Coming from the gentry Protestant, poor, he worked and became a tailor. He left the Dauphiné and went to Navarre. There he met Henry of Navarre, the future Henry IV of France. Then, in 1576, he became a "silver merchant" for the king. In 1579, the king owes his supplier 483 491 pounds. He had to borrow the money for his business, paid in annuities. In a memoir, Laffemas wrote that he lifted "..the silverware shop of the king, and borrowed over two hundred thousand crowns ...". These annuities are not as good and he was pursued by the creditors, and imprisoned for debt. When Henry of Navarre became King of France he was freed. General of Trade In 1596, in his "memory to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Investment
Fixed investment in economics is the purchasing of newly produced fixed capital. It is measured as a flow variable – that is, as an amount per unit of time. Thus, fixed investment is the accumulation of physical assets such as machinery, land, buildings, installations, vehicles, or technology. Normally, a company balance sheet will state both the amount of expenditure on fixed assets during the quarter or year, and the total value of the stock of fixed assets owned. Fixed investment contrasts with investments in labour, ongoing operating expenses, materials or financial assets. Financial assets may also be held for a fixed term (for example, bonds) but they are not usually called "fixed investment" because they do not involve the purchase of physical fixed assets. The more usual term for such financial investments is "fixed-term investments". Bank deposits committed for a fixed term such as one or two years in a savings account are similarly called "fixed-term deposits". Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 pamphlet '' The Communist Manifesto'' and the four-volume (1867–1883). Marx's political and philosophical thought had enormous influence on subsequent intellectual, economic, and political history. His name has been used as an adjective, a noun, and a school of social theory. Born in Trier, Germany, Marx studied law and philosophy at the universities of Bonn and Berlin. He married German theatre critic and political activist Jenny von Westphalen in 1843. Due to his political publications, Marx became stateless and lived in exile with his wife and children in London for decades, where he continued to develop his thought in collaboration with German philosopher Friedrich Engels and publish his writings, researching in the British Museu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Das Kapital
''Das Kapital'', also known as ''Capital: A Critique of Political Economy'' or sometimes simply ''Capital'' (german: Das Kapital. Kritik der politischen Ökonomie, link=no, ; 1867–1883), is a foundational theoretical text in materialist philosophy, critique of political economy and politics by Karl Marx. Marx aimed to reveal the economic patterns underpinning the capitalist mode of production in contrast to classical political economists such as Adam Smith, Jean-Baptiste Say, David Ricardo and John Stuart Mill. While Marx did not live to publish the planned second, third and fourth parts, the second and third volumes were completed from his notes and published after his death by his colleague Friedrich Engels; the fourth volume was completed and published after Engels's death by Marxist philosoper Karl Kautsky. ''Das Kapital'' is the most cited book published before 1950 in the social sciences. Themes In ''Das Kapital'' (1867), Marx proposes that the motivating force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |