|
Umbilical Venous Catheterization
An umbilical line is a catheter that is inserted into one of the two arteries or the vein of the umbilical cord. Generally the UAC/UVC (Umbilical Artery Catheter/Umbilical Vein Catheter) is used in Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICU) as it provides quick access to the central circulation of premature infants. UAC/UVC lines can be placed at the time of birth and allow medical staff to quickly infuse fluids, inotropic drugs, and blood if required. It is sometimes used in term or near-term newborns in whom the umbilical cord stump is still connected to the circulatory system. Medications, fluids, and blood can be given through this catheter and it allows monitoring of blood gasses and withdrawing of blood samples. ''Transumbilical catheter intervention'' is also a method of gaining access to the heart, for example to surgically correct a patent ductus arteriosus. Complications The complications of umbilical lines are similar to those of Central venous catheter mainly Infections su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artery
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it (lungs and placenta, respectively). The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system. The arteries are part of the circulatory system, that is responsible for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all cells, as well as the removal of carbon dioxide and waste products, the maintenance of optimum blood pH, and the circulation of proteins and cells of the immune system. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry blood back towards the heart. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic level, and microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neonatal Sepsis
Neonatal sepsis is a type of neonatal infection and specifically refers to the presence in a newborn baby of a bacterial blood stream infection (BSI) (such as meningitis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, or gastroenteritis) in the setting of fever. Older textbooks may refer to neonatal sepsis as "sepsis neonatorum". Criteria with regards to hemodynamic compromise or respiratory failure are not useful clinically because these symptoms often do not arise in neonates until death is imminent and unpreventable. Neonatal sepsis is divided into two categories: early-onset sepsis (EOS) and late-onset sepsis (LOS). EOS refers to sepsis presenting in the first 7 days of life (although some refer to EOS as within the first 72 hours of life), with LOS referring to presentation of sepsis after 7 days (or 72 hours, depending on the system used). Neonatal sepsis is the single most common cause of neonatal death in hospital as well as community in developing country. It is difficult to clinically exclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
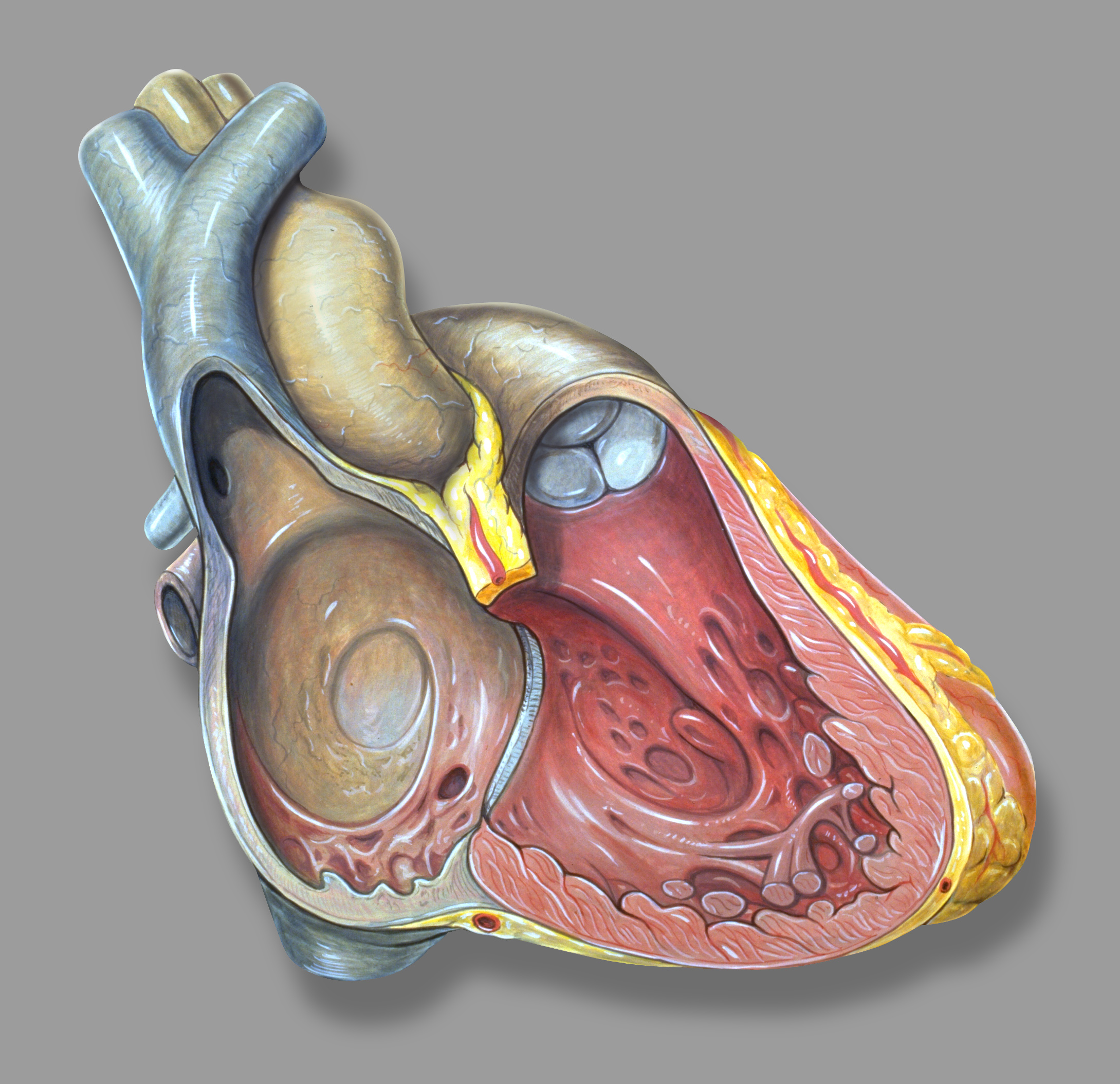
Right Atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Vena Cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra. The inferior vena cava is the lower (" inferior") of the two venae cavae, the two large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart: the inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower half of the body whilst the superior vena cava carries blood from the upper half of the body. Together, the venae cavae (in addition to the coronary sinus, which carries blood from the muscle of the heart itself) form the venous counterparts of the aorta. It is a large retroperitoneal vein that lies posterior to the abdominal cavity and runs along the right side of the vertebral column. It enters the right auricle at the lower right, back side of the heart. The name derives from la, vena, "vei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ductus Venosus
In the fetus, the ''ductus venosus'' (Arantius' duct after Julius Caesar Aranzi) shunts a portion of umbilical vein blood flow directly to the inferior vena cava. Thus, it allows oxygenated blood from the placenta to bypass the liver. Compared to the 50% shunting of umbilical blood through the ''ductus venosus'' found in animal experiments, the degree of shunting in the human fetus under physiological conditions is considerably less, 30% at 20 weeks, which decreases to 18% at 32 weeks, suggesting a higher priority of the fetal liver than previously realized. In conjunction with the other fetal shunts, the ''foramen ovale'' and ''ductus arteriosus'', it plays a critical role in preferentially shunting oxygenated blood to the fetal brain. It is a part of fetal circulation. Anatomic course The pathway of fetal umbilical venous flow is umbilical vein to left portal vein to ''ductus venosus'' to ''inferior vena cava'' and eventually the right atrium. This anatomic course is important i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portal Vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins. The portal vein is not a true vein, because it conducts blood to capillary beds in the liver and not directly to the heart. It is a major component of the hepatic portal system, one of only two portal venous systems in the body – with the hypophyseal portal system being the other. The portal vein is usually formed by the confluence of the superior mesenteric, splenic veins, inferior mesenteric, left, right gastric veins and the pancreatic vein. Conditions involving the portal vein cause considerable illness and death. An important example of such a condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navel
The navel (clinically known as the umbilicus, commonly known as the belly button or tummy button) is a protruding, flat, or hollowed area on the abdomen at the attachment site of the umbilical cord. All placental mammals have a navel, although it is generally more conspicuous in humans. Structure The umbilicus is used to visually separate the abdomen into quadrants. The umbilicus is a prominent scar on the abdomen, with its position being relatively consistent among humans. The skin around the waist at the level of the umbilicus is supplied by the tenth thoracic spinal nerve (T10 dermatome). The umbilicus itself typically lies at a vertical level corresponding to the junction between the L3 and L4 vertebrae, with a normal variation among people between the L3 and L5 vertebrae. Parts of the adult navel include the "umbilical cord remnant" or "umbilical tip", which is the often protruding scar left by the detachment of the umbilical cord. This is located in the center of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbilical Vein
The umbilical vein is a vein present during fetal development that carries oxygenated blood from the placenta into the growing fetus. The umbilical vein provides convenient access to the central circulation of a neonate for restoration of blood volume and for administration of glucose and drugs. The blood pressure inside the umbilical vein is approximately 20 mmHg.Wang, Y. Vascular biology of the placenta. in Colloquium Series on Integrated Systems Physiology: from Molecule to Function. 2010. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences. Fetal circulation The unpaired umbilical vein carries oxygen and nutrient rich blood derived from fetal-maternal blood exchange at the chorionic villi. More than two-thirds of fetal hepatic circulation is via the main portal vein, while the remainder is shunted from the left portal vein via the ductus venosus to the inferior vena cava, eventually being delivered to the fetal right atrium. Closure Closure of the umbilical vein usually occurs after the umbilica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Vertebra
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae, with the lower ones being much larger than the upper. They are distinguished by the presence of facets on the sides of the bodies for articulation with the heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region. General characteristics These are the general characteristics of the second through eighth thoracic vertebrae. The first and ninth through twelfth vertebrae contain certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Iliac Artery
The internal iliac artery (formerly known as the hypogastric artery) is the main artery of the pelvis. Structure The internal iliac artery supplies the walls and viscera of the pelvis, the buttock, the reproductive organs, and the medial compartment of the thigh. The vesicular branches of the internal iliac arteries supply the bladder. It is a short, thick vessel, smaller than the external iliac artery, and about 3 to 4 cm in length. Course The internal iliac artery arises at the bifurcation of the common iliac artery, opposite the lumbosacral articulation, and, passing downward to the upper margin of the greater sciatic foramen, divides into two large trunks, an anterior and a posterior. It is posterior to the ureter, anterior to the internal iliac vein, anterior to the lumbosacral trunk, and anterior to the piriformis muscle. Near its origin, it is medial to the external iliac vein, which lies between it and the psoas major muscle. It is above the obturator nerve. Bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
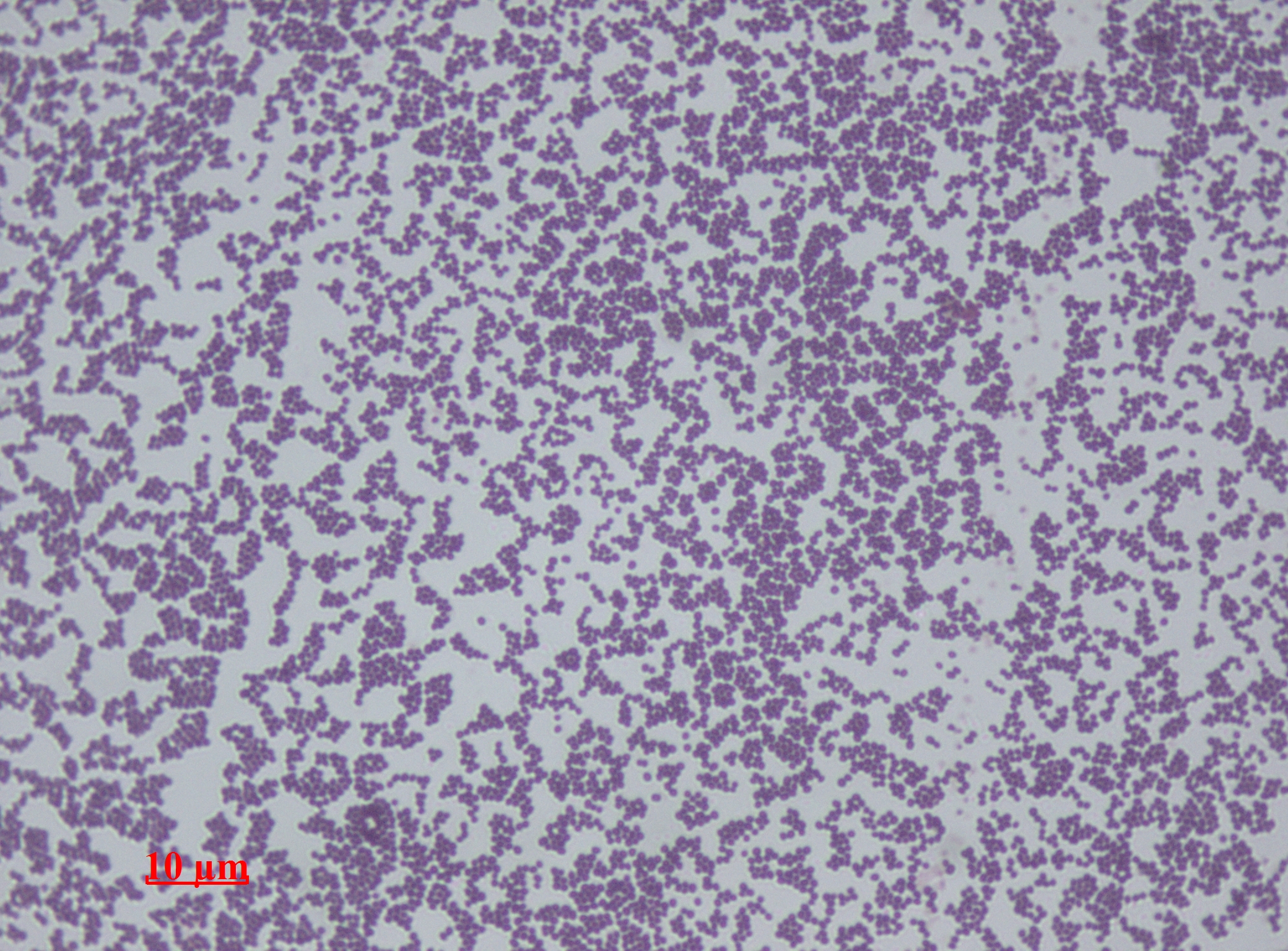
Staphylococcus Epidermidis
''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus '' Staphylococcus''. It is part of the normal human microbiota, typically the skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although ''S. epidermidis'' is not usually pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally hospital-acquired. ''S. epidermidis'' is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, ''S. epidermidis'' is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory. Some strains of ''S. epidermidis'' are highly salt tolerant and commonly found in marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and identified salt tolerant strains of ''S. epiderm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically). The name was coined in 1880 by Scottish surgeon and bacteriologist Alexander Ogston (1844–1929), following the pattern established five years earlier with the naming of ''Streptococcus''. It combines the prefix "staphylo-" (from grc, σταφυλή, staphylē, bunch of grapes), and suffixed by the Modern (from ). Staphylococcus was one of the leading infections in hospitals and many strains of this bacterium have become antibiotic resistant. Despite strong attempts to get rid of them, staph bacteria stay present in hospitals, where they can infect people who are most at risk of infection. Staphylococcus includes at least 43 species. Of these, nine have two su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |