|
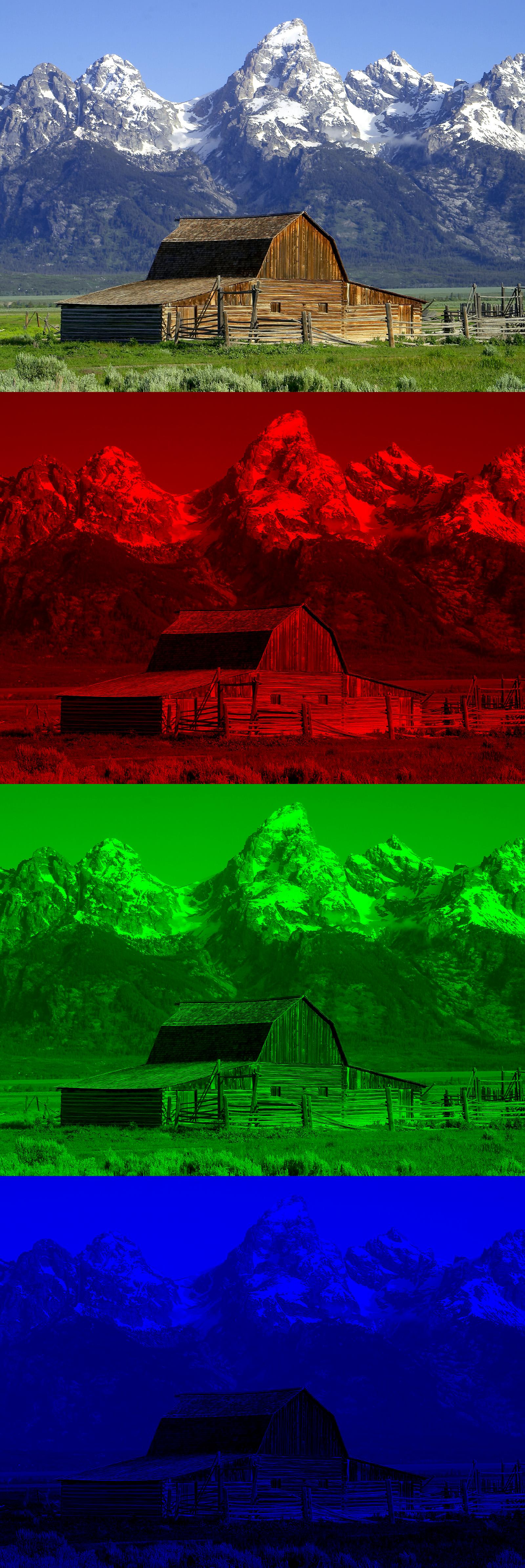
Unsharp Masking
Unsharp masking (USM) is an image sharpening technique, first implemented in darkroom photography, but now commonly used in digital image processing software. Its name derives from the fact that the technique uses a blurred, or "unsharp", negative image to create a mask of the original image. The unsharp mask is then combined with the original positive image, creating an image that is less blurry than the original. The resulting image, although clearer, may be a less accurate representation of the image's subject. In the context of signal processing, an unsharp mask is generally a linear or nonlinear filter that amplifies the high-frequency components of a signal. Photographic darkroom unsharp masking For the photographic darkroom process, a large-format glass plate negative is contact-copied onto a low-contrast film or plate to create a positive image. However, the positive copy is made with the copy material in contact with the back of the original, rather than emulsion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchromatic
Panchromatic emulsion is a type of black-and-white photographic emulsion that is sensitive to all wavelengths of visible light. Description A panchromatic emulsion renders a realistic reproduction of a scene as it appears to the human eye, although with no colors. Almost all modern photographic film is panchromatic. Some older types of film were orthochromatic and were not sensitive to certain wavelengths of light. As naturally prepared, a silver halide photographic emulsion is much more sensitive to blue and UV light than to green and red wavelengths. The German chemist Hermann W. Vogel found out how to extend the sensitivity into the green, and later the orange, by adding sensitising dyes to the emulsion. By the addition of erythrosine the emulsion could be made orthochromatic while some cyanine derivatives confer sensitivity to the whole visible spectrum making it panchromatic. However, his technique was not extended to achieve a fully panchromatic film until the early 190 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deconvolution
In mathematics, deconvolution is the operation inverse to convolution. Both operations are used in signal processing and image processing. For example, it may be possible to recover the original signal after a filter (convolution) by using a deconvolution method with a certain degree of accuracy. Due to the measurement error of the recorded signal or image, it can be demonstrated that the worse the SNR, the worse the reversing of a filter will be; hence, inverting a filter is not always a good solution as the error amplifies. Deconvolution offers a solution to this problem. The foundations for deconvolution and time-series analysis were largely laid by Norbert Wiener of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in his book ''Extrapolation, Interpolation, and Smoothing of Stationary Time Series'' (1949). The book was based on work Wiener had done during World War II but that had been classified at the time. Some of the early attempts to apply these theories were in the fields of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tone Mapping
Tone mapping is a technique used in image processing and computer graphics to map one set of colors to another to approximate the appearance of high-dynamic-range images in a medium that has a more limited dynamic range. Print-outs, CRT or LCD monitors, and projectors all have a limited dynamic range that is inadequate to reproduce the full range of light intensities present in natural scenes. Tone mapping addresses the problem of strong contrast reduction from the scene radiance to the displayable range while preserving the image details and color appearance important to appreciate the original scene content. Inverse tone mapping is the inverse technique that allows to expand the luminance range, mapping a low dynamic range image into a higher dynamic range image. It is notably used to upscale SDR videos to HDR videos. Background The introduction of film-based photography created issues since capturing the enormous dynamic range of lighting from the real world on a chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
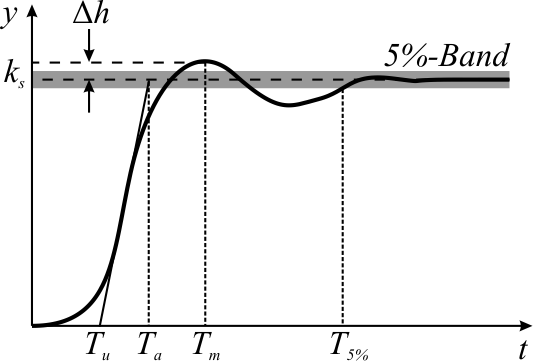
Overshoot (signal)
In signal processing, control theory, electronics, and mathematics, overshoot is the occurrence of a signal or function exceeding its target. Undershoot is the same phenomenon in the opposite direction. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as low-pass filters. It is often followed by ringing, and at times conflated with the latter. Definition Maximum overshoot is defined in Katsuhiko Ogata's ''Discrete-time control systems'' as "the maximum peak value of the response curve measured from the desired response of the system." Control theory In control theory, overshoot refers to an output exceeding its final, steady-state value. For a step input, the ''percentage overshoot'' (PO) is the maximum value minus the step value divided by the step value. In the case of the unit step, the ''overshoot'' is just the maximum value of the step response minus one. Also see the definition of ''overshoot'' in an electronics context. For second-order system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge Detection
Edge detection includes a variety of mathematical methods that aim at identifying edges, curves in a digital image at which the image brightness changes sharply or, more formally, has discontinuities. The same problem of finding discontinuities in one-dimensional signals is known as ''step detection'' and the problem of finding signal discontinuities over time is known as ''change detection''. Edge detection is a fundamental tool in image processing, machine vision and computer vision, particularly in the areas of feature detection and feature extraction. Motivations The purpose of detecting sharp changes in image brightness is to capture important events and changes in properties of the world. It can be shown that under rather general assumptions for an image formation model, discontinuities in image brightness are likely to correspond to: * discontinuities in depth, * discontinuities in surface orientation, * changes in material properties and * variations in scene illumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIELAB
The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'' , is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination (abbreviated CIE) in 1976. (Referring to CIELAB as "Lab" without asterisks should be avoided to prevent confusion with Hunter Lab). It expresses color as three values: ''L*'' for perceptual lightness and ''a*'' and ''b*'' for the four unique colors of human vision: red, green, blue and yellow. CIELAB was intended as a perceptually uniform space, where a given numerical change corresponds to a similar perceived change in color. While the LAB space is not truly perceptually uniform, it nevertheless is useful in industry for detecting small differences in color. Like the CIEXYZ space it derives from, CIELAB color space is a device-independent, "standard observer" model. The colors it defines are not relative to any particular device such as a computer monitor or a printer, but instead relate to the CIE standard observer which is an averaging of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RGB Color Model
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three additive primary colors, red, green, and blue. The main purpose of the RGB color model is for the sensing, representation, and display of images in electronic systems, such as televisions and computers, though it has also been used in conventional photography. Before the electronic age, the RGB color model already had a solid theory behind it, based in human perception of colors. RGB is a ''device-dependent'' color model: different devices detect or reproduce a given RGB value differently, since the color elements (such as phosphors or dyes) and their response to the individual red, green, and blue levels vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, or even in the same device over time. Thus an RGB value does not define the same ''color'' across d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel (digital Image)
Color digital images are made of pixels, and pixels are made of combinations of primary colors represented by a series of code. A channel in this context is the grayscale image of the same size as a color image, made of just one of these primary colors. For instance, an image from a standard digital camera will have a red, green and blue channel. A grayscale image has just one channel. In geographic information systems, channels are often referred to as raster bands. Another closely related concept is feature maps, which are used in convolutional neural networks. Overview In the digital realm, there can be any number of conventional primary colors making up an image; a channel in this case is extended to be the grayscale image based on any such conventional primary color. By extension, a channel is any grayscale image of the same dimension as and associated with the original image. ''Channel'' is a conventional term used to refer to a certain component of an image. In reality, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Noise
Image noise is random variation of brightness or color information in images, and is usually an aspect of electronic noise. It can be produced by the image sensor and circuitry of a Image scanner, scanner or digital camera. Image noise can also originate in film grain and in the unavoidable shot noise of an ideal photon detector. Image noise is an undesirable by-product of image capture that obscures the desired information. Typically the term “image noise” is used to refer to noise in 2D images, not 3D images. The original meaning of "noise" was "unwanted signal"; Noise (radio), unwanted electrical fluctuations in signals received by AM radios caused audible acoustic noise ("static"). By analogy, unwanted electrical fluctuations are also called "noise". Image noise can range from almost imperceptible specks on a digital photograph taken in good light, to Optical astronomy, optical and Radioastronomy, radioastronomical images that are almost entirely noise, from which a sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanned Images
An image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting or an object and converts it to a digital image. Commonly used in offices are variations of the desktop ''flatbed scanner'' where the document is placed on a glass window for scanning. ''Hand-held scanners'', where the device is moved by hand, have evolved from text scanning "wands" to 3D scanners used for industrial design, reverse engineering, test and measurement, orthotics, gaming and other applications. Mechanically driven scanners that move the document are typically used for large-format documents, where a flatbed design would be impractical. Modern scanners typically use a charge-coupled device (CCD) or a contact image sensor (CIS) as the image sensor, whereas ''drum scanners'', developed earlier and still used for the highest possible image quality, use a photomultiplier tube (PMT) as the image sensor. A ''rotary scanner,'' used for high-speed document ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GIMP
GIMP ( ; GNU Image Manipulation Program) is a free and open-source raster graphics editor used for image manipulation (retouching) and image editing, free-form drawing, transcoding between different image file formats, and more specialized tasks. It is not designed to be used for drawing, though some artists and creators have used it for such. GIMP is released under the GPL-3.0-or-later license and is available for Linux, macOS, and Microsoft Windows. History In 1995, Spencer Kimball and Peter Mattis began developing GIMP – originally named ''General Image Manipulation Program –'' as a semester-long project at the University of California, Berkeley for the eXperimental Computing Facility''.'' The acronym was coined first, with the letter ''G'' being added to ''-IMP'' as a reference to "the gimp" in the scene from the 1994 ''Pulp Fiction'' film. In 1996 was the initial public release of GIMP (0.54). The editor was quickly adopted and a community of contributors formed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)