|
Unpitched
An unpitched percussion instrument is a percussion instrument played in such a way as to produce sounds of indeterminate pitch, or an instrument normally played in this fashion. Unpitched percussion is typically used to maintain a rhythm or to provide accents, and its sounds are unrelated to the melody and harmony of the music. Within the orchestra unpitched percussion is termed auxiliary percussion, and this subsection of the percussion section includes all unpitched instruments of the orchestra however they are played, for example the pea whistle and siren. A common and typical example of an unpitched instrument is the snare drum, which is perceived as unpitched for three reasons: * The snares produce sounds similar to white noise, masking definite frequencies. * The drum heads produce inharmonic sounds. * The strongest frequencies that are present are unrelated to pitched sounds produced by other instruments in the ensemble. Although the drum is ''tuned'' by the player, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise In Music
In music, noise is variously described as unpitched, indeterminate, uncontrolled, loud, unmusical, or unwanted sound. Noise is an important component of the sound of the human voice and all musical instruments, particularly in unpitched percussion instruments and electric guitars (using distortion). Electronic instruments create various colours of noise. Traditional uses of noise are unrestricted, using all the frequencies associated with pitch and timbre, such as the white noise component of a drum roll on a snare drum, or the transients present in the prefix of the sounds of some organ pipes. The influence of modernism in the early 20th century lead composers such as Edgard Varèse to explore the use of noise-based sonorities in an orchestral setting. In the same period the Italian Futurist Luigi Russolo created a "noise orchestra" using instruments he called intonarumori. Later in the 20th century the term noise music came to refer to works consisting primarily of noise-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percussion Instrument
A percussion instrument is a musical instrument that is sounded by being struck or scraped by a beater including attached or enclosed beaters or rattles struck, scraped or rubbed by hand or struck against another similar instrument. Excluding zoomusicological instruments and the human voice, the percussion family is believed to include the oldest musical instruments.''The Oxford Companion to Music'', 10th edition, p.775, In spite of being a very common term to designate instruments, and to relate them to their players, the percussionists, percussion is not a systematic classificatory category of instruments, as described by the scientific field of organology. It is shown below that percussion instruments may belong to the organological classes of ideophone, membranophone, aerophone and cordophone. The percussion section of an orchestra most commonly contains instruments such as the timpani, snare drum, bass drum, tambourine, belonging to the membranophones, and cym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
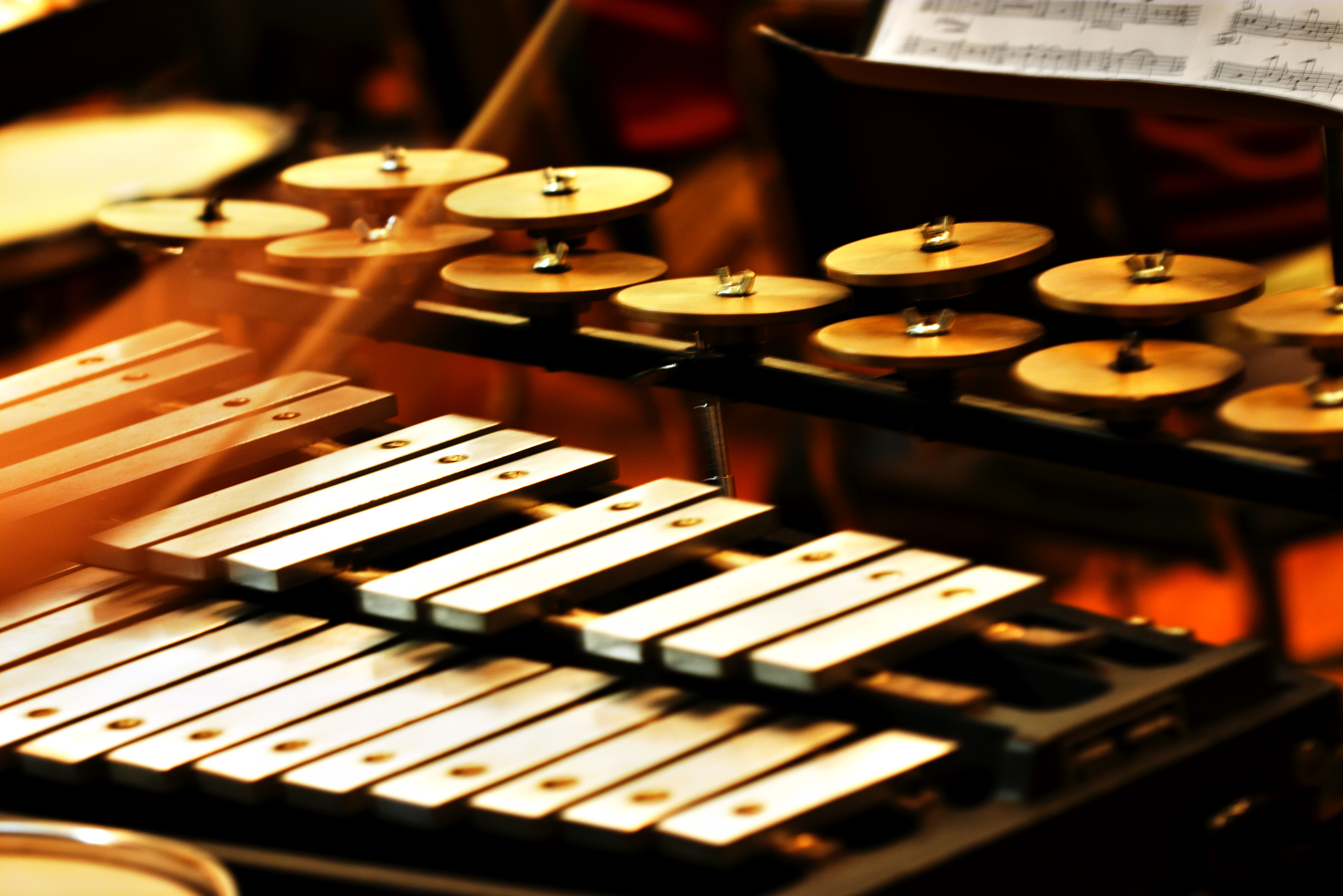
Auxiliary Percussion
The percussion section is one of the main divisions of the orchestra and the concert band. It includes most percussion instruments and all unpitched instruments. The percussion section is itself divided into three subsections: * Pitched percussion, consisting of pitched instruments such as glockenspiel and tubular bells. * Auxiliary percussion, consisting of all unpitched instruments such as snare drum and cymbals. * Timpani. These three subsections reflect the three main skill areas that a percussionist studies. Percussion sections, consisting of similar instruments, may also be found in stage bands and other musical ensembles. Tuned percussion :''See also untuned percussion'' This subsection is traditionally called tuned percussion, however the corresponding term ''untuned percussion'' is avoided in modern organology in favour of the term ''unpitched percussion'', so the instruments of this subsection are similarly termed ''pitched percussion''. All instruments of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percussion Section
The percussion section is one of the main divisions of the orchestra and the concert band. It includes most percussion instruments and all unpitched instruments. The percussion section is itself divided into three subsections: * Pitched percussion, consisting of pitched instruments such as glockenspiel and tubular bells. * Auxiliary percussion, consisting of all unpitched instruments such as snare drum and cymbals. * Timpani. These three subsections reflect the three main skill areas that a percussionist studies. Percussion sections, consisting of similar instruments, may also be found in stage bands and other musical ensembles. Tuned percussion :''See also untuned percussion'' This subsection is traditionally called tuned percussion, however the corresponding term ''untuned percussion'' is avoided in modern organology in favour of the term ''unpitched percussion'', so the instruments of this subsection are similarly termed ''pitched percussion''. All instruments of this sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitched Percussion
A pitched percussion instrument (also known as a melodic or tuned percussion instrument) is a percussion instrument used to produce musical notes of one or more pitches, as opposed to an unpitched percussion instrument which is used to produce sounds of indefinite pitch. Pitching of percussion instruments is achieved through a variety of means. *Membranophones (such as timpani) are tuned by altering the surface tension of the face that is struck. *Idiophones (such as crotales) gain their pitch through the physical characteristics (such as composition, density, and physical dimensions) of each respective bar. The term ''pitched percussion'' is now preferred to the traditional term ''tuned percussion'': * Many ''untuned'' percussion instruments (such as the bass drum) are ''tuned'' by the player, but this tuning does not relate to a particular pitch. * ''Untuned'' percussion instruments can and frequently do make sounds that could be used as pitched notes in an appropriate co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indeterminate Pitch
Pitch is a perceptual property of sounds that allows their ordering on a frequency-related scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies. Pitch is a major auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration, loudness, and timbre. Pitch may be quantified as a frequency, but pitch is not a purely objective physical property; it is a subjective psychoacoustical attribute of sound. Historically, the study of pitch and pitch perception has been a central problem in psychoacoustics, and has been instrumental in forming and testing theories of sound representation, processing, and perception in the auditory system. Perception Pitch and frequency Pitch is an auditory sensation in which a listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based primarily on their perception of the frequency of vibration. Pitch is closely related to frequency, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell (instrument)
A bell is a directly struck idiophone percussion instrument. Most bells have the shape of a hollow cup that when struck vibrates in a single strong strike tone, with its sides forming an efficient resonator. The strike may be made by an internal "clapper" or "uvula", an external hammer, or—in small bells—by a small loose sphere enclosed within the body of the bell (jingle bell). Bells are usually cast from bell metal (a type of bronze) for its resonant properties, but can also be made from other hard materials. This depends on the function. Some small bells such as ornamental bells or cowbells can be made from cast or pressed metal, glass or ceramic, but large bells such as a church, clock and tower bells are normally cast from bell metal. Bells intended to be heard over a wide area can range from a single bell hung in a turret or bell-gable, to a musical ensemble such as an English ring of bells, a carillon or a Russian zvon which are tuned to a common scale and instal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (music)
Pitch is a perceptual property of sounds that allows their ordering on a frequency-related scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies. Pitch is a major auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration, loudness, and timbre. Pitch may be quantified as a frequency, but pitch is not a purely objective physical property; it is a subjective psychoacoustical attribute of sound. Historically, the study of pitch and pitch perception has been a central problem in psychoacoustics, and has been instrumental in forming and testing theories of sound representation, processing, and perception in the auditory system. Perception Pitch and frequency Pitch is an auditory sensation in which a listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based primarily on their perception of the frequency of vibration. Pitch is closely related to frequency, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overtone
An overtone is any resonant frequency above the fundamental frequency of a sound. (An overtone may or may not be a harmonic) In other words, overtones are all pitches higher than the lowest pitch within an individual sound; the fundamental is the lowest pitch. While the fundamental is usually heard most prominently, overtones are actually present in any pitch except a true sine wave. The relative volume or amplitude of various overtone partials is one of the key identifying features of timbre, or the individual characteristic of a sound. Using the model of Fourier analysis, the fundamental and the overtones together are called partials. Harmonics, or more precisely, harmonic partials, are partials whose frequencies are numerical integer multiples of the fundamental (including the fundamental, which is 1 times itself). These overlapping terms are variously used when discussing the acoustic behavior of musical instruments. Alexander J. Ellis (translating Hermann von Helmholtz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
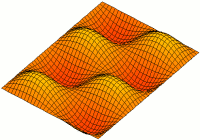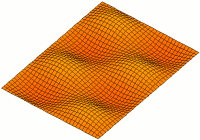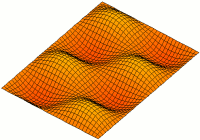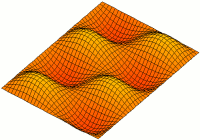
Acoustic Membrane
An acoustic membrane is a thin layer that vibrates and is used in acoustics to produce or transfer sound, such as a drum, microphone, or loudspeaker. See also * Membranophone * Vibrations of a circular membrane A two-dimensional elastic membrane under tension can support transverse vibrations. The properties of an idealized drumhead can be modeled by the vibrations of a circular membrane of uniform thickness, attached to a rigid frame. Due to the ph ... Acoustics Sound {{acoustics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensations Of Tone
''On the Sensations of Tone as a Physiological Basis for the Theory of Music'' (German ), commonly referred to as ''Sensations of Tone'', is a foundational work on music acoustics and the perception of sound by Hermann von Helmholtz. The first German edition was published in 1863. The English translation by Alexander J. Ellis was first published in 1875 (the first English edition was from the 1870 third German edition; the second English edition from the 1877 fourth German edition was published in 1885; the 1895 and 1912 third and fourth English editions were reprints of the second edition). The editions translated into English contain detailed commentary and notes (titled "Additions by the Translator") by Ellis. Helmholtz declared that he started working on his book in 1854, which concluded in 1862. Helmholtz started publishing on acoustics in 1852. His last article on acoustics was in 1878, reviewing the book by Lord Rayleigh (Theory of Sound). Therefore, Helmholtz published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)