|
Uniformly Continuous
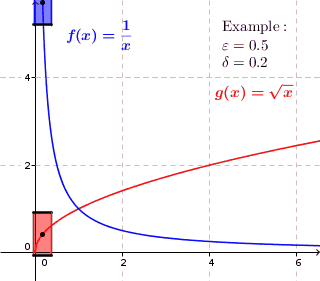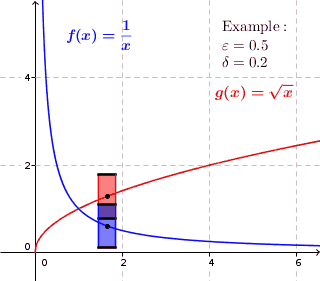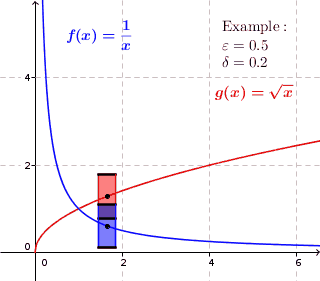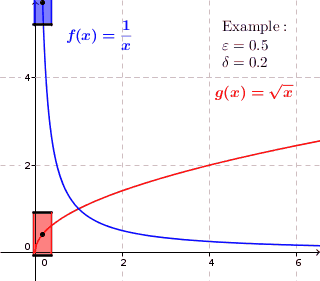
In mathematics, a real function f of real numbers is said to be uniformly continuous if there is a positive real number \delta such that function values over any function domain interval of the size \delta are as close to each other as we want. In other words, for a uniformly continuous real function of real numbers, if we want function value differences to be less than any positive real number \varepsilon, then there is a positive real number \delta such that , f(x) - f(y), 0 there exists a real number \delta > 0 such that for every x,y \in X with d_1(x,y) 0 such that for every x,y \in X , , x - y, 0 \; \forall x \in X \; \forall y \in X : \, d_1(x,y) 0 , \forall x \in X , and \forall y \in X ) are used. * Equivalently, f is uniformly continuous if it admits a modulus of continuity. Definition of (ordinary) continuity * f is called continuous \underline if for every real number \varepsilon > 0 there exists a real number \delta > 0 such that for every y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuity And Uniform Continuity 2
Continuity or continuous may refer to: Mathematics * Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include ** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics ** Continuous game, a generalization of games used in game theory ** Law of continuity, a heuristic principle of Gottfried Leibniz * Continuous function, in particular: ** Continuity (topology), a generalization to functions between topological spaces ** Scott continuity, for functions between posets ** Continuity (set theory), for functions between ordinals ** Continuity (category theory), for functors ** Graph continuity, for payoff functions in game theory * Continuity theorem may refer to one of two results: ** Lévy's continuity theorem, on random variables ** Kolmogorov continuity theorem, on stochastic processes * In geometry: ** Parametric continuity, for parametrised curves ** Geometric continuity, a concept primarily applied to the conic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniform Continuity
In mathematics, a real function f of real numbers is said to be uniformly continuous if there is a positive real number \delta such that function values over any function domain interval of the size \delta are as close to each other as we want. In other words, for a uniformly continuous real function of real numbers, if we want function value differences to be less than any positive real number \varepsilon, then there is a positive real number \delta such that , f(x) - f(y), 0 there exists a real number \delta > 0 such that for every x,y \in X with d_1(x,y) 0 such that for every x,y \in X , , x - y, 0 \; \forall x \in X \; \forall y \in X : \, d_1(x,y) 0 , \forall x \in X , and \forall y \in X ) are used. * Equivalently, f is uniformly continuous if it admits a modulus of continuity. Definition of (ordinary) continuity * f is called continuous \underline if for every real number \varepsilon > 0 there exists a real number \delta > 0 such that for every y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipschitz Continuous
In mathematical analysis, Lipschitz continuity, named after Germany, German mathematician Rudolf Lipschitz, is a strong form of uniform continuity for function (mathematics), functions. Intuitively, a Lipschitz continuous function is limited in how fast it can change: there exists a real number such that, for every pair of points on the graph of this function, the absolute value of the slope of the line connecting them is not greater than this real number; the smallest such bound is called the ''Lipschitz constant'' of the function (and is related to the ''modulus of continuity, modulus of uniform continuity''). For instance, every function that is defined on an interval and has a bounded first derivative is Lipschitz continuous. In the theory of differential equations, Lipschitz continuity is the central condition of the Picard–Lindelöf theorem which guarantees the existence and uniqueness of the solution to an initial value problem. A special type of Lipschitz continuity, cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Function
In mathematics, the term linear function refers to two distinct but related notions: * In calculus and related areas, a linear function is a function whose graph is a straight line, that is, a polynomial function of degree zero or one. For distinguishing such a linear function from the other concept, the term ''affine function'' is often used. * In linear algebra, mathematical analysis, and functional analysis, a linear function is a linear map. As a polynomial function In calculus, analytic geometry and related areas, a linear function is a polynomial of degree one or less, including the zero polynomial (the latter not being considered to have degree zero). When the function is of only one variable, it is of the form :f(x)=ax+b, where and are constants, often real numbers. The graph of such a function of one variable is a nonvertical line. is frequently referred to as the slope of the line, and as the intercept. If ''a > 0'' then the gradient is positive an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darboux Integral
In real analysis, the Darboux integral is constructed using Darboux sums and is one possible definition of the integral of a function. Darboux integrals are equivalent to Riemann integrals, meaning that a function is Darboux-integrable if and only if it is Riemann-integrable, and the values of the two integrals, if they exist, are equal. The definition of the Darboux integral has the advantage of being easier to apply in computations or proofs than that of the Riemann integral. Consequently, introductory textbooks on calculus and real analysis often develop Riemann integration using the Darboux integral, rather than the true Riemann integral. Moreover, the definition is readily extended to defining Riemann–Stieltjes integration. Darboux integrals are named after their inventor, Gaston Darboux (1842–1917). Definition The definition of the Darboux integral considers upper and lower (Darboux) integrals, which exist for any bounded real-valued function f on the interval ,b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Set
In mathematics, specifically general topology, compactness is a property that seeks to generalize the notion of a closed and bounded subset of Euclidean space. The idea is that a compact space has no "punctures" or "missing endpoints", i.e., it includes all ''limiting values'' of points. For example, the open interval (0,1) would not be compact because it excludes the limiting values of 0 and 1, whereas the closed interval ,1would be compact. Similarly, the space of rational numbers \mathbb is not compact, because it has infinitely many "punctures" corresponding to the irrational numbers, and the space of real numbers \mathbb is not compact either, because it excludes the two limiting values +\infty and -\infty. However, the ''extended'' real number line ''would'' be compact, since it contains both infinities. There are many ways to make this heuristic notion precise. These ways usually agree in a metric space, but may not be equivalent in other topological spaces. One su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heine–Cantor Theorem
In mathematics, the Heine–Cantor theorem states that a continuous function between two metric spaces is uniformly continuous if its domain is compact. The theorem is named after Eduard Heine and Georg Cantor. An important special case of the Cantor theorem is that every continuous function from a closed bounded interval to the real numbers is uniformly continuous. For an alternative proof in the case of M = , b/math>, a closed interval, see the article Non-standard calculus. See also * Cauchy-continuous function In mathematics, a Cauchy-continuous, or Cauchy-regular, function is a special kind of continuous function between metric spaces (or more general spaces). Cauchy-continuous functions have the useful property that they can always be (uniquely) extende ... External links * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Heine-Cantor theorem Theory of continuous functions Metric geometry Theorems in mathematical analysis Articles containing proofs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Metric
In mathematics, the Euclidean distance between two points in Euclidean space is the length of the line segment between them. It can be calculated from the Cartesian coordinates of the points using the Pythagorean theorem, and therefore is occasionally called the Pythagorean distance. These names come from the ancient Greek mathematicians Euclid and Pythagoras. In the Greek deductive geometry exemplified by Euclid's ''Elements'', distances were not represented as numbers but line segments of the same length, which were considered "equal". The notion of distance is inherent in the compass tool used to draw a circle, whose points all have the same distance from a common center point. The connection from the Pythagorean theorem to distance calculation was not made until the 18th century. The distance between two objects that are not points is usually defined to be the smallest distance among pairs of points from the two objects. Formulas are known for computing distances betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Metric
Discrete may refer to: *Discrete particle or quantum in physics, for example in quantum theory *Discrete device, an electronic component with just one circuit element, either passive or active, other than an integrated circuit *Discrete group, a group with the discrete topology *Discrete category, category whose only arrows are identity arrows *Discrete mathematics, the study of structures without continuity *Discrete optimization, a branch of optimization in applied mathematics and computer science *Discrete probability distribution, a random variable that can be counted *Discrete space, a simple example of a topological space *Discrete spline interpolation, the discrete analog of ordinary spline interpolation *Discrete time, non-continuous time, which results in discrete-time samples *Discrete variable In mathematics and statistics, a quantitative variable may be continuous or discrete. If it can take on two real values and all the values between them, the variable is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totally Bounded Space
In topology and related branches of mathematics, total-boundedness is a generalization of compactness for circumstances in which a set is not necessarily closed. A totally bounded set can be covered by finitely many subsets of every fixed “size” (where the meaning of “size” depends on the structure of the ambient space). The term precompact (or pre-compact) is sometimes used with the same meaning, but precompact is also used to mean relatively compact. These definitions coincide for subsets of a complete metric space, but not in general. In metric spaces A metric space (M,d) is ''totally bounded'' if and only if for every real number \varepsilon > 0, there exists a finite collection of open balls of radius \varepsilon whose centers lie in ''M'' and whose union contains . Equivalently, the metric space ''M'' is totally bounded if and only if for every \varepsilon >0, there exists a finite cover such that the radius of each element of the cover is at most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantor Function
In mathematics, the Cantor function is an example of a function (mathematics), function that is continuous function, continuous, but not absolute continuity, absolutely continuous. It is a notorious Pathological_(mathematics)#Pathological_example, counterexample in analysis, because it challenges naive intuitions about continuity, derivative, and Measure (mathematics), measure. Although it is continuous everywhere, and has zero derivative almost everywhere, its value still goes from 0 to 1 as its argument goes from 0 to 1. Thus, while the function seems like a constant one that cannot grow, it does indeed Monotonic function, monotonically grow. It is also called the Cantor ternary function, the Lebesgue function, Lebesgue's singular function, the Cantor–Vitali function, the Devil's staircase, the Cantor staircase function, and the Cantor–Lebesgue function. introduced the Cantor function and mentioned that Scheeffer pointed out that it was a counterexample to an extension of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolutely Continuous
In calculus and real analysis, absolute continuity is a smoothness property of functions that is stronger than continuity and uniform continuity. The notion of absolute continuity allows one to obtain generalizations of the relationship between the two central operations of calculus— differentiation and integration. This relationship is commonly characterized (by the fundamental theorem of calculus) in the framework of Riemann integration, but with absolute continuity it may be formulated in terms of Lebesgue integration. For real-valued functions on the real line, two interrelated notions appear: absolute continuity of functions and absolute continuity of measures. These two notions are generalized in different directions. The usual derivative of a function is related to the '' Radon–Nikodym derivative'', or ''density'', of a measure. We have the following chains of inclusions for functions over a compact subset of the real line: : ''absolutely continuous'' ⊆ '' u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |