|
Tꜣwj
In Egyptian history, the Upper and Lower Egypt period (also known as The Two Lands) was the final stage of prehistoric Egypt and directly preceded the unification of the realm. The conception of Egypt as the Two Lands was an example of the dualism in ancient Egyptian culture and frequently appeared in texts and imagery, including in the titles of Egyptian pharaohs. The Egyptian title '' zmꜣ- tꜣwj'' (Egyptological pronunciation ''sema-tawy'') is usually translated as "Uniter of the Two Lands" and was depicted as a human trachea entwined with the papyrus and lily plant. The trachea stood for unification, while the papyrus and lily plant represent Lower and Upper Egypt. Standard titles of the pharaoh included the prenomen, quite literally "Of the Sedge and Bee" (nswt-bjtj, the symbols of Upper and Lower Egypt) and "lord of the Two Lands" (written '' nb-tꜣwj''). Queens regnant were addressed as pharaohs and male. Queens consort might use a feminine versions of the second titl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tꜣwj
In Egyptian history, the Upper and Lower Egypt period (also known as The Two Lands) was the final stage of prehistoric Egypt and directly preceded the unification of the realm. The conception of Egypt as the Two Lands was an example of the dualism in ancient Egyptian culture and frequently appeared in texts and imagery, including in the titles of Egyptian pharaohs. The Egyptian title '' zmꜣ- tꜣwj'' (Egyptological pronunciation ''sema-tawy'') is usually translated as "Uniter of the Two Lands" and was depicted as a human trachea entwined with the papyrus and lily plant. The trachea stood for unification, while the papyrus and lily plant represent Lower and Upper Egypt. Standard titles of the pharaoh included the prenomen, quite literally "Of the Sedge and Bee" (nswt-bjtj, the symbols of Upper and Lower Egypt) and "lord of the Two Lands" (written '' nb-tꜣwj''). Queens regnant were addressed as pharaohs and male. Queens consort might use a feminine versions of the second titl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Ancient Egypt
The history of ancient Egypt spans the period from the early prehistoric settlements of the northern Nile valley to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 BC. The pharaonic period, the period in which Egypt was ruled by a pharaoh, is dated from the 32nd century BC, when Upper and Lower Egypt were unified, until the country fell under Macedonian rule in 332 BC. Chronology ;Note: For alternative 'revisions' to the chronology of Egypt, see Egyptian chronology. Egypt's history is split into several different periods according to the ruling dynasty of each pharaoh. The dating of events is still a subject of research. The conservative dates are not supported by any reliable absolute date for a span of about three millennia. The following is the list according to conventional Egyptian chronology. * Prehistoric Egypt (prior to 3100 BC) * Naqada III ("the protodynastic period", approximately 3100–3000 BC; sometimes referred to as "Dynasty 0") * Early Dynastic Period (First– Second D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ar, مصر السفلى '; ) is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, the Nile River split into seven branches of the delta in Lower Egypt. Lower Egypt was divided into nomes and began to advance as a civilization after 3600 BC. Today, it contains two major channels that flow through the delta of the Nile River – Mahmoudiyah Canal (ancient Agathos Daimon) and Muways Canal (, "waterway of Moses"). Name In Ancient Egyptian, Lower Egypt was as ''mḥw'' and means ''"north"''. Later on, during Antiquity and the Middle Ages, Greeks and Romans called it ''Κάτω Αἴγυπτος'' or ''Aegyptus Inferior'' both meaning "Lower Egypt", but Copts carried on using the old name related to the north – ''Tsakhet'' () or ''Psanemhit'' () meaning the "Northern part". It was further divided into number of regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
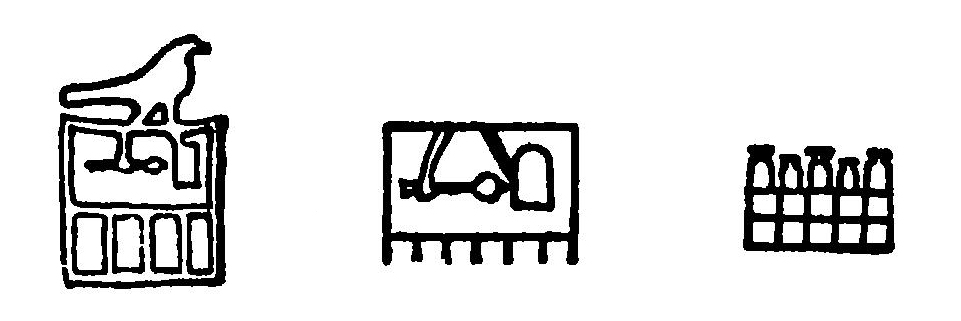
Narmer Palette
The Narmer Palette, also known as the Great Hierakonpolis Palette or the Palette of Narmer, is a significant Egyptian archeological find, dating from about the 31st century BC, belonging, at least nominally, to the category of cosmetic palettes. It contains some of the earliest Egyptian hieroglyphs, hieroglyphic inscriptions ever found. The tablet is thought by some to depict the unification of Upper Egypt, Upper and Lower Egypt under the king Narmer. Along with the Scorpion Macehead and the Narmer Maceheads, also found together in the main deposit at Nekhen, the Narmer Palette provides one of the earliest known depictions of an Egyptian king. On one side, the king is depicted with the bulbed Hedjet, White Crown of Upper (southern) Egypt, and the other side depicts the king wearing the level Deshret, Red Crown of Lower (northern) Egypt, which also makes it the earliest known example of a king wearing both types of headdress. The Palette shows many of the classic conventions of Anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narmer
Narmer ( egy, Wiktionary:nꜥr-mr, nꜥr-mr, meaning "painful catfish," "stinging catfish," "harsh catfish," or "fierce catfish;" ) was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the Early Dynastic Period (Egypt), Early Dynastic Period. He was the successor to the Naqada III, Protodynastic king Ka (pharaoh), Ka. Many scholars consider him the unifier of Egypt and founder of the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty, and in turn the first king of a unified Egypt. He also had a prominently noticeable presence in Canaan, compared to his predecessors and successors. A majority of Egyptologists believe that Narmer was the same person as Menes.Neithhotep is thought to be his queen consort or his daughter. Historical identity Although highly interrelated, the questions of "who was Menes?" and "who unified Egypt?" are actually two separate issues. Narmer is often credited with the unification of Egypt by means of the conquest of Lower Egypt by Upper Egypt. While Menes is traditionally considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menes
Menes (fl. c. 3200–3000 BC; ; egy, mnj, probably pronounced *; grc, Μήνης) was a pharaoh of the Early Dynastic Period of ancient Egypt credited by classical tradition with having united Upper and Lower Egypt and as the founder of the First Dynasty. The identity of Menes is the subject of ongoing debate, although mainstream Egyptological consensus identifies Menes with the Naqada III ruler Narmer or First Dynasty pharaoh Hor-Aha. Both pharaohs are credited with the unification of Egypt to different degrees by various authorities. Name and identity The commonly-used name ''Menes'' derives from Manetho, an Egyptian historian and priest who lived during the Ptolemaic Kingdom. Manetho noted the name in Greek as Μήνης (transliterated: ''Mênês'').Manetho, Fr. 6, 7a, 7b. Text and translation in ''Manetho'', translated by W.G. Waddell (Cambridge: Harvard University, 1940), pp.26–35 An alternative Greek form, Μιν (transliterated: ''Min''), was cited by the fift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pschent
The pschent (; Greek '' ψχέντ'') was the double crown worn by rulers in ancient Egypt. The ancient Egyptians generally referred to it as sekhemty (''sḫm.ty''), the Two Powerful Ones. It combined the White Hedjet Crown of Upper Egypt and the Red Deshret Crown of Lower Egypt. The Pschent represented the pharaoh's power over all of unified Egypt. It bore two animal emblems: an Egyptian cobra, known as the uraeus, ready to strike, which symbolized the Lower Egyptian goddess Wadjet; and an Egyptian vulture representing the Upper Egyptian tutelary goddess Nekhbet. These were fastened to the front of the Pschent and referred to as the ''Two Ladies''. History The invention of the Pschent is generally attributed to the First Dynasty pharaoh Menes, but the first one known to wear a Double Crown was the First Dynasty pharaoh Djet: a rock inscription shows his Horus wearing it. The king list on the Palermo Stone, which begins with the names of Lower Egyptian pharaohs (nowada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deshret
Deshret ( egy, dšrt "Red One") was the formal name for the Red Crown of Lower Egypt and for the desert Red Land on either side of Kemet (Black Land), the fertile Nile river basin. When combined with the Hedjet (White Crown) of Upper Egypt, it forms the Pschent (Double Crown), in ancient Egyptian called the ''sekhemti''. The Red Crown in Egyptian language hieroglyphs eventually was used as the vertical letter "n" . The original "n" hieroglyph from the Predynastic Period and the Old Kingdom was the sign depicting ripples of water. Significance In mythology, the earth deity Geb, original ruler of Egypt, invested Horus with the rule over Lower Egypt. The Egyptian pharaohs, who saw themselves as successors of Horus, wore the ''deshret'' to symbolize their authority over Lower Egypt. Other deities wore the ''deshret'' too, or were identified with it, such as the protective serpent goddess Wadjet and the creator-goddess of Sais, Neith, who often is shown wearing the Red Crown. The Red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedjet
Hedjet ( egy, wikt:ḥḏt#Etymology 2, ḥḏt "White One") is the formal name for the White Crown of pharaoh, pharaonic Upper Egypt. After the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt, it was combined with the Deshret, the Red Crown of Lower Egypt, to form the Pschent, the double crown of Egypt. The symbol sometimes used for the White Crown was the vulture goddess Nekhbet shown next to the head of the cobra goddess Wadjet, the uraeus on the Pschent. History The white crown, along with the red crown, has a long history with each of their respective representations going back into the History of ancient Egypt#Predynastic period, Predynastic Period, indicating that kingship had been the base of Egyptian society for some time. The earliest image of the hedjet was thought to have been in the Qustul in Nubia. According to Jane Roy, "At the time of Williams’ argument, the Qustul cemetery and the ‘royal’ iconography found there was dated to the Naqada IIIA period, thus antedating roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The Sea has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. The Mediterranean Sea e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa: Due to the historical Omani Empire and colonial territories of the British East Africa Protectorate and German East Africa, the term ''East Africa'' is often (especially in the English language) used to specifically refer to the area now comprising the three countries of Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. However, this has never been the convention in many other languages, where the term generally had a wider, strictly geographic context and therefore typically included Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.Somaliland is not included in the United Nations geoscheme, as it is internationally recognized as a part of Somalia. *Tanzania, Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo and South Sudan are members of the East African Community. The firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downriver
Downriver is the unofficial name for a collection of 18 cities and townships in Wayne County, Michigan, south of Detroit, along the western shore of the Detroit River. The place is sometimes referred to as South Detroit. Etymology The name derives from the fact that the Detroit River, after running more or less west along the banks of Detroit and Windsor, Ontario Windsor is a city in southwestern Ontario, Canada, on the south bank of the Detroit River directly across from Detroit, Michigan, United States. Geographically located within but administratively independent of Essex County, it is the souther ..., then bends to flow largely south before emptying into Lake Erie. Communities to the south of the city can thus be accessed by traveling downriver (as opposed to upriver) along the waterway. The Downriver label can be controversial, and many communities and the businesses therein have made various attempts to embrace, reject, or redefine the Downriver name. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |