|
Twin Tail
A twin tail is a specific type of vertical stabilizer arrangement found on the empennage of some aircraft. Two vertical stabilizers—often smaller on their own than a single conventional tail would be—are mounted at the outside of the aircraft's horizontal stabilizer. This arrangement is also known as an H-tail,Schiff, Barry: ''Flying'', page 15. Golden Press, New York, 1971. Library of Congress 78-103424 as it resembles a capital "H" when viewed from the rear. The twin tail was used on a wide variety of World War II multi-engine designs that saw mass production, especially on the American B-24 Liberator and B-25 Mitchell bombers, the British Avro Lancaster and Handley Page Halifax heavy bombers, and the Soviet Union's Petlyakov Pe-2 attack bomber. Variations on the twin tail include the triple tail, twin boom tail and double tail. Design Separating the control surfaces allows for additional rudder area or vertical surface without requiring a massive single tail. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
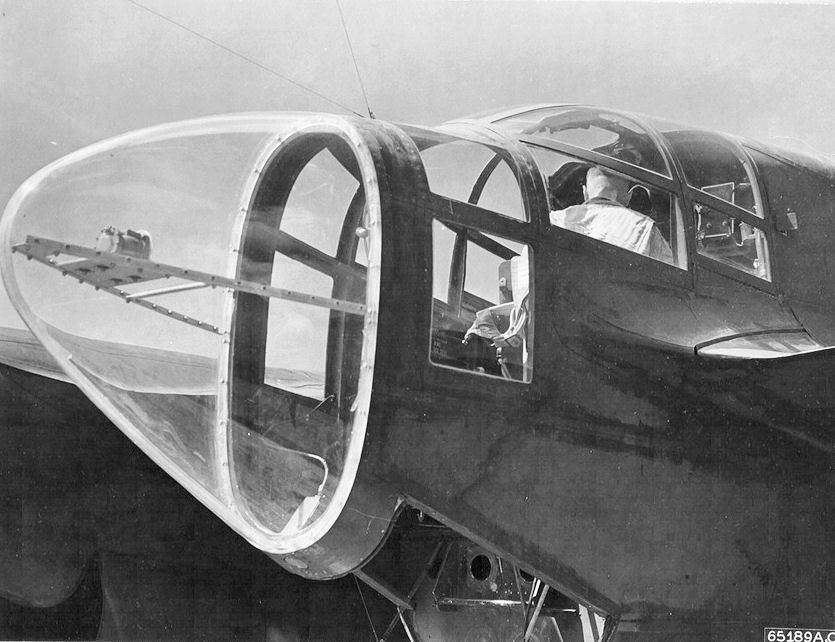
North American B-25C Mitchell (00910460 178)
The North American B-25 Mitchell is an American medium bomber that was introduced in 1941 and named in honor of Major General William "Billy" Mitchell, a pioneer of U.S. military aviation. Used by many Allied air forces, the B-25 served in every theater of World War II, and after the war ended, many remained in service, operating across four decades. Produced in numerous variants, nearly 10,000 B-25s were built. These included several limited models such as the F-10 reconnaissance aircraft, the AT-24 crew trainers, and the United States Marine Corps' PBJ-1 patrol bomber. Design and development The Air Corps issued a specification for a medium bomber in March 1939 that was capable of carrying a payload of over at North American Aviation used its NA-40B design to develop the NA-62, which competed for the medium bomber contract. No YB-25 was available for prototype service tests. In September 1939, the Air Corps ordered the NA-62 into production as the B-25, along with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxiing
Taxiing (rarely spelled taxying) is the movement of an aircraft on the ground, under its own power, in contrast to towing or pushback where the aircraft is moved by a tug. The aircraft usually moves on wheels, but the term also includes aircraft with skis or floats (for water-based travel). An airplane uses taxiways to taxi from one place on an airport to another; for example, when moving from a hangar to the runway. The term "taxiing" is not used for the accelerating run along a runway prior to takeoff, or the decelerating run immediately after landing, which are called the takeoff roll and landing rollout, respectively. Etymology As early as 1909 aviation journalists envisioned aeroplanes to replace the taxicab in traffic-congested cities. Some aviators and some linguists report that around the year 1911 the slang word "taxi" was in use for an "airplane". They suggest that the way aircraft move under power before they take off or after they land reminded someone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop P-61 Black Widow
The Northrop P-61 Black Widow is a twin-engine United States Army Air Forces fighter aircraft of World War II. It was the first operational U.S. warplane designed as a night fighter, and the first aircraft designed specifically as a night fighter. Named for the North American spider ''Latrodectus mactans'', it was an all-metal, twin-engine, twin-boom design armed with four forward-firing 20 mm (.79 in) Hispano M2 autocannon in the lower fuselage, and four M2 Browning machine guns in a dorsal gun turret. Developed during the war, the first test flight was made on May 26, 1942, with the first production aircraft rolling off the assembly line in October 1943. Although not produced in the large numbers of its contemporaries, the Black Widow was operated effectively as a night fighter by United States Army Air Forces squadrons in the European Theater, Pacific Theater, China Burma India Theater, and Mediterranean Theater during World War II. It replaced earlier Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed P-38 Lightning
The Lockheed P-38 Lightning is an American single-seat, twin piston-engined fighter aircraft that was used during World War II. Developed for the United States Army Air Corps by the Lockheed Corporation, the P-38 incorporated a distinctive twin boom, twin-boom design with a central nacelle containing the cockpit and armament. Along with its use as a general fighter aircraft, fighter, the P-38 was used in various aerial combat roles, including as a highly effective fighter-bomber, a night fighter, and a Range (aircraft), long-range escort fighter when equipped with drop tanks. The P-38 was also used as a bomber-pathfinder, guiding streams of medium bomber, medium and heavy bombers, or even other P-38s equipped with bombs, to their targets."P-38 Lightning" National M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-2 Hawkeye
The Northrop Grumman E-2 Hawkeye is an American all-weather, carrier-capable tactical airborne early warning (AEW) aircraft. This twin-turboprop aircraft was designed and developed during the late 1950s and early 1960s by the Grumman Aircraft Company for the United States Navy as a replacement for the earlier, piston-engined E-1 Tracer, which was rapidly becoming obsolete. The aircraft's performance has been upgraded with the E-2B and E-2C versions, where most of the changes were made to the radar and radio communications due to advances in electronic integrated circuits and other electronics. The fourth major version of the Hawkeye is the E-2D, which first flew in 2007. The E-2 was the first aircraft designed specifically for its role, as opposed to a modification of an existing airframe, such as the Boeing E-3 Sentry. Variants of the Hawkeye have been in continuous production since 1960, giving it the longest production run of any carrier-based aircraft. The E-2 also received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing 314 Clipper
The Boeing 314 Clipper was an American long-range flying boat produced by Boeing from 1938 to 1941. One of the largest aircraft of its time, it had the range to cross the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. For its wing, Boeing re-used the design from the earlier XB-15 bomber prototype. Twelve Clippers were built, nine of which served with Pan Am. Design and development Pan American had requested a truly trans-Pacific flying boat with unprecedented range and double the passenger payload of the airline's Martin M-130. Boeing's bid was successful and on July 21, 1936, Pan American signed a contract for six. Boeing engineers adapted the cancelled XB-15's wing, and replaced the Pratt & Whitney Twin Wasp radial engines with the Wright Twin Cyclone. Pan Am ordered six more aircraft with increased engine power and capacity for 77 daytime passengers as the Boeing 314A. The huge flying boat was assembled at Boeing's Plant 1 on the Duwamish River in Seattle, and towed to Ellio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed Constellation
The Lockheed Constellation ("Connie") is a propeller-driven, four-engined airliner built by Lockheed Corporation starting in 1943. The Constellation series was the first pressurized-cabin civil airliner series to go into widespread use. Its pressurized cabin enabled commercial passengers to fly well above most bad weather for the first time, thus significantly improving the general safety and ease of air travel. Several different models of the Constellation series were produced, although they all featured the distinctive triple-tail and dolphin-shaped fuselage. Most were powered by four 18-cylinder Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclones. In total, 856 were produced between 1943 and 1958 at Lockheed's plant in Burbank, California, and used as both a civil airliner and as a military and civilian cargo transport. Among their famous uses was during the Berlin and the Biafran airlifts. Three served as the presidential aircraft for Dwight D. Eisenhower, one of which is featured at the Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breguet Deux-Ponts
Breguet or Bréguet may refer to: * Breguet (watch), watch manufacturer ** Abraham-Louis Breguet (1747–1823), Swiss watchmaker ** Louis-François-Clement Breguet (1804–1883), French physicist, watchmaker, electrical and telegraph work * Bréguet Aviation, a defunct French aircraft manufacturer ** Louis Charles Bréguet (1880–1955), French airplane designer * Breguet School, now known as École supérieure d'ingénieurs en électronique et électrotechnique (ESIEE) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expressed as its lift-to-drag ratio. The lift a wing generates at a given speed and angle of attack can be one to two orders of magnitude greater than the total drag on the wing. A high lift-to-drag ratio requires a significantly smaller thrust to propel the wings through the air at sufficient lift. Lifting structures used in water include various foils, such as hydrofoils. Hydrodynamics is the governing science, rather than aerodynamics. Applications of underwater foils occur in hydroplanes, sailboats and submarines. Etymology and usage For many centuries, the word "wing", from the Old Norse ''vængr'', referred mainly to the foremost limbs of birds (in addition to the architectural aisle). But in recent centuries the word's meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canard (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, a canard is a wing configuration in which a small forewing or foreplane is placed forward of the main wing of a fixed-wing aircraft or a weapon. The term "canard" may be used to describe the aircraft itself, the wing configuration, or the foreplane.. Canard wings are also extensively used in guided missiles and smart bombs. The term "canard" arose from the appearance of the Santos-Dumont 14-bis of 1906, which was said to be reminiscent of a duck (''canard'' in French) with its neck stretched out in flight. Despite the use of a canard surface on the first powered aeroplane, the Wright Flyer of 1903, canard designs were not built in quantity until the appearance of the Saab Viggen jet fighter in 1967. The aerodynamics of the canard configuration are complex and require careful analysis. Rather than use the conventional tailplane configuration found on most aircraft, an aircraft designer may adopt the canard configuration to reduce the main wing loading, to bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dornier Do 19
The Dornier Do 19 was a German four-engine heavy bomber that first flew on 28 October 1936. Only one prototype flew, and it was converted to a transport in 1938. The other two were scrapped. The ''Luftwaffe'' had a shortcoming in the lack of an efficient heavy bomber fleet. ''Generalleutnant'' Walther Wever, the ''Luftwaffe''s first Chief of Staff, was the most persistent advocate of a German long-range strategic bomber fleet. It was built for the ''Luftwaffe''s Ural bomber program under General Wever, competing against the Junkers Ju 89. The RLM ''Technisches Amt'' issued a specification for a four-engine heavy bomber. But after Wever's death in an airplane crash in June 1936, Wever's successor, Albert Kesselring, canceled Germany's long-range bomber projects to concentrate on tactical bombers. Both Dornier and Junkers were competitors for the contract, and each received an order for three prototypes in late 1935. The Dornier design was given the project number Do 19, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitsubishi G3M
The was a Japanese bomber and transport aircraft used by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service (IJNAS) during World War II. The Yokosuka L3Y (Allied reporting name "Tina"), was a transport variant of the aircraft manufactured by the Yokosuka Naval Air Technical Arsenal. Design and development The G3M has its origins in a specification submitted to the Mitsubishi company from the Imperial Japanese Navy requesting a bomber aircraft with a range unprecedented at the time. This principally stemmed from Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto's influence in the Naval High Commission. The bomber was to have the capacity to accommodate an aerial torpedo capable of sinking an armoured battleship. The speed requirement submitted by the naval department was again also unprecedented, not only in Japanese but also in international bomber aviation, where in relation to the envisaged Japanese battlegrounds of China and the Pacific, the bomber would need to not only cover long distances, but neces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)






_(9256079273).jpg)

