|
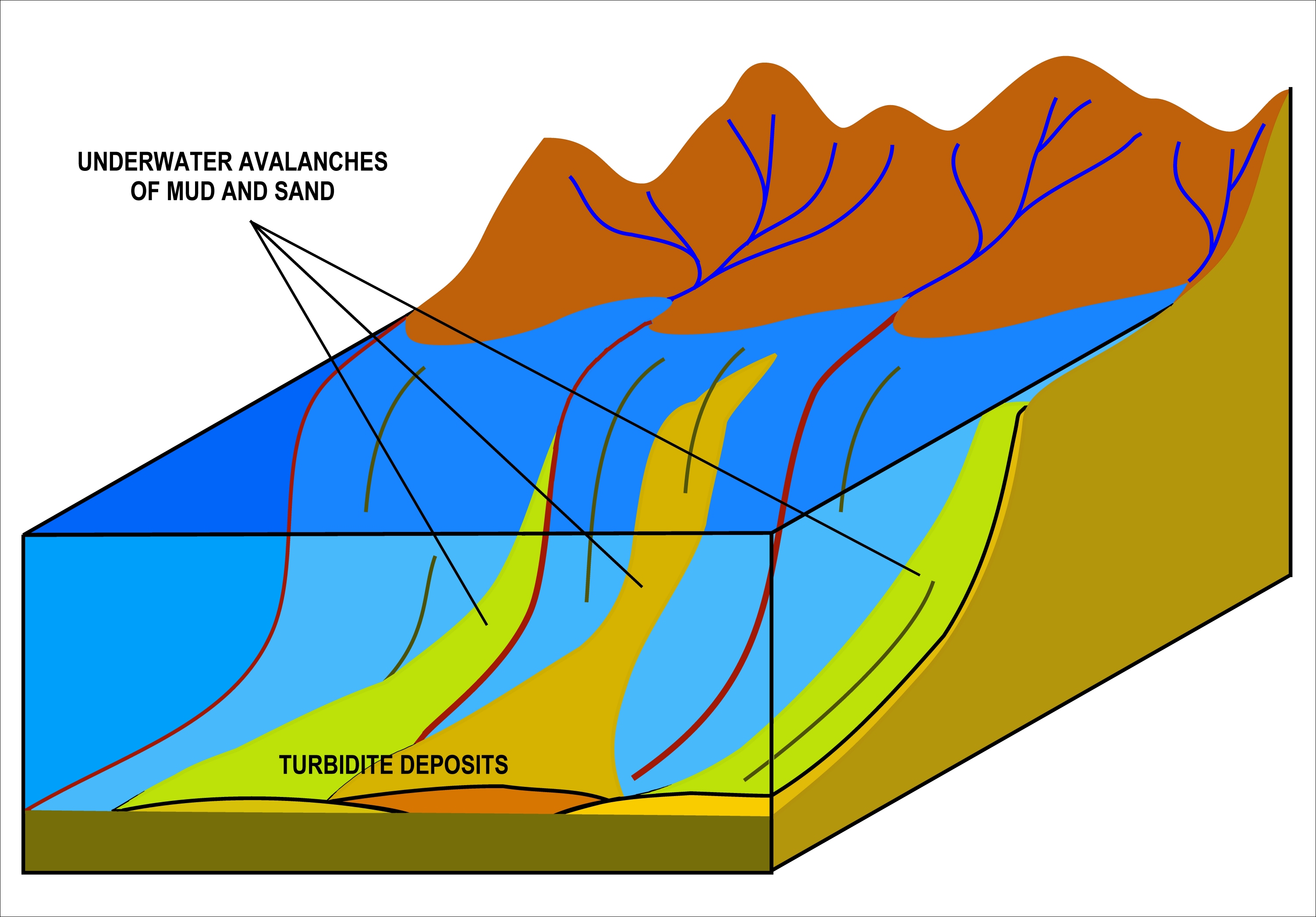
Turbidites
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean. Sequencing Turbidites were first properly described by Arnold H. Bouma (1962), who studied deepwater sediments and recognized particular "fining-up intervals" within deep water, fine-grained shales, which were anomalous because they started at pebble conglomerates and terminated in shales. This was anomalous because within the deep ocean it had historically been assumed that there was no mechanism by which tractional flow could carry and deposit coarse-grained sediments into the abyssal depths. Bouma cycles begin with an erosional contact of a coarse lower bed of pebble to granule conglomerate in a sandy matrix, and grade up through coarse then medium plane parallel sandstone; through cross-bedded sandstone; rippled cross-bedded sand/silty sand, and finally lamina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbidity Current
A turbidity current is most typically an underwater current of usually rapidly moving, sediment-laden water moving down a slope; although current research (2018) indicates that water-saturated sediment may be the primary actor in the process. Turbidity currents can also occur in other fluids besides water. Researchers from the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute found that a layer of water-saturated sediment moved rapidly over the seafloor and mobilized the upper few meters of the preexisting seafloor. Plumes of sediment-laden water were observed during turbidity current events but they believe that these were secondary to the pulse of the seafloor sediment moving during the events. The belief of the researchers is that the water flow is the tail-end of the process that starts at the seafloor. In the most typical case of oceanic turbidity currents, sediment laden waters situated over sloping ground will flow down-hill because they have a higher density than the adjacent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbidite Formation
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean. Sequencing Turbidites were first properly described by Arnold H. Bouma (1962), who studied deepwater sediments and recognized particular "fining-up intervals" within deep water, fine-grained shales, which were anomalous because they started at pebble conglomerates and terminated in shales. This was anomalous because within the deep ocean it had historically been assumed that there was no mechanism by which tractional flow could carry and deposit coarse-grained sediments into the abyssal depths. Bouma cycles begin with an erosional contact of a coarse lower bed of pebble to granule conglomerate in a sandy matrix, and grade up through coarse then medium plane parallel sandstone; through cross-bedded sandstone; rippled cross-bedded sand/silty sand, and finally lamina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbidites
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean. Sequencing Turbidites were first properly described by Arnold H. Bouma (1962), who studied deepwater sediments and recognized particular "fining-up intervals" within deep water, fine-grained shales, which were anomalous because they started at pebble conglomerates and terminated in shales. This was anomalous because within the deep ocean it had historically been assumed that there was no mechanism by which tractional flow could carry and deposit coarse-grained sediments into the abyssal depths. Bouma cycles begin with an erosional contact of a coarse lower bed of pebble to granule conglomerate in a sandy matrix, and grade up through coarse then medium plane parallel sandstone; through cross-bedded sandstone; rippled cross-bedded sand/silty sand, and finally lamina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbidite 2
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean. Sequencing Turbidites were first properly described by Arnold H. Bouma (1962), who studied deepwater sediments and recognized particular "fining-up intervals" within deep water, fine-grained shales, which were anomalous because they started at pebble conglomerates and terminated in shales. This was anomalous because within the deep ocean it had historically been assumed that there was no mechanism by which tractional flow could carry and deposit coarse-grained sediments into the abyssal depths. Bouma cycles begin with an erosional contact of a coarse lower bed of pebble to granule conglomerate in a sandy matrix, and grade up through coarse then medium plane parallel sandstone; through cross-bedded sandstone; rippled cross-bedded sand/silty sand, and finally lamina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sediment Gravity Flow
upright=1.25, This turbidite from the Devonian Becke-Oese Sandstone">Devonian.html" ;"title="turbidite from the Devonian">turbidite from the Devonian Becke-Oese Sandstone of Germany is an example of a deposit from a sediment gravity flow. Note the complete Bouma sequence. A sediment gravity flow is one of several types of sediment transport mechanisms, of which most geologists recognize four principal processes. These flows are differentiated by their dominant sediment support mechanisms, which can be difficult to distinguish as flows can be in transition from one type to the next as they evolve downslope. Sediment support mechanisms Sediment gravity flows are represented by four different mechanisms of keeping grains within the flow in suspension. *Grain flow – Grains in the flow are kept in suspension by grain-to-grain interactions, with the fluid acting only as a lubricant. As such, the grain-to-grain collisions generate a dispersive pressure that helps prevent grains from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouma Sequence
300px, thumbnail, Turbidite from the Devonian-age Becke-Oese Sandstone">Devonian.html" ;"title="Turbidite from the Devonian">Turbidite from the Devonian-age Becke-Oese Sandstone, Germany showing a complete Bouma sequence. The Bouma Sequence (after Arnold H. Bouma, 1932–2011) describes a classic set of sedimentary structures in turbidite beds deposited by turbidity currents at the bottoms of lakes, oceans and rivers. Description The Bouma sequence specifically describes the ideal vertical succession of structures deposited by low-density (i.e., low sand concentration, fine-grained) turbidity currents. An alternate classification scheme that is generally called the Lowe sequence exists for the ideal vertical sequence of structures deposited by high-density flows. The Bouma sequence is divided into 5 distinct layers labelled A through E, with A being at the bottom and E being at the top. Each layer described by Bouma has a specific set of sedimentary structures and a specific l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowe Sequence
The Lowe sequence describes a set of sedimentary structures in turbidite sandstone beds that are deposited by high-density turbidity currents. It is intended to complement, not replace, the better known Bouma sequence, which applies primarily to turbidites deposited by low-density (i.e., low-sand concentration) turbidity currents. Description The Lowe sequence adds three layers labelled S1 through S3 to Bouma's terminology, with S1 being at the bottom and S3 at the top of a sandy turbidite bed. As with the Bouma sequence, each layer has a specific set of sedimentary structures and lithology. And like the Bouma sequence, the layers become finer grained from bottom to top. The layers are described as follows. * S3 - Massive to graded, fine- to coarse-grained sandstones that overlie the S2 layer represent deposition from a turbulent suspension. Sometimes dish structures and dewatering pipes are present. This layer is essentially the same as the Bouma A layer. * S2 - Inverse (revers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
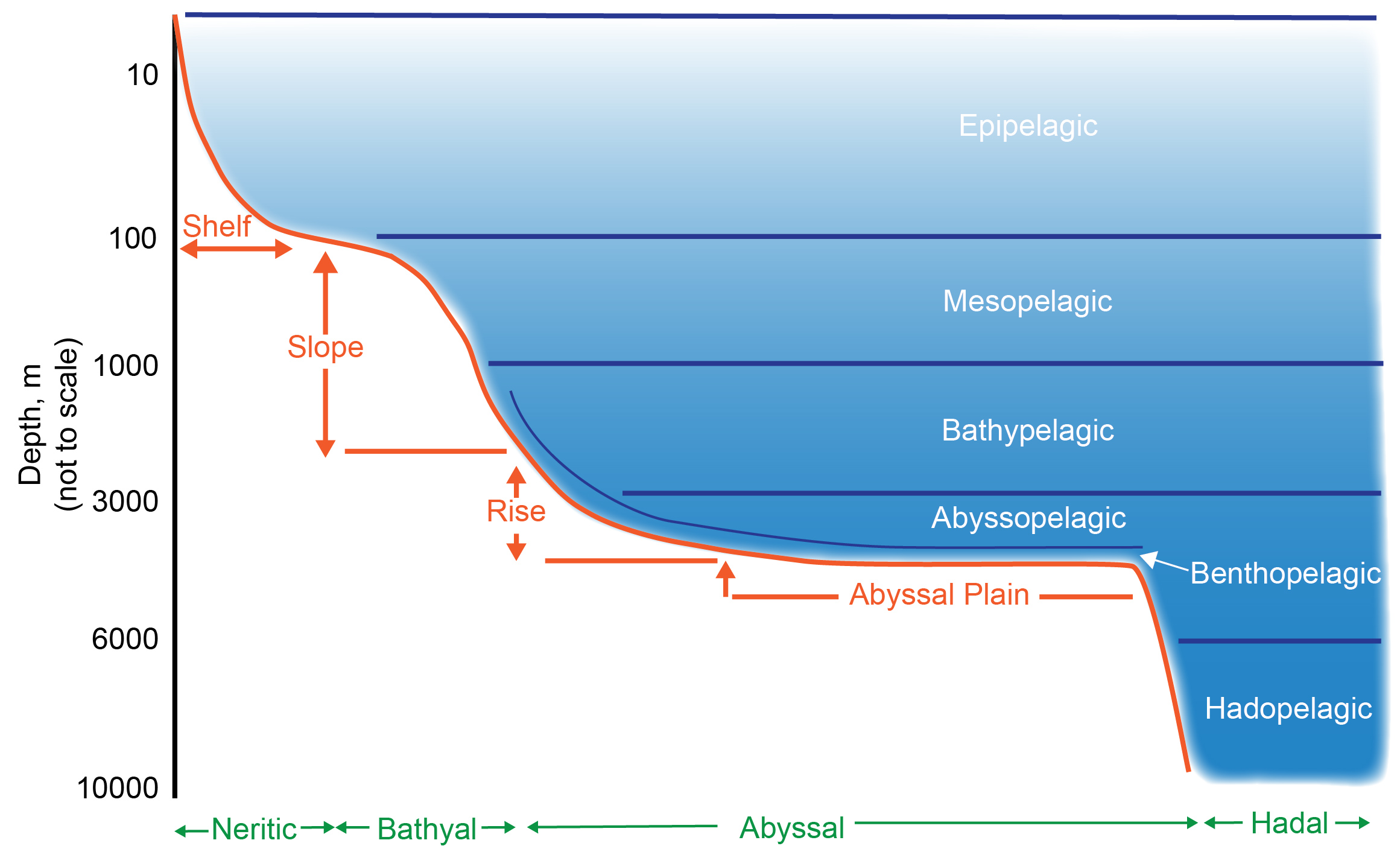
Deep Ocean
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 metres (656 feet) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combination of low temperatures, darkness and high pressure The deep sea is considered the least explored Earth biome, with the extreme conditions making the environment difficult to access and explore. Organisms living within the deep sea have a variety of adaptations to survive in these conditions. Organisms can survive in the deep sea through a number of feeding methods including scavenging, predation and filtration, with a number of organisms surviving by feeding on marine snow. Marine snow is organic material that has fallen from upper waters into the deep sea. In 1960, the bathyscaphe ''Trieste'' descended to the bottom of the Mariana Trench near Guam, at , the deepest known spot in any ocean. If Mount Everest () were submerged there, its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into ''static friction'' ("stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and ''kinetic friction'' between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities (see Figure 1). *Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other. *Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces. *Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. *Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ripple Marks
In geology, ripple marks are sedimentary structures (i.e., bedforms of the lower flow regime) and indicate agitation by water ( current or waves) or wind. Defining ripple cross-laminae and asymmetric ripples * ''Current ripple marks'', ''unidirectional ripples'', or ''asymmetrical ripple marks'' are asymmetrical in profile, with a gentle up-current slope and a steeper down-current slope. The down-current slope is the angle of repose, which depends on the shape of the sediment. These commonly form in fluvial and aeolian depositional environments, and are a signifier of the lower part of the Lower Flow Regime. * Ripple cross-laminae forms when deposition takes place during migration of current or wave ripples. A series of cross-laminae are produced by superimposing migrating ripples. The ripples form lateral to one another, such that the crests of vertically succeeding laminae are out of phase and appear to be advancing upslope. This process results in cross-bedded unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements. An ocean current flows for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth’s regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temperature of the area by warming the sea breezes that blow over them. Perhaps the most striking example is the Gulf Stream, which makes northwest Europe much more temperate for its high latitude compared to other are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graded Bedding
In geology, a graded bed is one characterized by a systematic change in grain or clast size from one side of the bed to the other. Most commonly this takes the form of normal grading, with coarser sediments at the base, which grade upward into progressively finer ones. Such a bed is also described as fining upward. Normally graded beds generally represent depositional environments which decrease in transport energy (rate of flow) as time passes, but these beds can also form during rapid depositional events. They are perhaps best represented in turbidite strata, where they indicate a sudden strong current that deposits heavy, coarse sediments first, with finer ones following as the current weakens. They can also form in terrestrial stream deposits. In reverse grading or inverse grading the bed coarsens upwards. This type of grading is relatively uncommon but is characteristic of sediments deposited by grain flow and debris flow. It is also observed in aeolian processes, such as in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |