|
Tune Shift With Amplitude
The tune shift with amplitude is an important concept in circular accelerators or synchrotrons. The machine may be described via a symplectic one turn map at each position, which may be thought of as the Poincaire section of the dynamics. A simple harmonic oscillator has a constant tune for all initial positions in phase space. Adding some non-linearity results in a variation of the tune with amplitude. Amplitude may refer to either the initial position, or more formally, the initial action of the particle. Definition Consider dynamics in phase space. These dynamics are assumed to be determined by a Hamiltonian, or a symplectic map. For each initial position, we follow the particle as it traces out its orbit. After transformation into action-angle coordinates, one compute the tune \nu and the action J. The tune shift with amplitude is then given by \frac. The transformation to action-angle variables out of which the tune may be derived may be considered as a transformatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined beams. Large accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle physics. The largest accelerator currently active is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) near Geneva, Switzerland, operated by the CERN. It is a collider accelerator, which can accelerate two beams of protons to an energy of 6.5 TeV and cause them to collide head-on, creating center-of-mass energies of 13 TeV. Other powerful accelerators are, RHIC at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York and, formerly, the Tevatron at Fermilab, Batavia, Illinois. Accelerators are also used as synchrotron light sources for the study of condensed matter physics. Smaller particle accelerators are used in a wide variety of applications, including particle therapy for oncological purposes, radioisotope production for medical diagnostics, ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchrotron
A synchrotron is a particular type of cyclic particle accelerator, descended from the cyclotron, in which the accelerating particle beam travels around a fixed closed-loop path. The magnetic field which bends the particle beam into its closed path increases with time during the accelerating process, being ''synchronized'' to the increasing kinetic energy of the particles. The synchrotron is one of the first accelerator concepts to enable the construction of large-scale facilities, since bending, beam focusing and acceleration can be separated into different components. The most powerful modern particle accelerators use versions of the synchrotron design. The largest synchrotron-type accelerator, also the largest particle accelerator in the world, is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) near Geneva, Switzerland, built in 2008 by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN). It can accelerate beams of protons to an energy of 6.5 tera electronvolts (TeV or 1012 eV). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
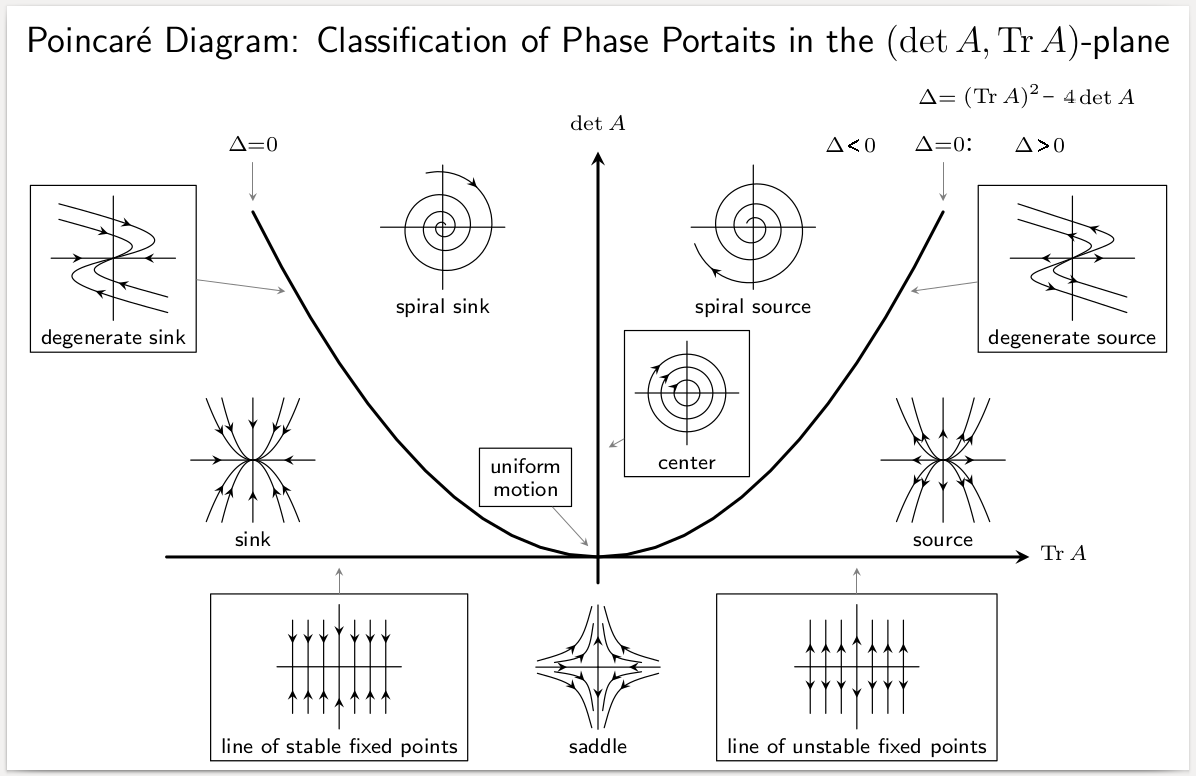
Phase Space
In dynamical system theory, a phase space is a space in which all possible states of a system are represented, with each possible state corresponding to one unique point in the phase space. For mechanical systems, the phase space usually consists of all possible values of position and momentum variables. It is the outer product of direct space and reciprocal space. The concept of phase space was developed in the late 19th century by Ludwig Boltzmann, Henri Poincaré, and Josiah Willard Gibbs. Introduction In a phase space, every degree of freedom or parameter of the system is represented as an axis of a multidimensional space; a one-dimensional system is called a phase line, while a two-dimensional system is called a phase plane. For every possible state of the system or allowed combination of values of the system's parameters, a point is included in the multidimensional space. The system's evolving state over time traces a path (a phase-space trajectory for the system) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symplectomorphism
In mathematics, a symplectomorphism or symplectic map is an isomorphism in the category of symplectic manifolds. In classical mechanics, a symplectomorphism represents a transformation of phase space that is volume-preserving and preserves the symplectic structure of phase space, and is called a canonical transformation. Formal definition A diffeomorphism between two symplectic manifolds f: (M,\omega) \rightarrow (N,\omega') is called a symplectomorphism if :f^*\omega'=\omega, where f^* is the pullback of f. The symplectic diffeomorphisms from M to M are a (pseudo-)group, called the symplectomorphism group (see below). The infinitesimal version of symplectomorphisms gives the symplectic vector fields. A vector field X \in \Gamma^(TM) is called symplectic if :\mathcal_X\omega=0. Also, X is symplectic iff the flow \phi_t: M\rightarrow M of X is a symplectomorphism for every t. These vector fields build a Lie subalgebra of \Gamma^(TM). Here, \Gamma^(TM) is the set of smooth vector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action-angle Coordinates
In classical mechanics, action-angle coordinates are a set of canonical coordinates useful in solving many integrable systems. The method of action-angles is useful for obtaining the frequency, frequencies of oscillatory or rotational motion without solving the equations of motion. Action-angle coordinates are chiefly used when the Hamilton–Jacobi equations are completely separable. (Hence, the Hamiltonian (quantum mechanics), Hamiltonian does not depend explicitly on time, i.e., the conservation of energy, energy is conserved.) Action-angle variables define an invariant torus, so called because holding the action constant defines the surface of a torus, while the angle variables parameterize the coordinates on the torus. The Bohr–Sommerfeld quantization conditions, used to develop quantum mechanics before the advent of Schrödinger equation#Particles as waves, wave mechanics, state that the action must be an integral multiple of Planck's constant; similarly, Albert Einstein, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action (physics)
In physics, action is a scalar quantity describing how a physical system has dynamics (physics), changed over time. Action is significant because the equations of motion of the system can be derived through the principle of stationary action. In the simple case of a single particle moving with a constant velocity (uniform linear motion), the action is the momentum of the particle times the distance it moves, integral (mathematics), added up along its path; equivalently, action is twice the particle's kinetic energy times the duration for which it has that amount of energy. For more complicated systems, all such quantities are combined. More formally, action is a functional (mathematics), mathematical functional which takes the trajectory (also called path or history) of the system as its argument and has a real number as its result. Generally, the action takes different values for different paths. Action has dimensional analysis, dimensions of energy × time or momentu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Form (mathematics)
In mathematics and computer science, a canonical, normal, or standard form of a mathematical object is a standard way of presenting that object as a mathematical expression. Often, it is one which provides the simplest representation of an object and which allows it to be identified in a unique way. The distinction between "canonical" and "normal" forms varies from subfield to subfield. In most fields, a canonical form specifies a ''unique'' representation for every object, while a normal form simply specifies its form, without the requirement of uniqueness. The canonical form of a positive integer in decimal representation is a finite sequence of digits that does not begin with zero. More generally, for a class of objects on which an equivalence relation is defined, a canonical form consists in the choice of a specific object in each class. For example: *Jordan normal form is a canonical form for matrix similarity. *The row echelon form is a canonical form, when one consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stability Theory
In mathematics, stability theory addresses the stability of solutions of differential equations and of trajectories of dynamical systems under small perturbations of initial conditions. The heat equation, for example, is a stable partial differential equation because small perturbations of initial data lead to small variations in temperature at a later time as a result of the maximum principle. In partial differential equations one may measure the distances between functions using Lp norms or the sup norm, while in differential geometry one may measure the distance between spaces using the Gromov–Hausdorff distance. In dynamical systems, an orbit is called ''Lyapunov stable'' if the forward orbit of any point is in a small enough neighborhood or it stays in a small (but perhaps, larger) neighborhood. Various criteria have been developed to prove stability or instability of an orbit. Under favorable circumstances, the question may be reduced to a well-studied problem involvi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Aperture (accelerator Physics)
The dynamic aperture is the stability region of phase space in a circular accelerator. For hadrons In the case of protons or heavy ion accelerators, (or synchrotrons, or storage rings), there is minimal radiation, and hence the dynamics is symplectic. For long term stability, tiny dynamical diffusion (or Arnold diffusion In applied mathematics, Arnold diffusion is the phenomenon of instability of integrable Hamiltonian systems. The phenomenon is named after Vladimir Arnold who was the first to publish a result in the field in 1964. More precisely, Arnold diffusio ...) can lead an initially stable orbit slowly into an unstable region. This makes the dynamic aperture problem particularly challenging. One may be considering stability over billions of turns. A scaling law for Dynamic aperture vs. number of turns has been proposed by Giovannozzi. For electrons For the case of electrons, the electrons will radiate which causes a damping effect. This means that one typically only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Mechanics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For objects governed by classical mechanics, if the present state is known, it is possible to predict how it will move in the future (determinism), and how it has moved in the past (reversibility). The earliest development of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Joseph-Louis Lagrange, Leonhard Euler, and other contemporaries, in the 17th century to describe the motion of bodies under the influence of a system of forces. Later, more abstract methods were developed, leading to the reformulations of classical mechanics known as Lagrangian mechanics and Hamiltonian mechanics. These advances, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position. When released, the restoring force acting on the pendulum's mass causes it to oscillate about the equilibrium position, swinging back and forth. The time for one complete cycle, a left swing and a right swing, is called the period. The period depends on the length of the pendulum and also to a slight degree on the amplitude, the width of the pendulum's swing. From the first scientific investigations of the pendulum around 1602 by Galileo Galilei, the regular motion of pendulums was used for timekeeping and was the world's most accurate timekeeping technology until the 1930s. The pendulum clock invented by Christiaan Huygens in 1658 became the world's standard timekeeper, used in homes and offices for 270 years, and ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextupole Magnet
A sextupole magnet (also known as a hexapole magnet) consist of six magnetic poles set out in an arrangement of alternating north and south poles arranged around an axis. They are used in particle accelerators for the control of chromatic aberrations and for damping the head tail instability. Two sets of sextupole magnet A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, ...s are used in transmission electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopes to correct for spherical aberration. The design of sextupoles using electromagnets generally involves six steel pole tips of alternating polarity. The steel is magnetised by a large electric current that flows in the coils of wire wrapped around the poles. The coils may be formed from hollow copper magnet wire that carry coolant, usu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |