|
Trochoidal Pump
A gerotor is a positive displacement pump. The name ''gerotor'' is derived from "generated rotor". A gerotor unit consists of an inner and outer rotor. The inner rotor has ''n'' teeth, while the outer rotor has ''n''+1 teeth; with ''n'' defined as a natural number greater than or equal to 2. The axis of the inner rotor is offset from the axis of the outer rotor and both rotors rotate on their respective axes. The geometry of the two rotors partitions the volume between them into ''n'' different dynamically-changing volumes. During the assembly's rotation cycle, each of these volumes changes continuously, so any given volume first increases, and then decreases. An increase creates a vacuum. This vacuum creates suction, and hence, this part of the cycle is where the inlet is located. As a volume decreases compression occurs. During this compression period, fluids can be pumped, or, if they are gaseous fluids, compressed. Gerotor pumps are generally designed using a trochoidal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerotor Anm
A gerotor is a positive displacement pump. The name ''gerotor'' is derived from "generated rotor". A gerotor unit consists of an inner and outer rotor. The inner rotor has ''n'' teeth, while the outer rotor has ''n''+1 teeth; with ''n'' defined as a natural number greater than or equal to 2. The axis of the inner rotor is offset from the axis of the outer rotor and both rotors rotate on their respective axes. The geometry of the two rotors partitions the volume between them into ''n'' different dynamically-changing volumes. During the assembly's rotation cycle, each of these volumes changes continuously, so any given volume first increases, and then decreases. An increase creates a vacuum. This vacuum creates suction, and hence, this part of the cycle is where the inlet is located. As a volume decreases compression occurs. During this compression period, fluids can be pumped, or, if they are gaseous fluids, compressed. Gerotor pumps are generally designed using a trochoidal inner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Compressor
A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor. Compressors are similar to pumps: both increase the pressure on a fluid and both can transport the fluid through a pipe. The main distinction is that the focus of a compressor is to change the density or volume of the fluid, which is mostly only achievable on gases. Gases are compressible, while liquids are relatively incompressible, so compressors are rarely used for liquids. The main action of a pump is to pressurize and transport liquids. Many compressors can be staged, that is, the fluid is compressed several times in steps or stages, to increase discharge pressure. Often, the second stage is physically smaller than the primary stage, to accommodate the already compressed gas without reducing its pressure. Each stage further compresses the gas and increases its pressure and also temperature (if inter cooling between stages i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the most prestigious and highly ranked academic institutions in the world. Founded in response to the increasing industrialization of the United States, MIT adopted a European polytechnic university model and stressed laboratory instruction in applied science and engineering. MIT is one of three private land grant universities in the United States, the others being Cornell University and Tuskegee University. The institute has an urban campus that extends more than a mile (1.6 km) alongside the Charles River, and encompasses a number of major off-campus facilities such as the MIT Lincoln Laboratory, the Bates Center, and the Haystack Observatory, as well as affiliated laboratories such as the Broad and Whitehead Institutes. , 98 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology Review
''MIT Technology Review'' is a bimonthly magazine wholly owned by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and editorially independent of the university. It was founded in 1899 as ''The Technology Review'', and was re-launched without "The" in its name on April 23, 1998 under then publisher R. Bruce Journey. In September 2005, it was changed, under its then editor-in-chief and publisher, Jason Pontin, to a form resembling the historical magazine. Before the 1998 re-launch, the editor stated that "nothing will be left of the old magazine except the name." It was therefore necessary to distinguish between the modern and the historical ''Technology Review''. The historical magazine had been published by the MIT Alumni Association, was more closely aligned with the interests of MIT alumni, and had a more intellectual tone and much smaller public circulation. The magazine, billed from 1998 to 2005 as "MIT's Magazine of Innovation," and from 2005 onwards as simply "published by MIT" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conical Screw Compressor
The relatively recently developed conical screw compressor is a type of rotary-screw compressor using a different topology from the typical dual-screw type, in effect it is a conical spiral extension of a gerotor A gerotor is a positive displacement pump. The name ''gerotor'' is derived from "generated rotor". A gerotor unit consists of an inner and outer rotor. The inner rotor has ''n'' teeth, while the outer rotor has ''n''+1 teeth; with ''n'' defined a .... Because of this it does not have the inherent "blow-hole" leakage path which in typical screw compressors is responsible for significant leakage through the assembly and makes low-speed operation impractical. This theoretically allows much smaller rotors to have practical efficiency since at smaller sizes the leakage area does not become as large a portion of the pumping area as in straight screw compressors. In conjunction with the decreasing diameter of the cone shaped rotor this may also allows much higher compression r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
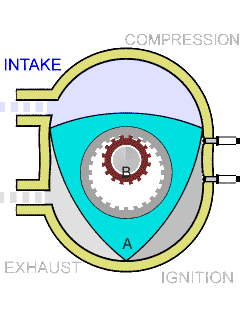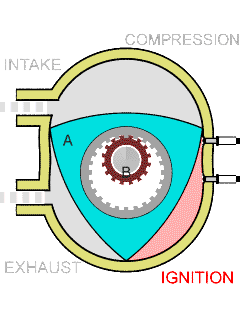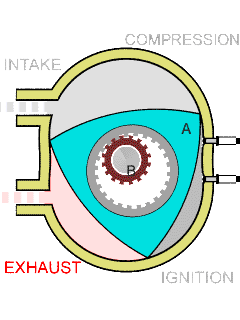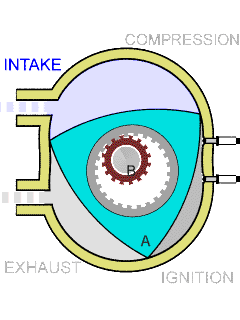
Wankel Engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an Eccentric (mechanism), eccentric rotary combustion engine, rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. It was invented by German engineer Felix Wankel, and designed by German engineer Hanns-Dieter Paschke. The Wankel engine's rotor, which creates the turning motion, is similar in shape to a Reuleaux triangle, with the sides having less curvature. The rotor rotates inside an oval-like epitrochoidal housing, around a central output shaft. The rotor spins in a hula-hoop fashion around the central output shaft, spinning the shaft via toothed gearing. Due to its inherent poor thermodynamics, the Wankel engine has a significantly worse thermal efficiency and worse exhaust gas behaviour when compared against the Otto engine or the Diesel engine, which is why the Wankel engine has seen limited use since its introduction in the 1960s. However, its advantages of compact design, smoothness, lower weight and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasiturbine
The Quasiturbine or Qurbine engine is a proposed pistonless rotary engine using a rhomboidal rotor whose sides are hinged at the vertices. The volume enclosed between the sides of the rotor and the rotor casing provide compression and expansion in a fashion similar to the more familiar Wankel engine, but the hinging at the edges allows the volume ratio to increase. A geometrical indetermination (not uniquely defined) of the Quasiturbine confinement stator shape allows for a variety of profiles (including asymetrical) and design characteristics. Unlike vane pumps, in which vane extension is generally important and against which the pressure acts to generate the rotation, the Quasiturbine contour seals have a minimal extension and the rotation does not result from pressure against these seals. Since the rotational force within the Quasiturbine comes from the pressure on the entire pivoting-blade, and not on an extensible vanes which impose a geometric back flow at chamber overlap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gear Pump
A gear pump uses the meshing of gears to pump fluid by displacement. They are one of the most common types of pumps for hydraulic machinery, hydraulic fluid power applications. The gear pump was invented around 1600 by Johannes Kepler. Gear pumps are also widely used in chemical installations to pump high viscosity fluids. There are two main variations: ''external gear pumps'' which use two external spur gears, and ''internal gear pumps'' which use an external and an internal spur gear (internal spur gear teeth face inwards, see below). Gear pumps are positive displacement pump, ''positive displacement'' (or ''fixed displacement''), meaning they pump a constant amount of fluid for each revolution. Some gear pumps are designed to function as either a Hydraulic motor, motor or a pump. Theory of operation As the gears rotate they separate on the intake side of the pump, creating a void and suction which is filled by fluid. The fluid is carried by the gears to the discharge sid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
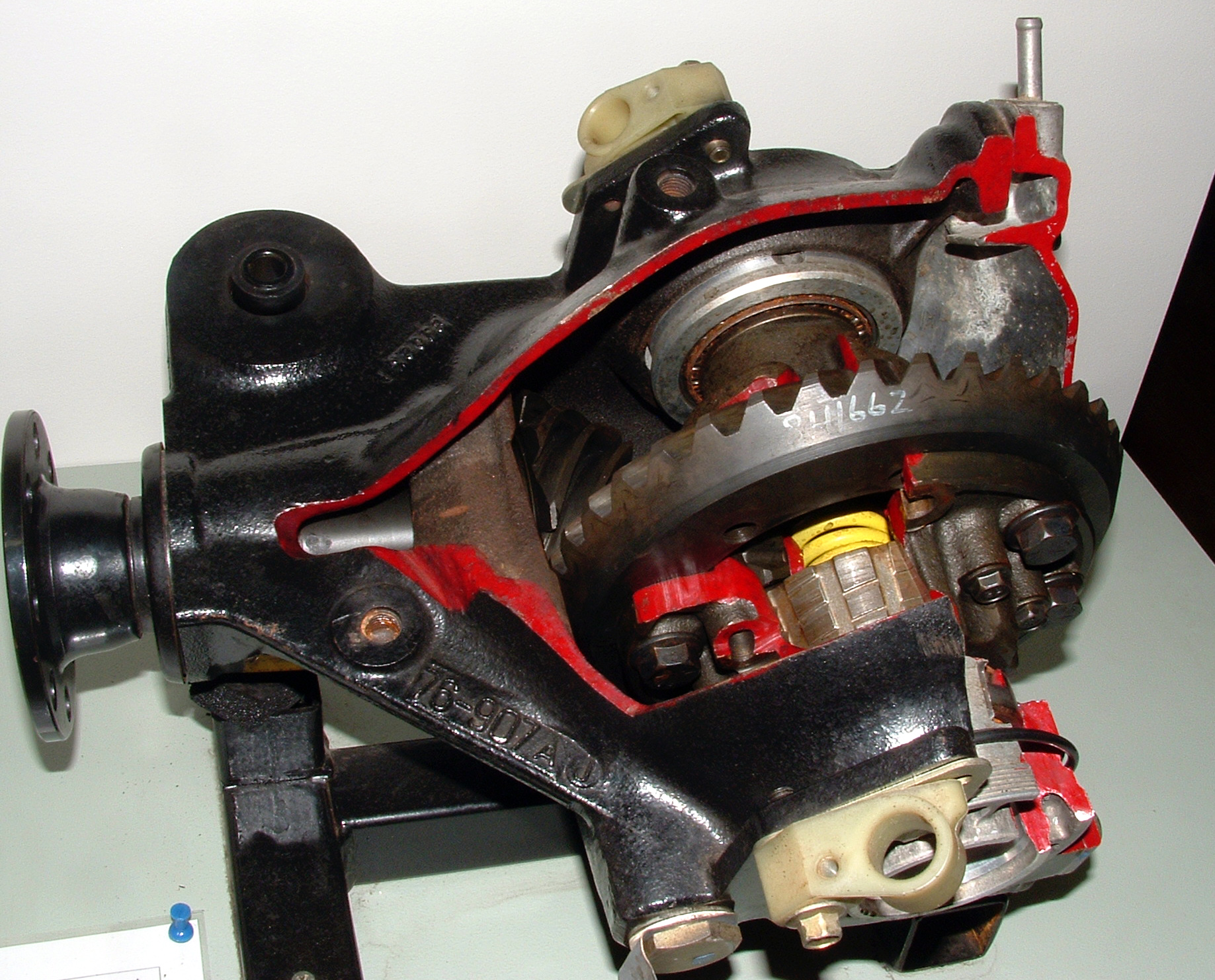
Limited-slip Differential
A limited-slip differential (LSD) is a type of differential that allows its two output shafts to rotate at different speeds but limits the maximum difference between the two shafts. Limited-slip differentials are often known by the generic trademark Positraction, a brand name owned by General Motors. In an automobile, such limited-slip differentials are sometimes used in place of a standard differential, where they convey certain dynamic advantages, at the expense of greater complexity. Early history In 1932, Ferdinand Porsche designed a Grand Prix racing car for the Auto Union company. The high power of the design caused one of the rear wheels to experience excessive wheel spin at any speed up to . In 1935, Porsche commissioned the engineering firm ZF to design a limited-slip differential to improve performance. The ZF "sliding pins and cams" became available, and one example was the Type B-70 used during the Second World War in the military VWs ( Kübelwagen and Schwimmwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Steering
A power steering is a mechanical device equipped on a motor vehicle that helps drivers steer the vehicle by reducing steering effort needed to turn the steering wheel, making it easier for the vehicle to turn or maneuver at lower speeds. Hydraulic or electric actuators add controlled energy to the steering mechanism, so the driver can provide less effort to turn the steered wheels when driving at typical speeds, and reduce considerably the physical effort necessary to turn the wheels when a vehicle is stopped or moving slowly. Power steering can also be engineered to provide some artificial feedback of forces acting on the steered wheels. Hydraulic power steering systems for cars augment steering effort via an actuator, a hydraulic cylinder that is part of a servo system. These systems have a direct mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the linkage that steers the wheels. This means that power-steering system failure (to augment effort) still permits the vehicle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Motor
A hydraulic motor is a mechanical actuator that converts hydraulics, hydraulic pressure and flow into torque and angular displacement (rotation). The hydraulic motor is the rotary counterpart of the hydraulic cylinder as a linear actuator. Most broadly, the category of devices called hydraulic motors has sometimes included those that run on hydropower (namely, water engine, water engines and water motors) but in today's terminology the name usually refers more specifically to motors that use hydraulic fluid as part of closed hydraulic circuits in modern hydraulic machinery. Conceptually, a hydraulic motor should be interchangeable parts, interchangeable with a hydraulic pump because it performs the opposite function - similar to the way a DC electric motor is theoretically interchangeable with a DC electrical generator. However, many hydraulic pumps cannot be used as hydraulic motors because they cannot be backdriven. Also, a hydraulic motor is usually designed for working pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy. Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power generation), heat energy (e.g. geothermal), chemical energy, electric potential and nuclear energy (from nuclear fission or nuclear fusion). Many of these processes generate heat as an intermediate energy form, so heat engines have special importance. Some natural processes, such as atmospheric convection cells convert environmental heat into motion (e.g. in the form of rising air currents). Mechanical energy is of particular importance in transportation, but also plays a role in many industrial processes such as cutting, grinding, crushing, and mixing. Mechanical heat engines convert heat into work via various thermodynamic processes. The internal combustion engine is perhaps the most common example of a mechanical heat engine, in which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)