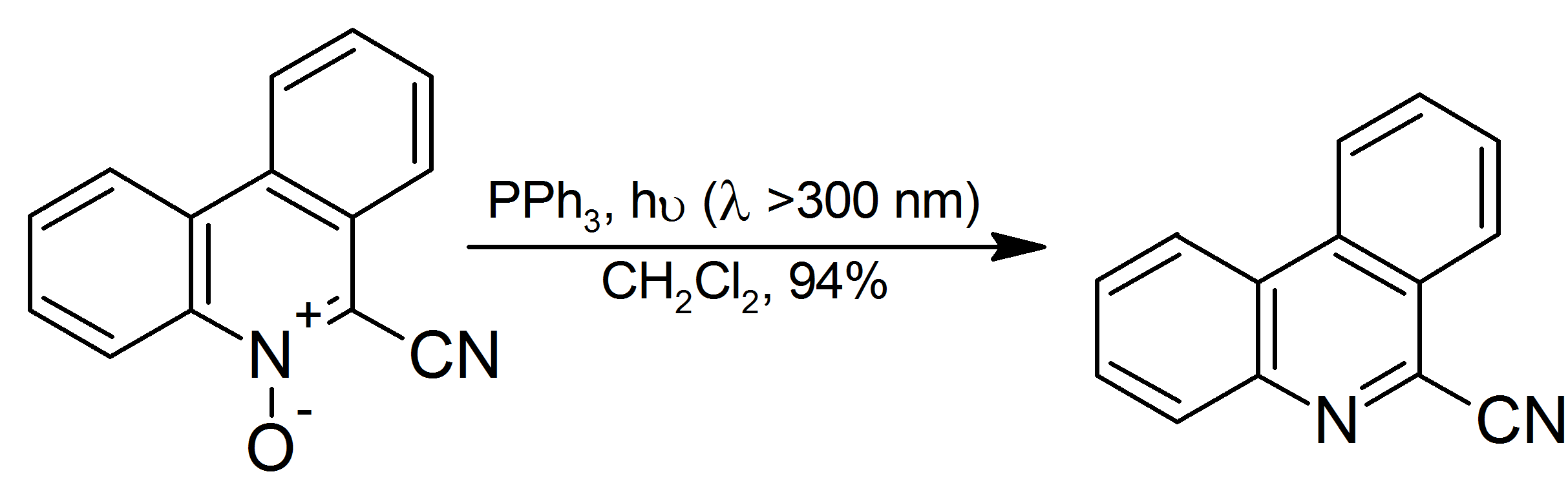
|
Triphenyl Phosphine
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether. Preparation and structure Triphenylphosphine can be prepared in the laboratory by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyllithium. The industrial synthesis involves the reaction between phosphorus trichloride, chlorobenzene, and sodium: :PCl3 + 3 PhCl + 6 Na → PPh3 + 6 NaCl Triphenylphosphine crystallizes in triclinic and monoclinic modification. In both cases, the molecule adopts a pyramidal structure with propeller-like arrangement of the three phenyl groups. Principal reactions with chalcogens, halogens, and acids Oxidation Triphenylphosphine undergoes sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term " metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols (that is, sulfur takes the place of oxygen in the hydroxyl () group of an alcohol), and the word is a blend of "''thio-''" with "alcohol". Many thiols have strong odors resembling that of garlic or rotten eggs. Thiols are used as odorants to assist in the detection of natural gas (which in pure form is odorless), and the "smell of natural gas" is due to the smell of the thiol used as the odorant. Thiols are sometimes referred to as mercaptans () or mercapto compounds, a term introduced in 1832 by William Christopher Zeise and is derived from the Latin ('capturing mercury')''Oxford American Dictionaries'' (Mac OS X Leopard). because the thiolate group () bonds very strong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysulfide
Polysulfides are a class of chemical compounds containing chains of sulfur atoms. There are two main classes of polysulfides: inorganic and organic. Among the inorganic polysulfides, there are ones which contain anions, which have the general formula . These anions are the conjugate bases of the hydrogen polysulfides . Organic polysulfides generally have the formulae , where R = alkyl or aryl. Polysulfide salts and complexes The alkali metal polysulfides arise by treatment of a solution of sulfide, e.g. sodium sulfide, with elemental sulfur: : In some cases, these anions have been obtained as organic salts, which are soluble in organic solvents. The energy released in the reaction of sodium and elemental sulfur is the basis of battery technology. The sodium–sulfur battery and the lithium–sulfur battery require high temperatures to maintain liquid polysulfide and -conductive membranes that are unreactive toward sodium, sulfur, and sodium sulfide. Polysulfides are ligands i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the production o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopropanol
Isopropyl alcohol (IUPAC name propan-2-ol and also called isopropanol or 2-propanol) is a colorless, flammable organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor. As an isopropyl group linked to a hydroxyl group (chemical formula ) it is the simplest example of a secondary alcohol, where the alcohol carbon atom is attached to two other carbon atoms. It is a structural isomer of propan-1-ol and ethyl methyl ether. It is used in the manufacture of a wide variety of industrial and household chemicals and is a common ingredient in products such as antiseptics, disinfectants, hand sanitizer and detergents. Well over one million tonnes is produced worldwide annually. Properties Isopropyl alcohol is miscible in water, ethanol, and chloroform as, like these compounds, isopropyl is a polar molecule. It dissolves ethyl cellulose, polyvinyl butyral, many oils, alkaloids, and natural resins. Unlike ethanol or methanol, isopropyl alcohol is not miscible with salt solutions and can be se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, Combustibility and flammability, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of Carbohydrate, sugars by yeasts or via Petrochemistry, petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of organic compounds, and as a Alcohol fuel, fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recrystallization (chemistry)
In chemistry, recrystallization is a technique used to purify chemicals. By dissolving a mixture of a compound and impurities in an appropriate solvent, either the desired compound or impurities can be removed from the solution, leaving the other behind. It is named for the crystals often formed when the compound precipitates out. Alternatively, ''recrystallization'' can refer to the natural growth of larger ice crystals at the expense of smaller ones. Chemistry In chemistry, recrystallization is a procedure for purifying compounds. The most typical situation is that a desired "compound A" is contaminated by a small amount of "impurity B". There are various methods of purification that may be attempted (see Separation process), recrystallization being one of them. There are also different recrystallization techniques that can be used such as: Single-solvent recrystallization Typically, the mixture of "compound A" and "impurity B" is dissolved in the smallest amount of hot solv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylphosphine Oxide
Triphenylphosphine oxide (often abbreviated TPPO) is the organophosphorus compound with the formula OP(C6H5)3, also written as Ph3PO or PPh3O (Ph = phenyl, C6H5). This colourless crystalline compound is a common but potentially useful waste product in reactions involving triphenylphosphine. It is a popular reagent to induce the crystallization, crystallizing of chemical compounds. Structure and properties Ph3PO is a tetrahedral molecule related to POCl3. The oxygen center is relatively basic. The rigidity of the backbone and the basicity of the oxygen center make this species a popular agent to crystallize otherwise difficult to crystallize molecules. This trick is applicable to molecules that have acidic hydrogen atoms, e.g. phenols. Up to now, several modifications of Ph3PO have been found: For example, a monoclinic form crystalizes in the space group ''P''21/''c'' with Z = 4 and a = 15.066(1) Å, b = 9.037(2) Å, c = 11.296(3) Å, and β = 98.47(1)°. The orthorhombic modif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorobenzene
Chlorobenzene is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals. Uses Historical The major use of chlorobenzene is as an intermediate in the production of herbicides, dyestuffs, and rubber. Chlorobenzene is also used as a high-boiling solvent in industrial applications as well as in the laboratory. Chlorobenzene is nitrated on a large scale to give a mixture of 2-nitrochlorobenzene and 4-nitrochlorobenzene, which are separated. These mononitrochlorobenzenes are converted to related 2-nitrophenol, 2-nitroanisole, bis(2-nitrophenyl)disulfide, and 2-nitroaniline by nucleophilic displacement of the chloride, with respectively sodium hydroxide, sodium methoxide, sodium disulfide, and ammonia. The conversions of the 4-nitro derivative are similar. Chlorobenzene once was used in the manufacture of pesticides, most notably DDT, by reaction with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenyllithium
Phenyllithium or lithobenzene is an organometallic agent with the empirical formula C6H5Li. It is most commonly used as a metalating agent in organic syntheses and a substitute for Grignard reagents for introducing phenyl groups in organic syntheses. Crystalline phenyllithium is colorless; however, solutions of phenyllithium are various shades of brown or red depending on the solvent used and the impurities present in the solute. Preparation Phenyllithium was first produced by the reaction of lithium metal with diphenylmercury: :(C6Η5)2Ηg + 2Li → 2C6Η5Li + Ηg Reaction of a phenyl halide with lithium metal produces phenyllithium: :X-Ph + 2Li → Ph-Li + LiX Phenyllithium can also be synthesized with a metal-halogen exchange reaction: :n-BuLi + X-Ph → n-BuX + Ph-Li The predominant method of producing phenyllithium today are the latter two syntheses. Reactions The primary use of PhLi is to facilitate formation of carbon-carbon bonds by nucleophilic addition and substitut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylmagnesium Bromide
Phenylmagnesium bromide, with the simplified formula , is a magnesium-containing organometallic compound. It is commercially available as a solution in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran (THF). Phenylmagnesium bromide is a Grignard reagent. It is often used as a synthetic equivalent for the phenyl "Ph−" synthon. Preparation Phenylmagnesium bromide is commercially available as solutions of diethyl ether or THF. Laboratory preparation involves treating bromobenzene with magnesium metal, usually in the form of turnings. A small amount of iodine may be used to activate the magnesium to initiate the reaction. Coordinating solvents such as ether or THF, are required to solvate (complex) the magnesium(II) center. The solvent must be aprotic since alcohols and water contain an acidic proton and thus react with phenylmagnesium bromide to give benzene. Carbonyl-containing solvents, such as acetone and ethyl acetate, are also incompatible with the reagent. Structure Although phenylmagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





nickel(II)-from-xtal-3D-balls.png)

