|
Trimethylsilyl Cyanide
Trimethylsilyl cyanide is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3SiCN. This volatile liquid consists of a cyanide group, that is CN, attached to a trimethylsilyl group. The molecule is used in organic synthesis as the equivalent of hydrogen cyanide. It is prepared by the reaction of lithium cyanide and trimethylsilyl chloride: :LiCN + (CH3)3SiCl → (CH3)3SiCN + LiCl Structure The molecule exhibits the expected structure of a nitrile-like compound. The compound exists in a facile equilibrium with a small amount of the isomeric isocyanide (CH3)3SiNC. By contrast, the nearly isostructural ''tert''-butyl nitrile does not readily isomerize to ''tert''-butyl isocyanide. Reactions Trimethylsilyl cyanide hydrolyzes to give hydrogen cyanide and trimethylsilanol: :(CH3)3SiCN + H2O → (CH3)3SiOH + HCN In its principal application, it adds across carbon-oxygen double bonds, for example in an aldehyde, to form a new carbon-carbon bond: : + (CH3)3SiC≡N → N≡C–Si(CH3)3 Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylsilyl Chloride
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound ( silyl halide), with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry. Preparation TMSCl is prepared on a large scale by the '' direct process'', the reaction of methyl chloride with a silicon-copper alloy. The principal target of this process is dimethyldichlorosilane, but substantial amounts of the trimethyl and monomethyl products are also obtained. The relevant reactions are (Me = CH3): : x MeCl + Si → Me3SiCl, Me2SiCl2, MeSiCl3, other products Typically about 2–4% of the product stream is the monochloride, which forms an azeotrope with MeSiCl3. Reactions and uses TMSCl is reactive toward nucleophiles, resulting in the replacement of the chloride. In a characteristic reaction of TMSCl, the nucleophile is water, resulting in hydrolysis to give the hexamethy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylsilanol
Trimethylsilanol (TMS) is an organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiOH. The Si centre bears three methyl groups and one hydroxyl group. It is a colourless volatile liquid.Paul D. Lickiss: ''The Synthesis and Structure of Organosilanols'', Advances in Inorganic Chemistry 1995, Volume 42, Pages 147–262, . Occurrence TMS is a contaminant in the atmospheres of spacecraft, where it arises from the degradation of silicone-based materials. Specifically, it is the volatile product from the hydrolysis of polydimethylsiloxane, which are generally terminated with trimethylsilyl groups: :(CH3)3SiO i(CH3)2Osub>nR + H2O → (CH3)3SiOH + HO i(CH3)2Osub>nR TMS and related volatile siloxanes are formed by hydrolysis of silicones-based containing materials, which are found in detergents and cosmetic products. Traces of trimethylsilanol, together with other volatile siloxanes, are present in biogas and landfill gas, again resulting from the degradation of silicones. As their combust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regioselectivity
In chemistry, regioselectivity is the preference of chemical bonding or breaking in one direction over all other possible directions. It can often apply to which of many possible positions a reagent will affect, such as which proton a strong base will abstract from an organic molecule, or where on a substituted benzene ring a further substituent will be added. A specific example is a halohydrin formation reaction with 2-propenylbenzene: : Because of the preference for the formation of one product over another, the reaction is selective. This reaction is regioselective because it selectively generates one constitutional isomer rather than the other. Various examples of regioselectivity have been formulated as rules for certain classes of compounds under certain conditions, many of which are named. Among the first introduced to chemistry students are Markovnikov's rule for the addition of protic acids to alkenes, and the Fürst-Plattner rule for the addition of nucleophiles to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzoyl Chloride
Benzoyl chloride, also known as benzenecarbonyl chloride, is an organochlorine compound with the formula . It is a colourless, fuming liquid with an irritating odour, and consists of a benzene ring () with an acyl chloride () substituent. It is mainly useful for the production of peroxides but is generally useful in other areas such as in the preparation of dyes, perfumes, pharmaceuticals, and resins. Preparation Benzoyl chloride is produced from benzotrichloride using either water or benzoic acid: :C6H5CCl3 + H2O -> C6H5COCl + 2 HCl :C6H5CCl3 + C6H5CO2H -> 2 C6H5COCl + HCl As with other acyl chlorides, it can be generated from the parent acid and standard chlorinating agents such as phosphorus pentachloride, thionyl chloride, and oxalyl chloride. It was first prepared by treatment of benzaldehyde with chlorine. An early method for production of benzoyl chloride involved chlorination of benzyl alcohol. Reactions It reacts with water to produce hydrochloric acid and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophile
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carries a partial positive charge, or have an atom that does not have an octet of electrons. Electrophiles mainly interact with nucleophiles through addition and substitution reactions. Frequently seen electrophiles in organic syntheses include cations such as H+ and NO+, polarized neutral molecules such as HCl, alkyl halides, acyl halides, and carbonyl compounds, polarizable neutral molecules such as Cl2 and Br2, oxidizing agents such as organic peracids, chemical species that do not satisfy the octet rule such as carbenes and radicals, and some Lewis acids such as BH3 and DIBAL. Organic chemistry Addition of halogens These occur between alkenes and electrophiles, often halogens as in halogen addition reactions. Common reactions i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
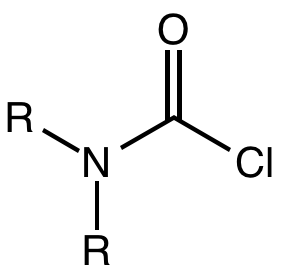
Carbamoyl Chloride
A carbamoyl chloride is the functional group with the formula R2NC(O)Cl. The parent carbamoyl chloride, H2NCOCl is unstable, but many N-substituted analogues are known. Most examples are moisture sensitive, colourless, and soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. An example is dimethylcarbamoyl chloride (m.p. −90 °C and b.p. 93 °C). Carbamoyl chlorides are used to prepare a number of pesticides, e.g. carbofuran and aldicarb. Production and examples Carbamoyl chlorides are prepared by the reaction of an amine with phosgene: :2 R2NH + COCl2 → R2NCOCl + 2NH2l They also arise by the addition of hydrogen chloride to isocyanates: :RNCO + HCl → RNHCOCl In this way, carbamonyl chlorides can be prepared with N-H functionality. Reactions In a reaction that is typically avoided, hydrolysis of carbamoyl chlorides gives carbamic acids: :R2NCOCl + H2O → R2NC(O)OH + HCl Owing to the influence of the amino group, these compounds are less hydrolytically sensitive than the usual acid chlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichloromethane
Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride, methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is slightly polar, and miscible with many organic solvents.Rossberg, M. ''et al.'' (2006) "Chlorinated Hydrocarbons" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . Occurrence Natural sources of dichloromethane include oceanic sources, macroalgae, wetlands, and volcanoes. However, the majority of dichloromethane in the environment is the result of industrial emissions. Production DCM is produced by treating either chloromethane or methane with chlorine gas at 400–500 °C. At these temperatures, both methane and chloromethane undergo a series of reactions producing progressively more chlorinated products. In this way, an estimated 400,000 tons were produced in the US, Europe, and Japan in 1993. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of oxides. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of Al2O3 (called a passivation layer) that protects the foil from further corrosion.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. . Stoichiometry (the measurable relationship between reactants and chemical equations of a equation or reaction) Oxides are extraordinarily diverse in terms of stoichiometries and in terms of the structures of each stoichiometry. Most elements form oxides of more than one stoichiometry. A well known example is carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide. Properties Physical properties The molecular electric dipole moment is 2.2 debyes. Pyridine is diamagnetic and has a diamagnetic susceptibility of −48.7 × 10−6 cm3·mol−1. The standard enthalpy of formation is 100.2 kJ·mol−1 in the liquid phase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanohydrin
In organic chemistry, a cyanohydrin or hydroxynitrile is a functional group found in organic compounds in which a cyano and a hydroxy group are attached to the same carbon atom. The general formula is , where R is H, alkyl, or aryl. Cyanohydrins are industrially important precursors to carboxylic acids and some amino acids. Cyanohydrins can be formed by the cyanohydrin reaction, which involves treating a ketone or an aldehyde with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in the presence of excess amounts of sodium cyanide (NaCN) as a catalyst: : In this reaction, the nucleophilic ion attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon in the ketone, followed by protonation by HCN, thereby regenerating the cyanide anion. Cyanohydrins are also prepared by displacement of sulfite by cyanide salts: : Cyanohydrins are intermediates in the Strecker amino acid synthesis. In aqueous acid, they are hydrolyzed to the α-hydroxy acid. Acetone cyanohydrins Acetone cyanohydrin, (CH3)2C(OH)CN is the cyano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are common and play important roles in the technology and biological spheres. Structure and bonding Aldehydes feature a carbon center that is connected by a double bond to oxygen and a single bond to hydrogen and single bond to a third substituent, which is carbon or, in the case of formaldehyde, hydrogen. The central carbon is often described as being sp2- hybridized. The aldehyde group is somewhat polar. The C=O bond length is about 120-122 picometers. Physical properties and characterization Aldehydes have properties that are diverse and that depend on the remainder of the molecule. Smaller aldehydes are more soluble in water, formaldehyde and acetaldehyde completely so. The volatile aldehydes have pungent odors. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |