|
Trilinear Filtering
Trilinear filtering is an extension of the bilinear texture filtering method, which also performs linear interpolation between mipmaps. Bilinear filtering has several weaknesses that make it an unattractive choice in many cases: using it on a full-detail texture when scaling to a very small size causes accuracy problems from missed texels, and compensating for this by using multiple mipmaps throughout the polygon leads to abrupt changes in blurriness, which is most pronounced in polygons that are steeply angled relative to the camera. To solve this problem, trilinear filtering interpolates between the results of bilinear filtering on the two mipmaps nearest to the detail required for the polygon at the pixel. If the pixel would take up 1/100 of the texture in one direction, trilinear filtering would interpolate between the result of filtering the 128×128 mipmap as y1 with x1 as 128, and the result of filtering on the 64×64 mipmap as y2 with x2 as 64, and then interpolate to . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bilinear Filtering
In mathematics, bilinear interpolation is a method for interpolating functions of two variables (e.g., ''x'' and ''y'') using repeated linear interpolation. It is usually applied to functions sampled on a 2D rectilinear grid, though it can be generalized to functions defined on the vertices of (a mesh of) arbitrary convex quadrilaterals. Bilinear interpolation is performed using linear interpolation first in one direction, and then again in another direction. Although each step is linear in the sampled values and in the position, the interpolation as a whole is not linear but rather quadratic in the sample location. Bilinear interpolation is one of the basic resampling techniques in computer vision and image processing, where it is also called bilinear filtering or bilinear texture mapping. Computation Suppose that we want to find the value of the unknown function ''f'' at the point (''x'', ''y''). It is assumed that we know the value of ''f'' at the four points ''Q''11 = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Texture Filtering
In computer graphics, texture filtering or texture smoothing is the method used to determine the texture color for a Texture mapping, texture mapped pixel, using the colors of nearby Texel (graphics), texels (ie. pixels of the texture). Filtering describes how a texture is applied at many different shapes, size, angles and scales. Depending on the chosen filter algorithm, the result will show varying degrees of blurriness, detail, Spatial anti-aliasing, spatial aliasing, Temporal anti-aliasing, temporal aliasing and blocking. Depending on the circumstances, filtering can be performed in software (such as a software rendering package) or in hardware, eg. with either real time or graphics processing unit, GPU accelerated rendering circuits, or in a mixture of both. For most common interactive graphical applications, modern texture filtering is performed by Texture mapping unit, dedicated hardware which optimizes memory access through memory cacheing and Cache prefetching, pre-fetch, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Linear Interpolation
In mathematics, linear interpolation is a method of curve fitting using linear polynomials to construct new data points within the range of a discrete set of known data points. Linear interpolation between two known points If the two known points are given by the coordinates (x_0,y_0) and the linear interpolant is the straight line between these points. For a value x in the interval the value y along the straight line is given from the equation of slopes \frac = \frac, which can be derived geometrically from the figure on the right. It is a special case of polynomial interpolation with Solving this equation for y, which is the unknown value at x, gives \begin y &= y_0 + (x-x_0)\frac \\ &= \frac + \frac\\ &= \frac \\ &= \frac, \end which is the formula for linear interpolation in the interval Outside this interval, the formula is identical to linear extrapolation. This formula can also be understood as a weighted average. The weights are inversely related to the dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
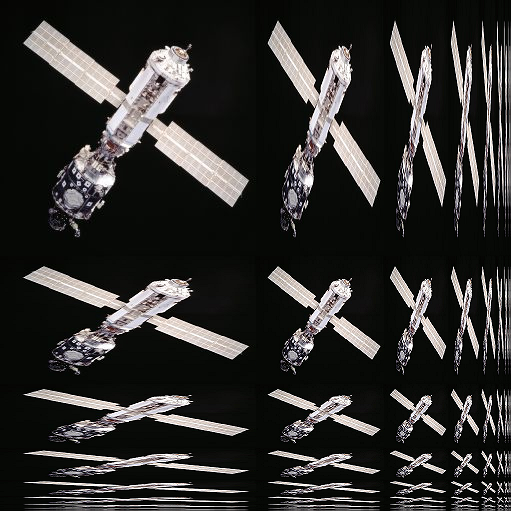
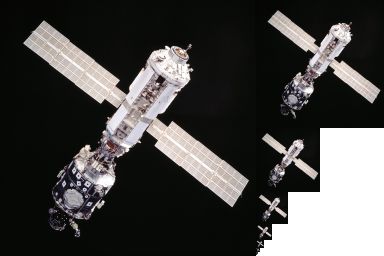
Mipmap
In computer graphics, a mipmap (''mip'' being an acronym of the Latin phrase ''multum in parvo'', meaning "much in little") is a pre-calculated, optimized sequence of images, each of which has an image resolution which is a factor of two smaller than the previous. Their use is known as ''mipmapping''. They are intended to increase rendering speed and reduce aliasing artifacts. A high-resolution mipmap image is used for high-density samples, such as for objects close to the camera; lower-resolution images are used as the object appears farther away. This is a more efficient way of downscaling a texture than sampling all texels in the original texture that would contribute to a screen pixel; it is faster to take a constant number of samples from the appropriately downfiltered textures. Since mipmaps, by definition, are pre-allocated, additional storage space is required to take advantage of them. They are also related to wavelet compression. Mipmaps are widely used in 3D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Texel (graphics)
In computer graphics, a texel, texture element, or texture pixel is the fundamental unit of a texture map. Textures are represented by arrays of texels representing the texture space, just as other images are represented by arrays of pixels. Texels can also be described by image regions that are obtained through simple procedures such as thresholding. Voronoi tesselation can be used to define their spatial relationships—divisions are made at the midpoints between the centroids of each texel and the centroids of every surrounding texel for the entire texture. This results in each texel centroid having a Voronoi polygon surrounding it, which consists of all points that are closer to its own texel centroid than any other centroid. Rendering When texturing a 3D surface or surfaces (a process known as texture mapping), the renderer maps texels to appropriate pixels in the geometric fragment (typically a triangle) in the output picture. On modern computers, this operat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
UV Coordinates
UV mapping is the 3D modeling process of projecting a 3D model's surface to a 2D image for texture mapping. The letters "U" and "V" denote the axes of the 2D texture because "X", "Y", and "Z" are already used to denote the axes of the 3D object in model space, while "W" (in addition to XYZ) is used in calculating quaternion rotations, a common operation in computer graphics. Process UV texturing permits polygons that make up a 3D object to be painted with color (and other surface attributes) from an ordinary image. The image is called a UV texture map.Mullen, T (2009). Mastering Blender. 1st ed. Indianapolis, Indiana: Wiley Publishing, Inc. The UV mapping process involves assigning pixels in the image to surface mappings on the polygon, usually done by "programmatically" copying a triangular piece of the image map and pasting it onto a triangle on the object.Murdock, K.L. (2008). 3ds Max 2009 Bible. 1st ed. Indianapolis, Indiana: Wiley Publishing, Inc. UV texturing is an alter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anisotropic Filtering
In 3D computer graphics, anisotropic filtering (AF) is a technique that improves the appearance of Texture filtering, textures, especially on surfaces viewed at sharp Viewing angle, angles. It helps make textures look sharper and more detailed by reducing blur and aliasing that can occur when surfaces are angled away from the viewer. Anisotropy, Anisotropic filtering works by applying different amounts of filtering in different directions, unlike simpler methods like Bilinear filtering, bilinear and trilinear filtering which filter equally in all directions. While it requires more processing power than these simpler methods, anisotropic filtering became a standard feature in most graphics cards in the late 1990s and is now commonly used in games and other 3D applications, often with user-adjustable settings. Comparison to isotropic algorithms Anisotropic filtering enhances texture sharpness, counteracting the blur introduced by mipmapping, a common Anti-aliasing filter, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
PC Gamer
''PC Gamer'' is a magazine and website founded in the United Kingdom in 1993 devoted to PC gaming and published monthly by Future plc. The magazine has several regional editions, with the UK and US editions becoming the best selling PC games magazines in their respective countries. The magazine features news on developments in the video game industry, previews of new games, and reviews of the latest popular PC games, along with other features relating to hardware, mods, "classic" games and various other topics. ''PC Gamer'' and parent Future began digital ''PC Gaming Show'' at E3 2015. Review system ''PC Gamer'' reviews are written by the magazine's editors and freelance writers, and rate games on a percent scale. In August 2023, '' Baldur's Gate 3'' became the first game to receive a rating of 97% in the UK edition. Prior to this, no game was awarded more than 96% by the UK edition (''Kerbal Space Program'', '' Civilization II'', ''Half-Life'', '' Half-Life 2'', ''Minecraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Maximum PC
''Maximum PC'', formerly known as ''boot'', was an American magazine and website published by Future US. It focuses on cutting-edge PC hardware, with an emphasis on product reviews, step-by-step tutorials, and in-depth technical briefs. Component coverage areas include CPUs, motherboards, core-logic chipsets, memory, videocards, mechanical hard drives, solid-state drives, optical drives, cases, component cooling, and anything else to do with recent tech news. Additional hardware coverage is directed at smartphones, tablet computers, cameras and other consumer electronic devices that interface with consumer PCs. Software coverage focuses on games, anti-virus suites, content-editing programs, and other consumer-level applications. Prior to September 1998, the magazine was called ''boot''. ''boot'' and sister magazine ''MacAddict'' (now ''Mac'', ''Life'') launched in September 1996, when Future US shut down '' CD-ROM Today''. In March 2016, Future US announced that the ''Maximum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Elsevier Science
Elsevier ( ) is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', '' Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, '' Trends'', the '' Current Opinion'' series, the online citation database Scopus, the SciVal tool for measuring research performance, the ClinicalKey search engine for clinicians, and the ClinicalPath evidence-based cancer care service. Elsevier's products and services include digital tools for data management, instruction, research analytics, and assessment. Elsevier is part of the RELX Group, known until 2015 as Reed Elsevier, a publicly traded company. According to RELX reports, in 2022 Elsevier published more than 600,000 articles annually in over 2,800 journals. As of 2018, its archives contained over 17 million documents and 40,000 e-books, with over one billion annual downloads. Researchers have criticized Elsevier for its high profit margins a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bilinear Filtering
In mathematics, bilinear interpolation is a method for interpolating functions of two variables (e.g., ''x'' and ''y'') using repeated linear interpolation. It is usually applied to functions sampled on a 2D rectilinear grid, though it can be generalized to functions defined on the vertices of (a mesh of) arbitrary convex quadrilaterals. Bilinear interpolation is performed using linear interpolation first in one direction, and then again in another direction. Although each step is linear in the sampled values and in the position, the interpolation as a whole is not linear but rather quadratic in the sample location. Bilinear interpolation is one of the basic resampling techniques in computer vision and image processing, where it is also called bilinear filtering or bilinear texture mapping. Computation Suppose that we want to find the value of the unknown function ''f'' at the point (''x'', ''y''). It is assumed that we know the value of ''f'' at the four points ''Q''11 = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anisotropic Filtering
In 3D computer graphics, anisotropic filtering (AF) is a technique that improves the appearance of Texture filtering, textures, especially on surfaces viewed at sharp Viewing angle, angles. It helps make textures look sharper and more detailed by reducing blur and aliasing that can occur when surfaces are angled away from the viewer. Anisotropy, Anisotropic filtering works by applying different amounts of filtering in different directions, unlike simpler methods like Bilinear filtering, bilinear and trilinear filtering which filter equally in all directions. While it requires more processing power than these simpler methods, anisotropic filtering became a standard feature in most graphics cards in the late 1990s and is now commonly used in games and other 3D applications, often with user-adjustable settings. Comparison to isotropic algorithms Anisotropic filtering enhances texture sharpness, counteracting the blur introduced by mipmapping, a common Anti-aliasing filter, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |