|
Treaty Of Senlis
The Treaty of Senlis concerning the Burgundian succession was signed at Senlis, Oise on 23 May 1493 between Maximilian I of Habsburg and his son Philip "the Handsome", Archduke of Austria, and King Charles VIII of France. Background After the last Valois Duke of Burgundy, Charles the Bold, had died without male heir at the 1477 Battle of Nancy, his cousin Louis XI of France was determined to come into his inheritance, especially the Burgundian Netherlands with the thriving County of Flanders. However, Mary the Rich, daughter of Charles the Bold, and her husband Maximilian also claimed their rights, which led to clashes of arms culminating at the 1479 Battle of Guinegate, concluded in favour of Mary and Maximilian. Nevertheless, Mary died in 1482 and according to the Treaty of Arras, Maximilian had to cede Burgundy, the County of Artois including the City of Arras and several minor lordships to France as dowry for the proposed marriage of their daughter, Margaret, with Loui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dole, Jura
Dole (, sometimes pronounced ) is a commune in the Jura department, of which it is a subprefecture (''sous-préfecture''), in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region, in Eastern France. In 2019, it had a population of 23,711. History Dole was the capital of Franche-Comté until Louis XIV conquered the region; he shifted the '' parlement'' from Dole to Besançon. The university, founded by Duke Philippe le Bon of Burgundy in 1422, was also transferred to Besançon at that time. In January 1573, Gilles Garnier was put to death after being found guilty of lycanthropy and witchcraft. He had confessed to murdering and cannibalizing at least six children. The 1995 film '' Happiness Is in the Field'' was set in Dole and The Widow Couderc was also partially filmed there. Geography Dole is located on the river Doubs. The commune has a land area of . Demographics It is the largest commune in Jura, although the préfecture is Lons-le-Saunier. Transport Dole-Ville station has r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free County Of Burgundy
The Free County of Burgundy or Franche-Comté (french: Franche Comté de Bourgogne; german: Freigrafschaft Burgund) was a medieval county (from 982 to 1678) of the Holy Roman Empire, predecessor to the modern region of Franche-Comté. The name ' derives from the title of its count, ', in German 'free count', denoting imperial immediacy. It should not be confused with the more westerly Duchy of Burgundy, a fiefdom of France since 843. History The area once formed part of the Kingdom of the Burgundians, which had been annexed by the Franks in 534 and incorporated into the Kingdom of the Franks. The Empire was partitioned in 843 by the Treaty of Verdun, with the area west of the Saône river being allotted to West Francia as the French Duchy of Burgundy, while the southern and eastern parts of the former Burgundian kingdom fell to Middle Francia under Emperor Lothair I. This Middle Frankish part became the two independent entities of southern Lower Burgundy in 879 and northern Uppe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dijon
Dijon (, , ) (dated) * it, Digione * la, Diviō or * lmo, Digion is the prefecture of the Côte-d'Or department and of the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in northeastern France. the commune had a population of 156,920. The earliest archaeological finds within the city limits of Dijon date to the Neolithic period. Dijon later became a Roman settlement named ''Divio'', located on the road between Lyon and Paris. The province was home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th centuries, and Dijon became a place of tremendous wealth and power, one of the great European centres of art, learning, and science. The city has retained varied architectural styles from many of the main periods of the past millennium, including Capetian, Gothic, and Renaissance. Many still-inhabited town-houses in the city's central district date from the 18th century and earlier. Dijon's architecture is distinguished by, among other things, '' toits bourguignons'' (Burgu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the Frankish Empire. Upon the 9th-century partitions, the French remnants of the Burgundian kingdom were reduced to a ducal rank by King Robert II of France in 1004. Robert II's son and heir, King Henry I of France, inherited the duchy but ceded it to his younger brother Robert in 1032. Other portions had passed to the Imperial Kingdom of Burgundy-Arles, including the County of Burgundy (Franche-Comté). Robert became the ancestor of the ducal House of Burgundy, a cadet branch of the royal Capet dynasty, ruling over a territory that roughly conformed to the borders and territories of the modern region of Burgundy (Bourgogne). Upon the extinction of the Burgundian male line with the death of Duke Philip I in 1361, the duchy reverted to King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. Andrew Holt characterizes it as "perhaps the most powerful European state of the Middle Ages". The functioning of government depended on the harmonic cooperation (dubbed ''consensual rulership'' by Bernd Schneidmüller) between monarch and vassals but this harmony was disturbed during the Salian Dynasty, Salian period. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power under the House of Hohenstaufen in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the List of Frankish kings, Frankish king Charlemagne as Carolingi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Habsburg, french: Maison des Habsbourg and also known as the House of Austriagerman: link=no, Haus Österreich, ; es, link=no, Casa de Austria; nl, Huis van Oostenrijk, pl, dom Austrii, la, Domus Austriæ, french: Maison d'Autriche; hu, Ausztria Háza; it, Casa d'Austria; pt, Casa da Áustria is one of the most prominent and important dynasties in European history. The house takes its name from Habsburg Castle, a fortress built in the 1020s in present-day Switzerland by Radbot of Klettgau, who named his fortress Habsburg. His grandson Otto II was the first to take the fortress name as his own, adding "Count of Habsburg" to his title. In 1273, Count Radbot's seventh-generation descendant Rudolph of Habsburg was elected King of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
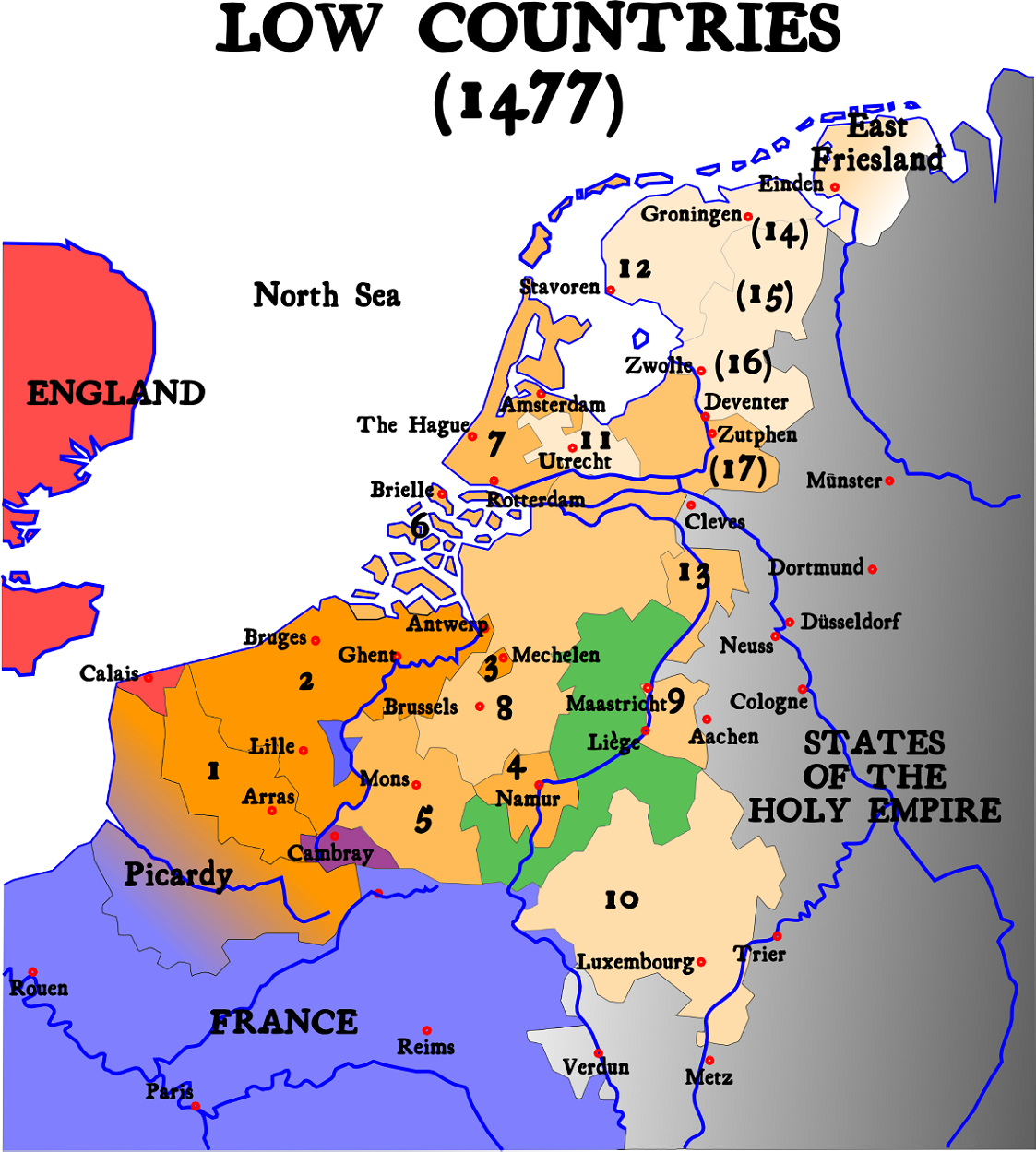
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (French Flanders and French Hainaut) and Pas-de-Calais (Artois). Also within this area were semi-independent fiefdoms, mainly ecclesiastical ones, such as Liège, Cambrai and Stavelot-Malmedy. The Seventeen Provinces arose from the Burgundian Netherlands, a number of fiefs held by the House of Valois-Burgundy and inherited by the Habsburg dynasty in 1482, and held by Habsburg Spain from 1556. Starting in 1512, the Provinces formed the major part of the Burgundian Circle. In 1581, the Seven United Provinces seceded to form the Dutch Republic. Composition After the Habsburg emperor Charles V had re-acquired the Duchy of Guelders from Duke William of Jülich-Cleves-Berg by the 1543 Treaty of Venlo, the Seventeen Provinces comprised: #th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfonso II Of Naples
Alfonso II (4 November 1448 – 18 December 1495) was Duke of Calabria and ruled as King of Naples from 25 January 1494 to 23 January 1495. He was a soldier and a patron of Renaissance architecture and the arts. Heir to his father Ferdinand I's Kingdom of Naples, Alfonso held the dukedom of Calabria for most of his life. In the 1480s Alfonso commanded the Neapolitan forces in Tuscany in 1478–79. He helped reverse the Ottoman invasion of Otranto in Apulia in 1480–81, and against the Republic of Venice in 1484. In 1486 Alfonso's repressive conduct towards the Neapolitan nobility prompted a revolt; the violent excesses of suppressing this uprising further discredited Alfonso and King Ferdinand. Under Alfonso's patronage the city of Naples was remodelled with new churches, straightened roads, and an aqueduct supplying fountains. Alfonso became King of Naples in 1494 on his father's death. Within a year he was forced by the approaching army of Charles VIII of France t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Charolais
Charolais (; also Charollais) is a historic region of France, named after the central town of Charolles, and located in today's Saône-et-Loire ''département'', in Burgundy. History It was held by the French noble house of Chalon-Arlay, until in 1237 Count John the Old ceded it to Duke Hugh IV of Burgundy. The county of Charolais was inherited by Hugh's granddaughter Beatrice, who in 1272 married Count Robert of Clermont, a younger son of King Louis IX of France and progenitor of the House of Bourbon. In 1314 it passed to Robert's second son John, whose daughter Beatrice married Count John I of Armagnac in 1327. John's grandson Count Bernard VII of Armagnac sold the county to Duke Philip II of Burgundy in 1390. It thus became part of the Duchy of Burgundy and the title 'Count of Charolais' was systematically given to the heir apparent of the incumbent duke. After the death of the last Valois-Burgundy duke Charles the Bold at the 1477 Battle of Nancy, the county was seized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Artois
The County of Artois (, ) was a historic province of the Kingdom of France, held by the Dukes of Burgundy from 1384 until 1477/82, and a state of the Holy Roman Empire from 1493 until 1659. Present Artois lies in northern France, on the border with Belgium. Its territory has an area of around 4000 km² and a population of about one million. Its principal cities are Arras (Atrecht), Calais (Kales), Boulogne-sur-Mer (Bonen), Saint-Omer (Sint-Omaars), Lens and Béthune. It forms the interior of the French département Pas-de-Calais. Originally a feudal county itself, Artois was annexed by the county of Flanders. It came to France in 1180 as a dowry of a Flemish princess, Isabelle of Hainaut, and was again made a separate county in 1237 for Robert, a grandson of Isabelle. Through inheritance, Artois came under the rule of the dukes of Burgundy in 1384. At the death of the fourth duke, Charles the Bold, Artois was inherited by the Habsburgs and passed to the dynasty's Spanish l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |