|
Transition State Analogue
Transition state analogs (transition state analogues), are chemical compounds with a chemical structure that resembles the transition state of a enzyme substrate, substrate molecule in an enzyme catalysis, enzyme-catalyzed chemical reaction. Enzymes interact with a substrate by means of strain or distortions, moving the substrate towards the transition state. Transition state analogs can be used as inhibitors in enzyme-catalyzed reactions by blocking the active site of the enzyme. Theory suggests that enzyme inhibitors which resembled the transition state structure would bind more tightly to the enzyme than the actual substrate. Examples of drugs that are transition state analog inhibitors include flu medications such as the neuraminidase inhibitor oseltamivir and the HIV protease inhibitors saquinavir in the treatment of AIDS. Transition state analogue The transition state of a structure can best be described in regards to statistical mechanics where the energies of bonds break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Isotope Effect
In physical organic chemistry, a kinetic isotope effect (KIE) is the change in the reaction rate of a chemical reaction when one of the atoms in the reactants is replaced by one of its isotopes. Formally, it is the ratio of rate constants for the reactions involving the light (''kL'') and the heavy (''kH'') isotopically substituted reactants (isotopologues): :\text=\frac This change in reaction rate is a quantum mechanical effect that primarily results from heavier isotopologues having lower vibrational frequencies compared to their lighter counterparts. In most cases, this implies a greater energetic input needed for heavier isotopologues to reach the transition state (or, in rare cases, the dissociation limit), and consequently, a slower reaction rate. The study of kinetic isotope effects can help the elucidation of the reaction mechanism of certain chemical reactions and is occasionally exploited in drug development to improve unfavorable pharmacokinetics by protecting m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature mRNA for translation. In many bacteria, the poly(A) tail promotes degradation of the mRNA. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression. The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene terminates. The 3′-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3′ end. In some genes these proteins add a poly(A) tail at one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing. The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylthioadenosine Nucleosidase
In enzymology, a methylthioadenosine nucleosidase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine + H2O \rightleftharpoons S-methyl-5-thio-D-ribose + adenine Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine and H2O, whereas its two products are S-methyl-5-thio-D-ribose and adenine. This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those glycosylases that hydrolyse N-glycosyl compounds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine adeninehyrolase. Other names in common use include 5'-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase, MTA nucleosidase, MeSAdo nucleosidase, and methylthioadenosine methylthioribohydrolase. This enzyme participates in urea cycle and metabolism of amino groups and methionine metabolism. Structural studies As of late 2007, 6 structures A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TSA 1
The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) is an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) that has authority over the security of transportation systems within, and connecting to the United States. It was created as a response to the September 11 attacks to improve airport security procedures and consolidate air travel security under a dedicated federal administrative law enforcement agency. The TSA develops broad policies to protect the U.S. transportation system, including highways, railroads, buses, mass transit systems, ports, pipelines, and intermodal freight facilities. It fulfills this mission in conjunction with other federal agencies and state partners. However, the TSA's primary focus is on airport security and the prevention of aircraft hijacking. It is responsible for screening passengers and baggage at more than 450 U.S. airports, employing screening officers in airports, armed Federal Air Marshals on planes, mobile teams of dog ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Mechanics
Molecular mechanics uses classical mechanics to model molecular systems. The Born–Oppenheimer approximation is assumed valid and the potential energy of all systems is calculated as a function of the nuclear coordinates using force fields. Molecular mechanics can be used to study molecule systems ranging in size and complexity from small to large biological systems or material assemblies with many thousands to millions of atoms. All-atomistic molecular mechanics methods have the following properties: * Each atom is simulated as one particle * Each particle is assigned a radius (typically the van der Waals radius), polarizability, and a constant net charge (generally derived from quantum calculations and/or experiment) * Bonded interactions are treated as ''springs'' with an equilibrium distance equal to the experimental or calculated bond length Variants on this theme are possible. For example, many simulations have historically used a ''united-atom'' representation in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent of quantum mechanics, describes many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at small (atomic and subatomic) scales. Most theories in classical physics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation valid at large (macroscopic) scale. Quantum mechanics differs from classical physics in that energy, momentum, angular momentum, and other quantities of a bound system are restricted to discrete values ( quantization); objects have characteristics of both particles and waves (wave–particle duality); and there are limits to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QM/MM
The hybrid QM/MM (quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics) approach is a molecular simulation method that combines the strengths of ''ab initio'' QM calculations (accuracy) and MM (speed) approaches, thus allowing for the study of chemical processes in solution and in proteins. The QM/MM approach was introduced in the 1976 paper of Warshel and Levitt. They, along with Martin Karplus, won the 2013 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for "the development of multiscale models for complex chemical systems". Efficiency An important advantage of QM/MM methods is their efficiency. The cost of doing classical molecular mechanics (MM) simulations in the most straightforward case scales as ''O''(''N''2), where ''N'' is the number of atoms in the system. This is mainly due to electrostatic interactions term (every particle interacts with everything else). However, use of cutoff radius, periodic pair-list updates and more recently the variations of the particle mesh Ewald (PME) method has reduced this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
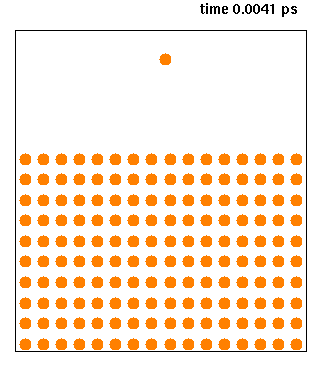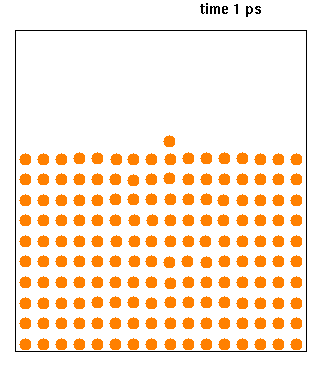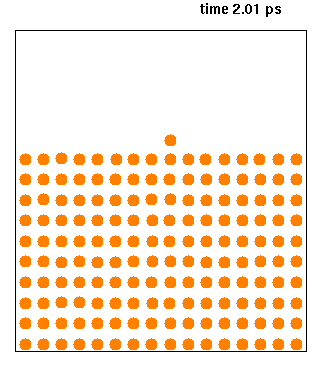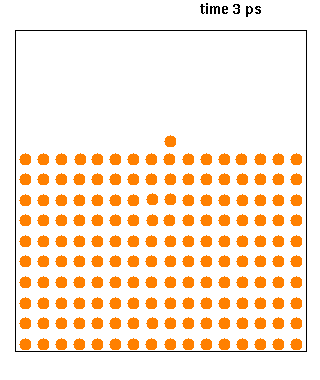
Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by numerically solving Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where forces between the particles and their potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanical force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics. Because molecular systems typically consist of a vast number of particles, it is impossible to determine the properties of such complex systems analytically; MD simulation circumvents this problem by using numerical methods. However, long MD simulations are mathematically ill-conditioned, generating cumulative errors in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, Mechanistic Organic Photochemistry, photochemical reactions and organic redox reaction, redox reactions. In organic synthesis, organic reactions are used in the construction of new organic molecules. The production of many man-made chemicals such as drugs, plastics, food additives, fabrics depend on organic reactions. The oldest organic reactions are combustion of organic fuels and saponification of fats to make soap. Modern organic chemistry starts with the Wöhler synthesis in 1828. In the history of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry awards have been given for the invention of specific organic reactions such as the Grignard reaction in 1912, the Diels-Alder reaction in 1950, the Wittig reaction in 1979 and olefin metathesis in 2005. Classifications Organic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Transfer
Electron transfer (ET) occurs when an electron relocates from an atom or molecule to another such chemical entity. ET is a mechanistic description of certain kinds of redox reactions involving transfer of electrons. Electrochemical processes are ET reaction. ET reactions are relevant to photosynthesis and respiration. ET reactions commonly involve transition metal complexes, In organic chemistry ET is a step in some commercial polymerization reactions. It is foundational to photoredox catalysis. Classes of electron transfer Inner-sphere electron transfer In inner-sphere ET, the two redox centers are covalently linked during the ET. This bridge can be permanent, in which case the electron transfer event is termed intramolecular electron transfer. More commonly, however, the covalent linkage is transitory, forming just prior to the ET and then disconnecting following the ET event. In such cases, the electron transfer is termed intermolecular electron transfer. A famous exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Mechanics
Molecular mechanics uses classical mechanics to model molecular systems. The Born–Oppenheimer approximation is assumed valid and the potential energy of all systems is calculated as a function of the nuclear coordinates using force fields. Molecular mechanics can be used to study molecule systems ranging in size and complexity from small to large biological systems or material assemblies with many thousands to millions of atoms. All-atomistic molecular mechanics methods have the following properties: * Each atom is simulated as one particle * Each particle is assigned a radius (typically the van der Waals radius), polarizability, and a constant net charge (generally derived from quantum calculations and/or experiment) * Bonded interactions are treated as ''springs'' with an equilibrium distance equal to the experimental or calculated bond length Variants on this theme are possible. For example, many simulations have historically used a ''united-atom'' representation in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(2).png)