|
Transition Metal Nitrile Complexes
Transition metal nitrile complexes are coordination compounds containing nitrile ligands. Because nitriles are weakly basic, the nitrile ligands in these complexes are often labile. Ligand properties According to the Covalent bond classification method, nitriles are classified as L ligands, i.e., charge-neutral Lewis bases. With respect to HSAB theory, they are classified as soft. Typical nitrile ligands are acetonitrile, propionitrile, and benzonitrile. The structures of u(NH3)5(NCPh)sup>n+ have been determined for the 2+ and 3+ oxidation states. Upon oxidation the Ru-NH3 distances contract and the Ru-NCPh distances elongate, consistent with amines serving as pure-sigma donor ligands and nitriles functioning as pi-acceptors. Synthesis and reactions Acetonitrile, propionitrile and benzonitrile are also popular solvents. Because nitrile solvents have high dielectric constants, cationic complexes containing a nitrile ligand are often soluble in a solution of that nitrile. Som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
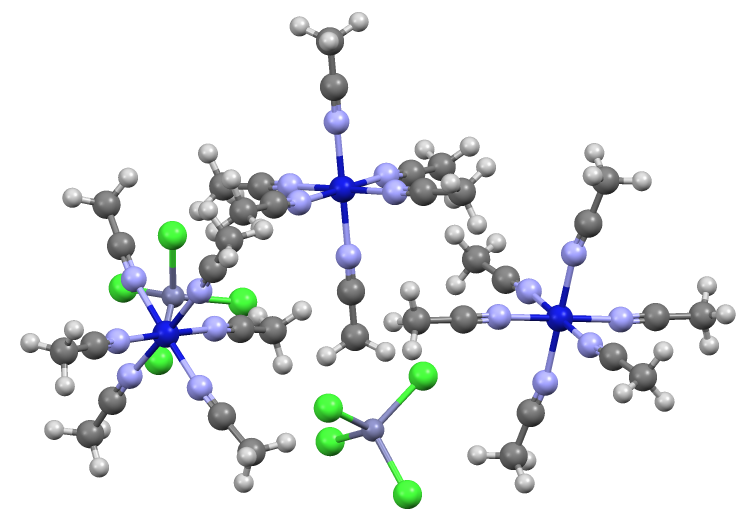
Tetrakis(acetonitrile)copper(I) Hexafluorophosphate
Tetrakis(acetonitrile)copper(I) hexafluorophosphate is a salt with the formula u(CH3CN)4F6. It is a colourless solid that is used in the synthesis of other copper complexes. The cation u(CH3CN)4sup>+ is a well-known example of a transition metal nitrile complex.Silvana F. Rach, Fritz E. Kühn "Nitrile Ligated Transition Metal Complexes with Weakly Coordinating Counteranions and Their Catalytic Applications" Chem. Rev., 2009, volume 109, pp 2061–2080. Structure As confirmed by X-ray crystallographic studies, the copper(I) ion is coordinated to four almost linear acetonitrile ligands in a nearly ideal tetrahedral geometry. Similar complexes with other anions including the perchlorate, tetrafluoroborate, and nitrate are known. Synthesis The cation was first reported in 1923 with a nitrate anion as a byproduct of the reduction of silver nitrate with a suspension of copper powder in acetonitrile. u(CH3CN)4F6 is generally produced by the addition of HPF6 to a suspension of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coordination Complexes
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cyanometalate
Cyanometallates or cyanometalates are a class of coordination compounds, most often consisting only of cyanide ligands. Most are anions. Cyanide is a highly basic and small ligand, hence it readily saturates the coordination sphere of metal ions. The resulting cyanometallate anions are often used as building blocks for more complex structures called coordination polymers, the best known example of which is Prussian blue, a common dyestuff.*Dunbar, K. R. and Heintz, R. A., "Chemistry of Transition Metal Cyanide Compounds: Modern Perspectives", Progress in Inorganic Chemistry, 1997, 45, 283-391. Examples Homoleptic cyanometallates ''Homoleptic'' cyanometallates are complexes where the only ligand is cyanide. For transition metals, well known homoleptic cyanometallates are the hexacyanides. Hexacyanometalates are known for Ti(III), V(III), Cr(III), Cr(II), Mn(IV), Mn(III), Mn(II), Fe(II), Fe(III), Co(III), Ru(III), Ru(II), Os(III), and Os(II). Other more labile derivatives are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oxidative Addition
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxidative addition is often a step in catalytic cycles, in conjunction with its reverse reaction, reductive elimination. Role in transition metal chemistry For transition metals, oxidative reaction results in the decrease in the d''n'' to a configuration with fewer electrons, often 2e fewer. Oxidative addition is favored for metals that are (i) basic and/or (ii) easily oxidized. Metals with a relatively low oxidation state often satisfy one of these requirements, but even high oxidation state metals undergo oxidative addition, as illustrated by the oxidation of Pt(II) with chlorine: : tCl4sup>2− + Cl2 → tCl6sup>2− In classical organometallic chemistry, the formal oxidation state of the metal and the electron count of the complex both in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nitrile Reduction
In nitrile reduction a nitrile is organic reduction, reduced to either an amine or an aldehyde with a suitable chemical reagent. Catalytic hydrogenation The Catalysis, catalytic hydrogenation of nitriles is often the most economical route available for the production of Primary (chemistry), primary amines. Catalysts for the reaction often include Group 10 element, group 10 metals such as Raney nickel, palladium black, or platinum dioxide. However, other catalysts, such as cobalt boride, also can be Regioselectivity, regioselective for primary amine production: : R-C≡N + 2 H2 → R-CH2NH2 A commercial application of this technology includes the production of hexamethylenediamine from adiponitrile, a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to Nylon 66. Depending on Organic synthesis#Methodology and applications, reaction conditions, reactive intermediate imines can also undergo attack by amine products to afford Secondary (chemistry), secondary and Tertiary (chemistry), tertiary amines: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hoesch Reaction
The Hoesch reaction or Houben–Hoesch reaction is an organic reaction in which a nitrile reacts with an arene compound to form an aryl ketone. The reaction is a type of Friedel–Crafts acylation with hydrogen chloride and a Lewis acid catalyst. The synthesis of 2,4,6-Trihydroxyacetophenone (THAP) from phloroglucinol is representative: If two-equivalents are added, 2,4-Diacetylphloroglucinol is the product. : An imine can be isolated as an intermediate reaction product. The attacking electrophile is possibly a species of the type R-C+=NHCl−. The arene must be electron-rich i.e. phenol or aniline type. A related reaction is the Gattermann reaction in which hydrocyanic acid not a nitrile is used. The reaction is named after Kurt Hoesch and Josef Houben''Über die Kern-Kondensation von Phenolen und Phenol-äthern mit Nitrilen zu Phenol- und Phenol-äther-Ketimiden und -Ketonen (I.)'' Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft (A and B Series) Volume 59, Issue 11, Date: 8. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bis(benzonitrile)palladium Dichloride
Bis(benzonitrile)palladium dichloride is the coordination complex with the formula PdCl2(NCC6H5)2. It is the adduct of two benzonitrile (PhCN) ligands with palladium(II) chloride. It is a yellow-brown solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The compound is a reagent and a precatalyst for reactions that require soluble Pd(II). A closely related compound is bis(acetonitrile)palladium dichloride. The complex is prepared by dissolving PdCl2 in warm benzonitrile. The PhCN ligands are labile, and the complex reverts to PdCl2 in noncoordinating solvents. According to X-ray crystallography X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring th ..., the two PhCN ligands are mutually trans.{{cite journal, author1=Olmstead, M. M. , author2=Wei, P.-P. , author3=Ginwalla, A. S. , author4=Balch, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iodosylbenzene
Iodosobenzene or iodosylbenzene is an organoiodine compound with the empirical formula . This colourless solid compound is used as an oxo transfer reagent in research laboratories examining organic and coordination chemistry. Preparation and structure Iodosobenzene is prepared from iodobenzene. It is prepared by first oxidizing iodobenzene by peracetic acid. Hydrolysis of resulting diacetate affords "PhIO": : : The structure of iodosobenzene has been verified by X-ray crystallography, crystallographically. Related derivatives are also oligomeric. Its low solubility in most solvents and vibrational spectroscopy indicate that it is not molecular, but is polymeric, consisting of –I–O–I–O– chains. The related diacetate, , illustrates the ability of iodine(III) to adopt a T-shaped geometry without multiple bonds. Theoretical studies show that the bonding between the iodine and oxygen atoms in iodosobenzene represents a single dative I-O sigma bond, confirming the absence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electron-rich
Electron-rich is jargon that is used in multiple related meanings with either or both kinetic and thermodynamic implications: * with regards to electron-transfer, electron-rich species have low ionization energy and/or are reducing agents. Tetrakis(dimethylamino)ethylene is an electron-rich alkene because, unlike ethylene, it forms isolable radical cation. In contrast, electron-poor alkene tetracyanoethylene is an electron acceptor, forming isolable anions. * with regards to acid-base reactions, electron-rich species have high pKa's and react with weak Lewis acids. * with regards to nucleophilic substitution reactions, electron-rich species are relatively strong nucleophiles, as judged by rates of attack by electrophiles. For example, compared to benzene, pyrrole is more rapidly attacked by electrophiles. Pyrrole is therefore considered to be an electron-rich aromatic ring. Similarly, benzene derivatives with electron-donating groups (EDGs) are attacked by electrophiles f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nitrile Hydratase
Nitrile hydratases (NHases; ) are mononuclear iron or non-corrinoid cobalt enzymes that catalyse the hydration of diverse nitriles to their corresponding amides: : R-C≡N + → Metal cofactor Nitrile hydratases use Fe(III) or Co(III) at their active sites. These ions are low-spin. The cobalt-based nitrile hydratases are rare examples of enzymes that use cobalt. Cobalt, when it occurs in enzymes, is usually bound to a corrin ring, as in vitamin B12. The mechanism by which the cobalt is transported to NHase without causing toxicity is unclear, although a cobalt permease has been identified, which transports cobalt across the cell membrane. The identity of the metal in the active site of a nitrile hydratase can be predicted by analysis of the sequence data of the alpha subunit in the region where the metal is bound. The presence of the amino acid sequence VCTLC indicates a Co-centred NHase and the presence of VCSLC indicates Fe-centred NHase. Metabolic pathway Nitrile h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |