|
Transcriptomic Clock
Transcriptomics technologies are the techniques used to study an organism's transcriptome, the sum of all of its RNA transcripts. The information content of an organism is recorded in the DNA of its genome and expressed through transcription. Here, mRNA serves as a transient intermediary molecule in the information network, whilst non-coding RNAs perform additional diverse functions. A transcriptome captures a snapshot in time of the total transcripts present in a cell. Transcriptomics technologies provide a broad account of which cellular processes are active and which are dormant. A major challenge in molecular biology is to understand how a single genome gives rise to a variety of cells. Another is how gene expression is regulated. The first attempts to study whole transcriptomes began in the early 1990s. Subsequent technological advances since the late 1990s have repeatedly transformed the field and made transcriptomics a widespread discipline in biological sciences. There ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcriptome
The transcriptome is the set of all RNA transcripts, including coding and non-coding, in an individual or a population of cells. The term can also sometimes be used to refer to all RNAs, or just mRNA, depending on the particular experiment. The term ''transcriptome'' is a portmanteau of the words ''transcript'' and ''genome''; it is associated with the process of transcript production during the biological process of transcription. The early stages of transcriptome annotations began with cDNA libraries published in the 1980s. Subsequently, the advent of high-throughput technology led to faster and more efficient ways of obtaining data about the transcriptome. Two biological techniques are used to study the transcriptome, namely DNA microarray, a hybridization-based technique and RNA-seq, a sequence-based approach. RNA-seq is the preferred method and has been the dominant transcriptomics technique since the 2010s. Single-cell transcriptomics allows tracking of transcript changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assay
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity of a target entity. The measured entity is often called the analyte, the measurand, or the target of the assay. The analyte can be a drug, biochemical substance, chemical element or compound, or cell in an organism or organic sample. An assay usually aims to measure an analyte's intensive property and express it in the relevant measurement unit (e.g. molarity, density, functional activity in enzyme international units, degree of effect in comparison to a standard, etc.). If the assay involves exogenous reactants (the reagents), then their quantities are kept fixed (or in excess) so that the quantity and quality of the target are the only limiting factors. The difference in the assay outcome is used to deduce the unknown quality or quantity o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequencing By Synthesis
Illumina dye sequencing is a technique used to determine the series of base pairs in DNA, also known as DNA sequencing. The reversible terminated chemistry concept was invented by Bruno Canard and Simon Sarfati at the Pasteur Institute in Paris. It was developed by Shankar Balasubramanian and David Klenerman of Cambridge University, who subsequently founded Solexa, a company later acquired by Illumina. This sequencing method is based on reversible dye-terminators that enable the identification of single nucleotides as they are washed over DNA strands. It can also be used for whole-genome and region sequencing, transcriptome analysis, metagenomics, small RNA discovery, methylation profiling, and genome-wide protein-nucleic acid interaction analysis. Overview This works in three basic steps: amplify, sequence, and analyze. The process begins with purified DNA. The DNA is fragmented and adapters are added that contain segments that act as reference points during amplification, seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expressed Sequence Tag
In genetics, an expressed sequence tag (EST) is a short sub-sequence of a cDNA sequence. ESTs may be used to identify gene transcripts, and were instrumental in gene discovery and in gene-sequence determination. The identification of ESTs has proceeded rapidly, with approximately 74.2 million ESTs now available in public databases (e.g. GenBank 1 January 2013, all species). EST approaches have largely been superseded by whole genome and transcriptome sequencing and metagenome sequencing. An EST results from one-shot sequencing of a cloned cDNA. The cDNAs used for EST generation are typically individual clones from a cDNA library. The resulting sequence is a relatively low-quality fragment whose length is limited by current technology to approximately 500 to 800 nucleotides. Because these clones consist of DNA that is complementary to mRNA, the ESTs represent portions of expressed genes. They may be represented in databases as either cDNA/mRNA sequence or as the reverse complement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanger Sequencing
Sanger sequencing is a method of DNA sequencing that involves electrophoresis and is based on the random incorporation of chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides by DNA polymerase during in vitro DNA replication. After first being developed by Frederick Sanger and colleagues in 1977, it became the most widely used sequencing method for approximately 40 years. It was first commercialized by Applied Biosystems in 1986. More recently, higher volume Sanger sequencing has been replaced by next generation sequencing methods, especially for large-scale, automated genome analyses. However, the Sanger method remains in wide use for smaller-scale projects and for validation of deep sequencing results. It still has the advantage over short-read sequencing technologies (like Illumina) in that it can produce DNA sequence reads of > 500 nucleotides and maintains a very low error rate with accuracies around 99.99%. Sanger sequencing is still actively being used in efforts for public health initiative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their linear chromosomes. Contrary to a widely held belief, the process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma, as transfers of information from RNA to DNA are explicitly held possible. Retroviral RT has three sequential biochemical activities: RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity, ribonuclease H (RNase H), and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity. Collectively, these activities enable the enzyme to convert single-stranded RNA into double-stranded cDNA. In retroviruses and retrotransposons, this cDNA can then integrate into the host genom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complementary DNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA synthesized from a single-stranded RNA (e.g., messenger RNA (mRNA) or microRNA (miRNA)) template in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. cDNA is often used to express a specific protein in a cell that does not normally express that protein (i.e., heterologous expression), or to sequence or quantify mRNA molecules using DNA based methods (qPCR, RNA-seq). cDNA that codes for a specific protein can be transferred to a recipient cell for expression, often bacterial or yeast expression systems. cDNA is also generated to analyze transcriptomic profiles in bulk tissue, single cells, or single nuclei in assays such as microarrays, qPCR, and RNA-seq. cDNA is also produced naturally by retroviruses (such as HIV-1, HIV-2, simian immunodeficiency virus, etc.) and then integrated into the host's genome, where it creates a provirus. The term ''cDNA'' is also used, typically in a bioinformatics context, to refer to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antheraea Polyphemus
''Antheraea polyphemus'', the Polyphemus moth, is a North American member of the family Saturniidae, the giant silk moths. It is a tan-colored moth, with an average wingspan of 15 cm (6 in). The most notable feature of the moth is its large, purplish eyespots on its two hindwings. The eyespots give it its name – from the Greek myth of the cyclops Polyphemus. The species was first described by Pieter Cramer in 1776. The species is widespread in continental North America, with local populations found throughout subarctic Canada and the United States. The caterpillar can eat 86,000 times its weight at emergence in a little less than two months. Life cycle The life cycle of the moth is much like that of any other Saturniidae species. It lays flat, light-brown eggs on the leaves of a number of host trees, preferring ''Ulmus americana'' (American elm), ''Betula'' (birch), ''Salix'' (willow), but also, more rarely, can survive on other trees, including: ''Quercus'' (oak), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
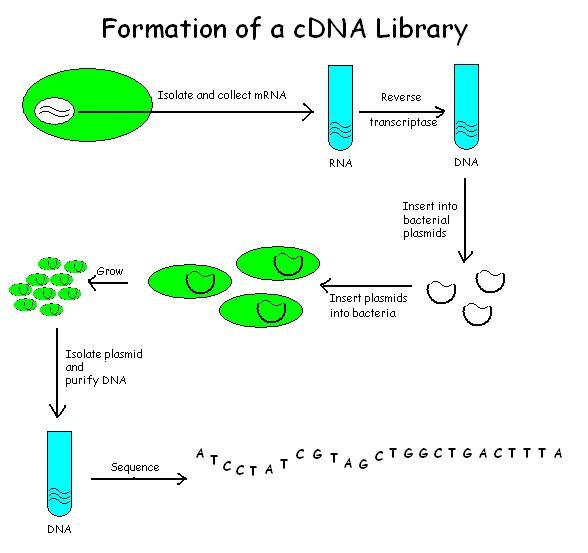
CDNA Library
A cDNA library is a combination of cloned cDNA (complementary DNA) fragments inserted into a collection of host cells, which constitute some portion of the transcriptome of the organism and are stored as a "library". cDNA is produced from fully transcribed mRNA found in the nucleus and therefore contains only the expressed genes of an organism. Similarly, tissue-specific cDNA libraries can be produced. In eukaryotic cells the mature mRNA is already spliced, hence the cDNA produced lacks introns and can be readily expressed in a bacterial cell. While information in cDNA libraries is a powerful and useful tool since gene products are easily identified, the libraries lack information about enhancers, introns, and other regulatory elements found in a genomic DNA library. cDNA Library Construction cDNA is created from a mature mRNA from a eukaryotic cell with the use of reverse transcriptase. In eukaryotes, a poly-(A) tail (consisting of a long sequence of adenine nucleotides) dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Transcript
A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing. Pre-mRNA is synthesized from a DNA template in the cell nucleus by transcription. Pre-mRNA comprises the bulk of heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA). Once pre-mRNA has been completely processed, it is termed " mature messenger RNA", or simply "messenger RNA". The term hnRNA is often used as a synonym for pre-mRNA, although, in the strict sense, hnRNA may include nuclear RNA transcripts that do not end up as cytoplasmic mRNA. There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue (biology)
In biology, tissue is a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" derives from the French word "tissu", the past participle of the verb tisser, "to weave". The study of tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, as histopathology. Xavier Bichat is considered as the "Father of Histology". Plant histology is studied in both plant anatomy and physiology. The classical tools for studying tissues are the paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the histological stain, and the optical microscope. Developments in electron microscopy, immunofluorescence, and the use of frozen tissue-sections have enhanced the detail that can be observed in tissues. With these tools, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |