|
Transcription Activator
A transcriptional activator is a protein (transcription factor) that increases transcription of a gene or set of genes. Activators are considered to have ''positive'' control over gene expression, as they function to promote gene transcription and, in some cases, are required for the transcription of genes to occur. Most activators are DNA-binding proteins that bind to enhancers or promoter-proximal elements. The DNA site bound by the activator is referred to as an "activator-binding site". The part of the activator that makes protein–protein interactions with the general transcription machinery is referred to as an "activating region" or "activation domain". Most activators function by binding sequence-specifically to a regulatory DNA site located near a promoter and making protein–protein interactions with the general transcription machinery (RNA polymerase and general transcription factors), thereby facilitating the binding of the general transcription machinery to the prom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their nonpolar core of carbon atoms and thus add chemical character to carbon chains. Fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP : ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
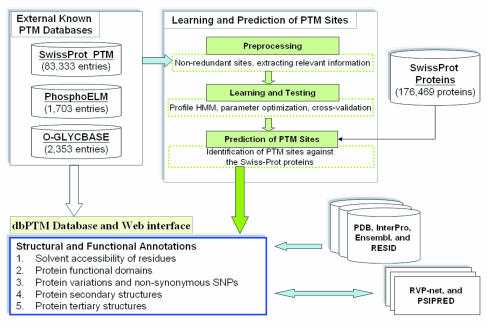
Post-translational Modification
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signaling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C- or N- termini. They can extend the chemical repertoire of the 20 standard amino acids by modifying an existing functional group or introducing a new one such as phosphate. Phosphorylation is a highly effective mechanism for regulating the activity of enzymes and is the most common post-translational modification. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydrate molecules attached to them in a process called glycosyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allosteric Effector
In biochemistry, an effector molecule is usually a small molecule that selectively binds to a protein and regulates its biological activity. In this manner, effector molecules act as ligands that can increase or decrease enzyme activity, gene expression, or cell signaling. Effector molecules can also directly regulate the activity of some mRNA molecules (riboswitches). Other examples of effector functions in biochemistry include hormone signaling and immune response. In some cases, specific proteins serve the same role as effector molecules (note: small molecules refers to organic compounds similar in size to amino acids or RNA strands. Most effector molecules are therefor much smaller than individual proteins, which consist of many amino acids). One example of this is in cellular signal transduction cascades. The term ''effector'' is used in other fields of biology. For instance, the effector end of a neuron is the terminus where an axon makes contact with the muscle or orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-translational Modification
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signaling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C- or N- termini. They can extend the chemical repertoire of the 20 standard amino acids by modifying an existing functional group or introducing a new one such as phosphate. Phosphorylation is a highly effective mechanism for regulating the activity of enzymes and is the most common post-translational modification. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydrate molecules attached to them in a process called glycosyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin Remodeling
Chromatin remodeling is the dynamic modification of chromatin architecture to allow access of condensed genomic DNA to the regulatory transcription machinery proteins, and thereby control gene expression. Such remodeling is principally carried out by 1) covalent histone modifications by specific enzymes, e.g., histone acetyltransferases (HATs), deacetylases, methyltransferases, and kinases, and 2) ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes which either move, eject or restructure nucleosomes. Besides actively regulating gene expression, dynamic remodeling of chromatin imparts an epigenetic regulatory role in several key biological processes, egg cells DNA replication and repair; apoptosis; chromosome segregation as well as development and pluripotency. Aberrations in chromatin remodeling proteins are found to be associated with human diseases, including cancer. Targeting chromatin remodeling pathways is currently evolving as a major therapeutic strategy in the treatment of several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleosome
A nucleosome is the basic structural unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes. The structure of a nucleosome consists of a segment of DNA wound around eight histone proteins and resembles thread wrapped around a spool. The nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin. Each nucleosome is composed of a little less than two turns of DNA wrapped around a set of eight proteins called histones, which are known as a histone octamer. Each histone octamer is composed of two copies each of the histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. DNA must be compacted into nucleosomes to fit within the cell nucleus. In addition to nucleosome wrapping, eukaryotic chromatin is further compacted by being folded into a series of more complex structures, eventually forming a chromosome. Each human cell contains about 30 million nucleosomes. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones. Nucleosome positions in the gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coactivator (genetics)
A coactivator is a type of transcriptional coregulator that binds to an activator (a transcription factor) to increase the rate of transcription of a gene or set of genes. The activator contains a DNA binding domain that binds either to a DNA promoter site or a specific DNA regulatory sequence called an enhancer. Binding of the activator-coactivator complex increases the speed of transcription by recruiting general transcription machinery to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. The use of activators and coactivators allows for highly specific expression of certain genes depending on cell type and developmental stage. Some coactivators also have histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity. HATs form large multiprotein complexes that weaken the association of histones to DNA by acetylating the N-terminal histone tail. This provides more space for the transcription machinery to bind to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. Activators are found in all li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics. Cofactors typically differ from ligands in that they often derive their function by remaining bound. Cofactors can be divided into two types: inorganic ions and complex organic molecules called coenzymes. Coenzymes are mostly derived from vitamins and other organic essential nutrients in small amounts. (Note that some scientists limit the use of the term "cofactor" for inorganic substances; both types are included here.) Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a "prosthetic group", which consists of a coenzyme that is tightly (or even covalently) and permanently bound to a protein. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene... must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messenger – which I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions) – alternating with regions which will be expressed – exons." (Gilbert 1978) The term ''intron'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and the corresponding RNA sequence in RNA transcripts. The non-intron sequences that become joined by this RNA processing to form the mature RNA are called exons. Introns are found in the genes of most organisms and many viruses and they can be located in both protein-coding genes and genes that function as RNA (noncoding genes). There are four main types of introns: tRNA introns, group I introns, group II introns, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
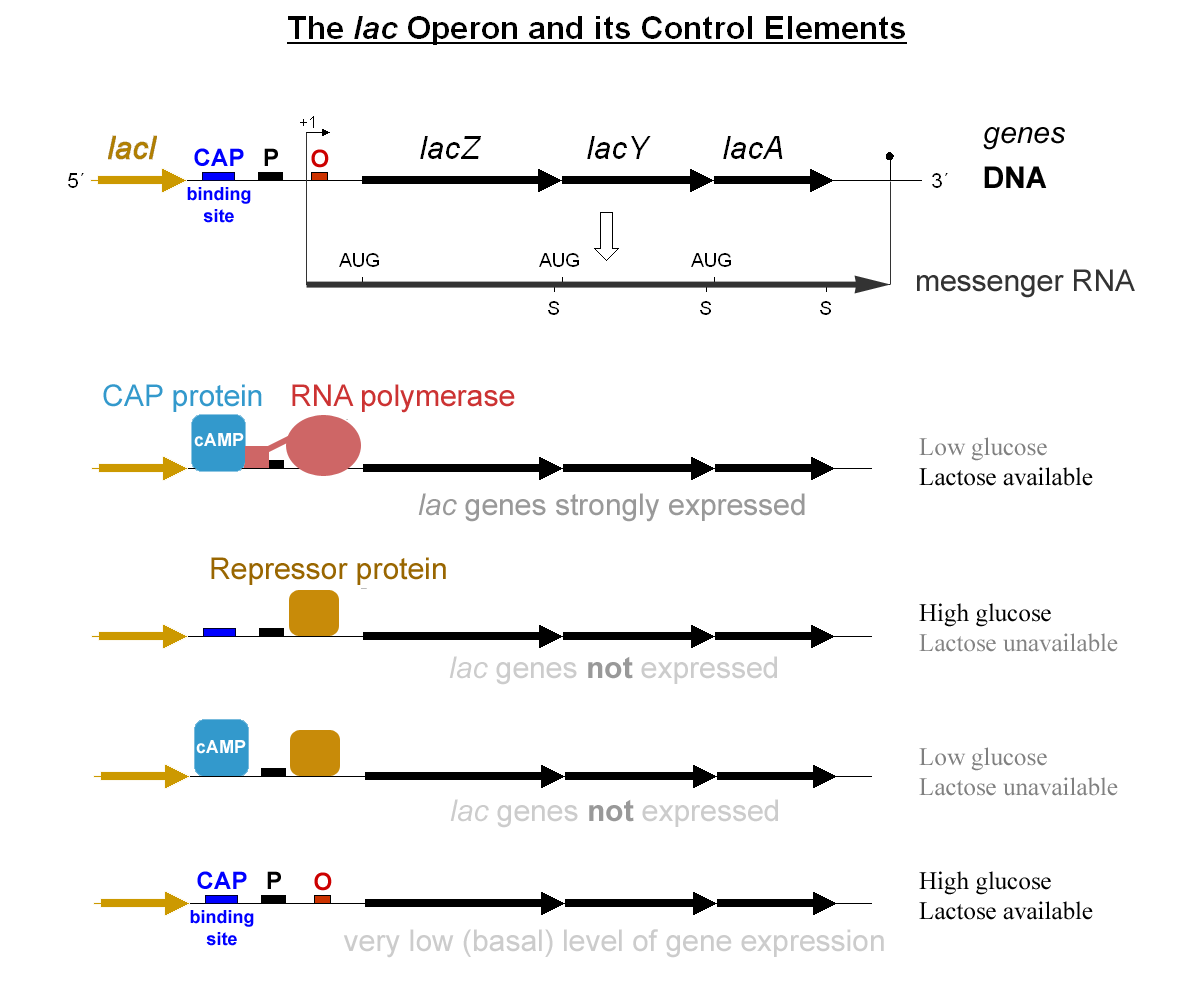
Operon
In genetics, an operon is a functioning unit of DNA containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter. The genes are transcribed together into an mRNA strand and either translated together in the cytoplasm, or undergo splicing to create monocistronic mRNAs that are translated separately, i.e. several strands of mRNA that each encode a single gene product. The result of this is that the genes contained in the operon are either expressed together or not at all. Several genes must be ''co-transcribed'' to define an operon. Originally, operons were thought to exist solely in prokaryotes (which includes organelles like plastids that are derived from bacteria), but since the discovery of the first operons in eukaryotes in the early 1990s, more evidence has arisen to suggest they are more common than previously assumed. In general, expression of prokaryotic operons leads to the generation of polycistronic mRNAs, while eukaryotic operons lead to monocistronic mRNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |