|
Tragicomic
Tragicomedy is a literary genre that blends aspects of both tragic and comic forms. Most often seen in dramatic literature, the term can describe either a tragic play which contains enough comic elements to lighten the overall mood or a serious play with a happy ending. Tragicomedy, as its name implies, invokes the intended response of both the tragedy and the comedy in the audience, the former being a genre based on human suffering that invokes an accompanying catharsis and the latter being a genre intended to be humorous or amusing by inducing laughter. In theatre Classical precedent There is no concise formal definition of tragicomedy from the classical age. It appears that the Greek philosopher Aristotle had something like the Renaissance meaning of the term (that is, a serious action with a happy ending) in mind when, in ''Poetics'', he discusses tragedy with a dual ending. In this respect, a number of Greek and Roman plays, for instance ''Alcestis'', may be called tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Battista Guarini
Giovanni Battista Guarini (10 December 1538 – 7 October 1612) was an Italian poet, dramatist, and diplomat. Life Guarini was born in Ferrara. On the termination of his studies at the universities of Pisa, Padua and Ferrara, he was appointed professor of literature at Ferrara. Soon after his appointment, he published some sonnets which obtained for him great popularity as a poet. In 1567, he entered the service of Alfonso II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara. After about 20 years of service, differences with the Duke led him to resign. After residing successively in Savoy, Mantua, Florence and Urbino, he returned to his native Ferrara. There he discharged one final public mission, that of congratulating Pope Paul V on his election (1605). He died in Venice, where he had been summoned to attend a lawsuit, aged 73. He was the father of Anna Guarini, one of the famous ''virtuose'' singers of the Ferrara court, the three women of the ''concerto di donne''. She was murdered by her husband in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tragedy
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful events that befall a main character. Traditionally, the intention of tragedy is to invoke an accompanying catharsis, or a "pain hatawakens pleasure", for the audience. While many cultures have developed forms that provoke this paradoxical response, the term ''tragedy'' often refers to a specific tradition of drama that has played a unique and important role historically in the self-definition of Western civilization. That tradition has been multiple and discontinuous, yet the term has often been used to invoke a powerful effect of cultural identity and historical continuity—"the Greeks and the Elizabethans, in one cultural form; Hellenes and Christians, in a common activity," as Raymond Williams puts it. From its origins in the theatre of ancient Greece 2500 years ago, from which there survives only a fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcestis (play)
''Alcestis'' (; grc-gre, Ἄλκηστις, ''Alkēstis'') is an Athenian tragedy by the ancient Greek playwright Euripides. It was first produced at the City Dionysia festival in 438 BC. Euripides presented it as the final part of a tetralogy of unconnected plays in the competition of tragedies, for which he won second prize; this arrangement was exceptional, as the fourth part was normally a satyr play. Its ambiguous, tragicomic tone—which may be "cheerfully romantic" or "bitterly ironic"—has earned it the label of a "problem play." ''Alcestis'' is, possibly excepting the '' Rhesus'', the oldest surviving work by Euripides, although at the time of its first performance he had been producing plays for 17 years. Events prior to the start of the play Long before the start of the play, King Admetus was granted by the Fates the privilege of living past the allotted time of his death. The Fates were persuaded to allow this by the god Apollo (who got them drunk). This unusual ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Fletcher (playwright)
John Fletcher (1579–1625) was a Jacobean playwright. Following William Shakespeare as house playwright for the King's Men, he was among the most prolific and influential dramatists of his day; during his lifetime and in the early Restoration, his fame rivalled Shakespeare's. He collaborated on writing plays with Francis Beaumont, and also with Shakespeare on three plays. Though his reputation has declined since, Fletcher remains an important transitional figure between the Elizabethan popular tradition and the popular drama of the Restoration. Biography Early life Fletcher was born in December 1579 (baptised 20 December) in Rye, Sussex, and died of the plague in August 1625 (buried 29 August in St. Saviour's, Southwark). His father Richard Fletcher was an ambitious and successful cleric who was in turn Dean of Peterborough, Bishop of Bristol, Bishop of Worcester and Bishop of London (shortly before his death), as well as chaplain to Queen Elizabeth. As Dean of Pete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakespeare's Late Romances
The late romances, often simply called the romances, are a grouping of William Shakespeare's last plays, comprising ''Pericles, Prince of Tyre''; ''Cymbeline''; ''The Winter's Tale''; and '' The Tempest''. ''The Two Noble Kinsmen'', of which Shakespeare was co-author, is sometimes also included in the grouping. The term "romances" was first used for these late works in Edward Dowden's ''Shakespeare: A Critical Study of His Mind and Art'' (1875). Later writers have generally been content to adopt Dowden's term. Shakespeare's plays cannot be precisely dated, but it is generally agreed that these comedies followed a series of tragedies including ''Othello'', ''King Lear'' and ''Macbeth''. Shakespeare wrote tragedies because their productions were financially successful, but he returned to comedy towards the end of his career, mixing it with tragic and mystical elements. Shakespeare's late romances were also influenced by the development of tragicomedy and the extreme elaboration of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Sidney
Philip, also Phillip, is a male given name, derived from the Greek language, Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who popularized the name include List of kings of Macedonia, kings of Macedonia and one of the apostles of early Christianity. ''Philip'' has #Philip in other languages, many alternative spellings. One derivation often used as a surname is Phillips (surname), Phillips. It was also found during ancient Greek times with two Ps as Philippides (other), Philippides and Philippos. It has many diminutive (or even hypocorism, hypocoristic) forms including Phil, Philly (other)#People, Philly, Lip (other), Lip, Pip (other), Pip, Pep (other), Pep or Peps. There are also feminine forms such as Philippine de Rothschild, Philippine and Philippa. Antiquity Kings of Macedon * Philip I of Macedon * Philip II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Burnell (author)
Henry Burnell (fl.1630s-40s, d.1656) was an Irish politician, playwright and landowner of the seventeenth century. The details of his life are not well recorded, but it is known that he was a prominent member of the Irish Confederacy which governed much of Ireland between 1642 and 1649. He was a member of a leading Dublin landowning family, who forfeited most of their possessions after the failure of the Irish Rebellion of 1641. He is now remembered mainly as the author of ''Landgartha'', the first play by an Irish playwright to be produced in an Irish theatre, and as the father of the poet Eleanor Burnell. Family He was the son of Christopher Burnell of Balgriffin, and grandson of Henry Burnell, Recorder of Dublin, who died in 1614. Nothing is known of his mother; his paternal grandmother was an O'Reilly of County Cavan. The Burnell family had been landowners in Dublin since the late fourteenth century and were Lords of the Manors of Balgriffin and Castleknock. They had a lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melodrama
A modern melodrama is a dramatic work in which the plot, typically sensationalized and for a strong emotional appeal, takes precedence over detailed characterization. Melodramas typically concentrate on dialogue that is often bombastic or excessively sentimental, rather than action. Characters are often flat, and written to fulfill stereotypes. Melodramas are typically set in the private sphere of the home, focusing on morality and family issues, love, and marriage, often with challenges from an outside source, such as a "temptress", a scoundrel, or an aristocratic villain. A melodrama on stage, filmed, or on television is usually accompanied by dramatic and suggestive music that offers cues to the audience of the drama being presented. In scholarly and historical musical contexts, ''melodramas'' are Victorian dramas in which orchestral music or song was used to accompany the action. The term is now also applied to stage performances without incidental music, novels, films, tel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aston Cockayne
Sir Aston Cockayne, 1st Baronet (1608–1684) was, in his day, a well-known Cavalier and a minor literary figure, now best remembered as a friend of Philip Massinger, John Fletcher, Michael Drayton, Richard Brome, Thomas Randolph, and other writers of his generation. Biography Aston Cockayne was the son of Thomas Cockayne and Ann, the daughter of Sir John Stanhope; Cockayne was born at Ashbourne Hall in Derbyshire, and baptised on 20 December 1608. He was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, the University of Oxford, and at the Inns of Court. Like many other aristocrats of his time, he travelled through Europe in his youth, spending much of 1632 in France and Italy; like a few, he became fluent in their languages, and translated works of literature into English. Cockayne was a Roman Catholic, and like other Catholics in his country in his era, was active in resistance against the Church of England and the social order that supported it. On 10 January 1641 Charles I eleva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
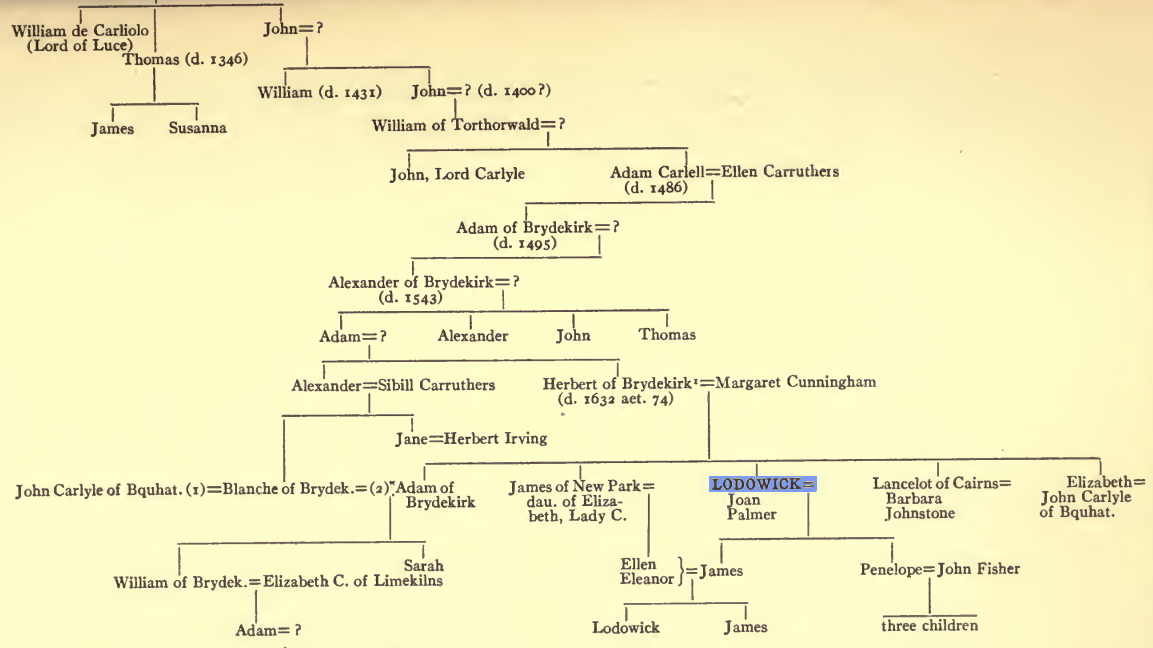
Lodowick Carlell
Lodowick Carlell (1602–1675), also Carliell or Carlile, was a seventeenth-century English playwright, was active mainly during the Caroline era and the Commonwealth period. Courtier Carlell's ancestry was Scottish. He was the son of Herbert Carlell of Bridekirk in Dumfriesshire, and the third of four brothers. He was not educated at university, though he did produce translations from French and Spanish during his lifetime; he probably had the informal though not always contemptible education of a courtier, which he was from about the age of 15. In his extra-literary life, Carlell was a courtier and royal functionary; he held the offices of Gentleman of the Bows to King Charles I, and Groom to the King and Queen's Privy Chamber. He was also Keeper of the Great Forest at Richmond Park. In the latter post, he assisted the King in his frequent hunts, and throughout the 1630s he lived in the Park at Petersham Lodge. In this same period he accomplished most of his dramatic autho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Ford (dramatist)
John Ford (1586c. 1639) was an English playwright and poet of the Jacobean and Caroline eras born in Ilsington in Devon, England. His plays deal mainly with the conflict between passion and conscience. Although remembered primarily as a playwright, he also wrote a number of poems on themes of love and morality. Origins John Ford was baptised 17 April 1586 at Ilsington Church, Devon. He was the second son of Thomas Ford (1556–1610) of Bagtor in the parish of Ilsington, and his wife Elizabeth Popham (died 1629) of the Popham family of Huntworth in Somerset. Her monument exists in Ilsington Church. Thomas Ford's grandfather was John Ford (died 1538) of Ashburton (the son and heir of William Ford of Chagford) who purchased the estate of Bagtor in the parish of Ilsington, which his male heirs successively made their seat. The Elizabethan mansion of the Fords survives today at Bagtor as the service wing of a later house appended in about 1700. Life and work Ford left home to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Brome
Richard Brome ; (c. 1590? – 24 September 1652) was an English dramatist of the Caroline era. Life Virtually nothing is known about Brome's private life. Repeated allusions in contemporary works, like Ben Jonson's ''Bartholomew Fair'', indicate that Brome started out as a servant of Jonson, in some capacity. Scholars have interpreted the allusions to mean that Brome may have begun as a menial servant but later became a sort of secretary and general assistant to the older playwright. A single brief mention of his family's need seems to show that he had a wife and children and struggled to support them. He may have had some experience as a professional actor: a 1628 warrant lists him as a member of the Queen of Bohemia's Men. Yet he had already started writing for the stage by this date. An early collaboration, ''A Fault in Friendship'' (now lost) was licensed in 1623 for Prince Charles's Men; a 1629 solo Brome effort, ''The Lovesick Maid'' (also lost), was a success for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |