|
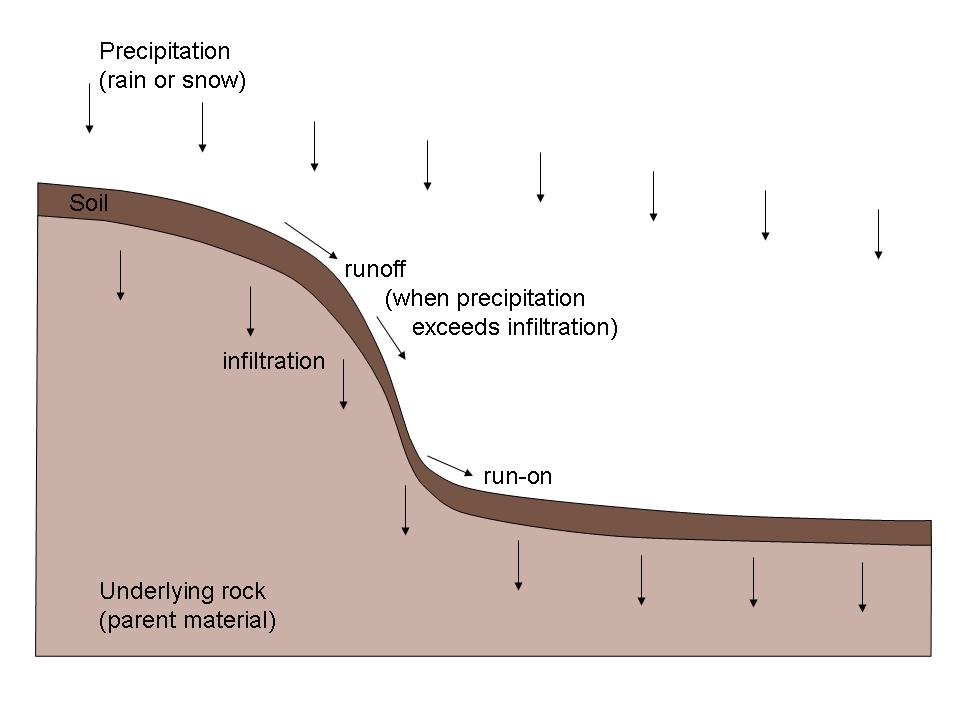
Topographic Wetness Index
The topographic wetness index (TWI), also known as the compound topographic index (CTI), is a steady state wetness index. It is commonly used to quantify topographic control on hydrological processes. The index is a function of both the slope and the upstream contributing area per unit width orthogonal to the flow direction. The index was designed for hillslope catenas. Accumulation numbers in flat areas will be very large, so TWI will not be a relevant variable. The index is highly correlated with several soil attributes such as horizon depth, silt percentage, organic matter content, and phosphorus. Methods of computing this index differ primarily in the way the upslope contributing area is calculated. Definition The topographic wetness index is defined as: \ln where a is the local upslope area draining through a certain point per unit contour length and \tan b is the local slope in radians. The TWI has been used to study spatial scale effects on hydrological processes. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is called a hydrologist. Hydrologists are scientists studying earth or environmental science, civil or environmental engineering, and physical geography. Using various analytical methods and scientific techniques, they collect and analyze data to help solve water related problems such as environmental preservation, natural disasters, and water management. Hydrology subdivides into surface water hydrology, groundwater hydrology (hydrogeology), and marine hydrology. Domains of hydrology include hydrometeorology, surface hydrology, hydrogeology, drainage-basin management, and water quality, where water plays the central role. Oceanography and meteorology are not included because water is only one of many important aspects within those fields. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slope
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line is a number that describes both the ''direction'' and the ''steepness'' of the line. Slope is often denoted by the letter ''m''; there is no clear answer to the question why the letter ''m'' is used for slope, but its earliest use in English appears in O'Brien (1844) who wrote the equation of a straight line as and it can also be found in Todhunter (1888) who wrote it as "''y'' = ''mx'' + ''c''". Slope is calculated by finding the ratio of the "vertical change" to the "horizontal change" between (any) two distinct points on a line. Sometimes the ratio is expressed as a quotient ("rise over run"), giving the same number for every two distinct points on the same line. A line that is decreasing has a negative "rise". The line may be practical – as set by a road surveyor, or in a diagram that models a road or a roof either as a description or as a plan. The ''steepness'', incline, or grade of a line is measured by the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogonal
In mathematics, orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. By extension, orthogonality is also used to refer to the separation of specific features of a system. The term also has specialized meanings in other fields including art and chemistry. Etymology The word comes from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "upright", and ('), meaning "angle". The Ancient Greek (') and Classical Latin ' originally denoted a rectangle. Later, they came to mean a right triangle. In the 12th century, the post-classical Latin word ''orthogonalis'' came to mean a right angle or something related to a right angle. Mathematics Physics * In optics, polarization states are said to be orthogonal when they propagate independently of each other, as in vertical and horizontal linear polarization or right- and left-handed circular polarization. * In special relativity, a time axis determined by a rapidity of motion is hyperbolic-orthogonal to a space axis of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catena (soil)
A catena in soil science (pedology) is a series of distinct but co-evolving soils arrayed down a slope. Each soil type or "facet" differs somewhat from its neighbours, but all occur in the same climate and on the same underlying parent material. A mature catena is in equilibrium as the processes of deposition and erosion are in balance. Concept The catena concept originated in Central Uganda, by chemist W.S. Martin to describe a hill slope sequence at the Bukalasa research station. The term catena (Latin: chain) was first coined by scientist Geoffrey Milne to describe these soil-topography units. The concept of a catena was developed in order to analyze the regular variation of soils across a slope. The example of this approach consists first in a structural component, the recurring pattern of certain soils in a landscape transects in which every chain element has its place in the chain, a soil has it in a landscape. Formation The term soil catena is used to describe the latera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Horizon
A soil horizon is a layer parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Horizons are defined in many cases by obvious physical features, mainly colour and texture. These may be described both in absolute terms (particle size distribution for texture, for instance) and in terms relative to the surrounding material, i.e. 'coarser' or 'sandier' than the horizons above and below. The identified horizons are indicated with symbols, which are mostly used in a hierarchical way. Master horizons (main horizons) are indicated by capital letters. Suffixes, in form of lowercase letters and figures, further differentiate the master horizons. There are many different systems of horizon symbols in the world. No one system is more correct—as artificial constructs, their utility lies in their ability to accurately describe local conditions in a consistent manner. Due to the different definitions of the horizon symb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel when dry, and lacks plasticity when wet. Silt also can be felt by the tongue as granular when placed on the front teeth (even when mixed with clay particles). Silt is a common material, making up 45% of average modern mud. It is found in many river deltas and as wind-deposited accumulations, particularly in central Asia, north China, and North America. It is produced in both very hot climates (through such processes as collisions of quartz grains in dust storms) and very cold climates (through such processes as glacial grinding of quartz grains.) Loess is soil rich in silt which makes up some of the most fertile agricultural land on Earth. However, silt is very vulnerable to erosion, and it has poor mechanical properties, making construction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram (compare copper at about 0.06 grams). In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate. Elemental phosphorus was first isolated as white phosphorus in 1669. White phosphorus emits a faint glow when exposed to oxygen – hence the name, taken from Greek mythology, meaning 'light-bearer' (Latin ), referring to the " Morning Star", the planet Venus. The term '' phosphorescence'', meaning glow after illumination, derives from this property of phosphorus, although the word has since been used for a different physical process that produces a glow. The glow of phosphorus is caused by oxidation of the white (but not red) phosphorus — a process now called chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contour Line
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensional graph of the function f(x,y) parallel to the (x,y)-plane. More generally, a contour line for a function of two variables is a curve connecting points where the function has the same particular value. In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height) above a given level, such as mean sea level. A contour map is a map illustrated with contour lines, for example a topographic map, which thus shows valleys and hills, and the steepness or gentleness of slopes. The contour interval of a contour map is the difference in elevation between successive contour lines. The gradient of the function is always perpendicular to the contour lines. When the lines are close together the magnitude of the grad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radian
The radian, denoted by the symbol rad, is the unit of angle in the International System of Units (SI) and is the standard unit of angular measure used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly an SI supplementary unit (before that category was abolished in 1995). The radian is defined in the SI as being a dimensionless unit, with 1 rad = 1. Its symbol is accordingly often omitted, especially in mathematical writing. Definition One radian is defined as the angle subtended from the center of a circle which intercepts an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle. More generally, the magnitude in radians of a subtended angle is equal to the ratio of the arc length to the radius of the circle; that is, \theta = \frac, where is the subtended angle in radians, is arc length, and is radius. A right angle is exactly \frac radians. The rotation angle (360°) corresponding to one complete revolution is the length of the circumference divided by the radius, which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keith Beven
Keith John Beven (born 23 July 1950) is a British hydrologist and distinguished Emeritus Professor in Hydrology at Lancaster University. According to Lancaster University he is the most highly cited hydrologist. In 2017, Beven was elected a member of the National Academy of Engineering for contributions to the understanding of hydrological processes and development of the foundations of modern hydrological modeling. Education Beven was educated at Chislehurst and Sidcup Grammar School, graduated with a Bachelor of Science degree in geography from the University of Bristol in 1971 and was awarded a PhD from the University of East Anglia (UEA) in 1975 for research on catchment hydrology supervised by Keith Clayton. Career and research Beven worked at the University of Leeds (1974–1977) and the Institute of Hydrology, Wallingford (1977–1979 and 1982–1985). He was an assistant professor at the University of Virginia from 1979 to 1982 and joined Lancaster University in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is called a hydrologist. Hydrologists are scientists studying earth or environmental science, civil or environmental engineering, and physical geography. Using various analytical methods and scientific techniques, they collect and analyze data to help solve water related problems such as environmental preservation, natural disasters, and water management. Hydrology subdivides into surface water hydrology, groundwater hydrology (hydrogeology), and marine hydrology. Domains of hydrology include hydrometeorology, surface hydrology, hydrogeology, drainage-basin management, and water quality, where water plays the central role. Oceanography and meteorology are not included because water is only one of many important aspects within those fields. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geochemistry
Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the entire Solar System, and has made important contributions to the understanding of a number of processes including mantle convection, the formation of planets and the origins of granite and basalt. It is an integrated field of chemistry and geology. History The term ''geochemistry'' was first used by the Swiss-German chemist Christian Friedrich Schönbein in 1838: "a comparative geochemistry ought to be launched, before geognosy can become geology, and before the mystery of the genesis of our planets and their inorganic matter may be revealed." However, for the rest of the century the more common term was "chemical geology", and there was little contact between geologists and chemists. Geochemistry emerged as a separate discipline after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |