|
Thiocarbamate
In organic chemistry, thiocarbamates (thiourethanes) are a family of organosulfur compounds. As the prefix ''thio-'' suggests, they are sulfur analogues of carbamates. There are two isomeric forms of thiocarbamates: ''O''-thiocarbamates, (esters), and ''S''-thiocarbamates, ( thioesters). Synthesis Thiocarbamates can be synthesised by the reaction of water or alcohols upon thiocyanates ( Riemschneider thiocarbamate synthesis): :RSCN + H2O → RSC(=O)NH2 :RSCN + R'OH → RSC(=O)NR'H Similar reactions are seen between alcohols and thiocarbamoyl chlorides such as dimethylthiocarbamoyl chloride; as well as between thiols and cyanates. Alternatively, they arise by the reaction of amines with carbonyl sulfide. :2 R2NH + COS → 2NH2+R2NCOS−] Reactions In the Newman-Kwart rearrangement ''O''-thiocarbamates can isomerise to ''S''-thiocarbamates. This reaction, which generally requires high temperatures, is an important method for the synthesis of thiophenols. Dithiocarbama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dithiocarbamate
In organic chemistry, a dithiocarbamate is a functional group with the general formula and structure . It is the analog of a carbamate in which both oxygen atoms are replaced by sulfur atoms (when only 1 oxygen is replaced the result is thiocarbamate). A common example is sodium diethyldithiocarbamate. Dithiocarbamates and their derivatives are widely used in the vulcanization of rubber. Formation Many primary and secondary amines react with carbon disulfide and sodium hydroxide to form dithiocarbamate salts: :R2NH + CS2 + NaOH → R2NCS2−Na+ + H2O Ammonia reacts with CS2 similarly: :2 NH3 + CS2 → H2NCS2−NH4+ Dithiocarbamate salts are pale colored solids that are soluble in water and polar organic solvents. Reactions Dithiocarbamates are readily S-alkylated. Thus, methyl dimethyldithiocarbamate can be prepared by methylation of the dithiocarbamate: :(CH3)2NCS2Na + (CH3O)2SO2 → (CH3)2NC(S)SCH3 + Na H3OSO3 Oxidation of dithiocarbamates gives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiocarbamates
In organic chemistry, thiocarbamates (thiourethanes) are a family of organosulfur compounds. As the prefix ''thio-'' suggests, they are sulfur analogues of carbamates. There are two isomeric forms of thiocarbamates: ''O''-thiocarbamates, (esters), and ''S''-thiocarbamates, ( thioesters). Synthesis Thiocarbamates can be synthesised by the reaction of water or alcohols upon thiocyanates ( Riemschneider thiocarbamate synthesis): :RSCN + H2O → RSC(=O)NH2 :RSCN + R'OH → RSC(=O)NR'H Similar reactions are seen between alcohols and thiocarbamoyl chlorides such as dimethylthiocarbamoyl chloride; as well as between thiols and cyanates. Alternatively, they arise by the reaction of amines with carbonyl sulfide. :2 R2NH + COS → 2NH2+R2NCOS−] Reactions In the Newman-Kwart rearrangement ''O''-thiocarbamates can isomerise to ''S''-thiocarbamates. This reaction, which generally requires high temperatures, is an important method for the synthesis of thiophenols. Dithiocarbam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
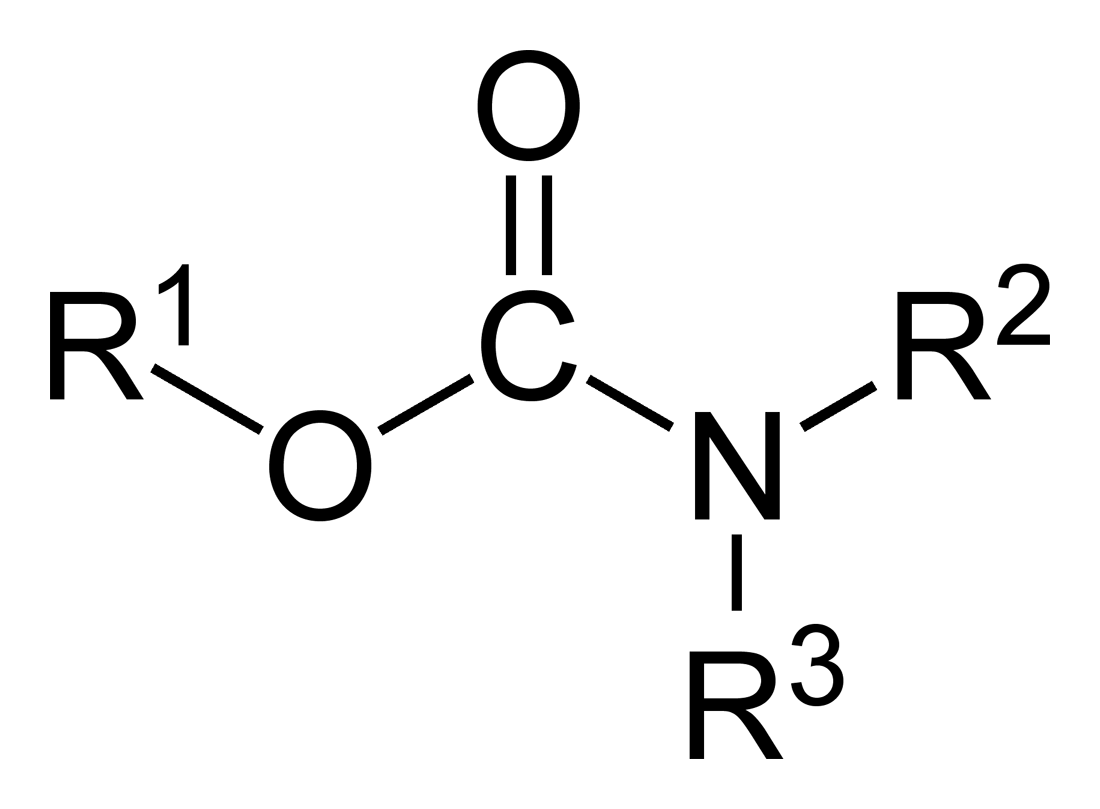
Carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonate imm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonate imm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riemschneider Thiocarbamate Synthesis
The Riemschneider thiocarbamate synthesis converts alkyl or aryl thiocyanates to thiocarbamates under acidic conditions, followed by hydrolysis with ice water. The reaction was discovered by the German chemist in 1951 as a more efficient method to produce thiocarbamates. Some references spell the name ''Riemenschneider''. 500px, center The Riemschneider reaction can also be used to create the corresponding ''N''-substituted thiocarbamate from an alcohol or alkene. Mechanism The mechanism for the conversion of an alcohol to the N-substituted thiocarbamate is shown below. The reaction proceeds under acidic conditions. The alcohol accepts a hydrogen ion from sulfuric acid to form a water, which then leaves, creating a carbocation A carbocation is an ion with a positively charged carbon atom. Among the simplest examples are the methenium , methanium and vinyl cations. Occasionally, carbocations that bear more than one positively charged carbon atom are also encount .... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolnaftate
Tolnaftate ( INN) is a synthetic thiocarbamate used as an anti-fungal agent that may be sold without medical prescription in most jurisdictions. It is supplied as a cream, powder, spray, liquid, and liquid aerosol. Tolnaftate is used to treat fungal conditions such as jock itch, athlete's foot and ringworm. Mechanism Although the exact mechanism of action is not entirely known, it is believed to inhibit squalene epoxidase, an important enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway of ergosterol (a key component of the fungal cell membrane) in a similar way to terbinafine. Uses Tolnaftate has been found to be generally slightly less effective than azoles when used to treat tinea pedis (athlete's foot). It is, however, useful when dealing with ringworm, especially when passed from pets to humans.Crawford F, Hart R, Bell-Syer S, Torgerson D, Young P, Russell I. Topical treatments for fungal infections of the skin and nails of the foot (Cochrane Review). In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylthiocarbamoyl Chloride
Dimethylthiocarbamoyl chloride is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2NC(S)Cl. A yellow solid, it is often encountered as a yellow syrup. It is a key reagent in the synthesis of arylthiols via the Newman-Kwart rearrangement. Synthesis and reactions Representative of other thiocarbamoyl chlorides, dimethylthiocarbamoyl chloride is electrophilic, serving as a source of R2NC(S)+.R. J. Cremlyn “An Introduction to Organosulfur Chemistry” John Wiley and Sons: Chichester (1996). It is analogous to dimethylcarbamoyl chloride (R2NC(O)Cl). Dimethylthiocarbamoyl chloride is prepared by chlorination of the related tetramethylthiuram disulfide: : e2NC(S)sub>2S2 + 3 Cl2 → 2 Me2NC(S)Cl + 2 SCl2 Dimethylthiocarbamoyl chloride reacts with dithiocarbamates (R2NCS{{su, b=2, p=−) to give thiuram sulfides 2NC(S)sub>2S. With methanethiolate, it gives methyl dimethyldithiocarbamate Methyl dimethyldithiocarbamate is the organosulfur compound with the formula (C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goitrin
Goitrin is a sulfur-containing oxazolidine, a cyclic thiocarbamate, that reduces the production of thyroid hormones such as thyroxine. It is found in cruciferous vegetables such as cabbage, brussels sprouts and rapeseed oil, and is formed by the hydrolysis of a glucosinolate: progoitrin or 2-hydroxy-3-butenyl glucosinolate. The unstable isothiocyanate (2-hydroxy-3-butenyl isothiocyanate) derived from the latter glucosinolate spontaneously cyclizes to goitrin, because the hydroxy group is situated in proximity to the isothiocyanate group (allowing a five-membered ring to be formed). Hence, the oxygen in the molecule stems from the hydroxy group of the original unstable isothiocyanate. Plants containing this specific glucosinolate (or glucosinolates such as glucobrassicin and sinalbin which liberate thiocyanate ion) have goitrogenic potential due to the goitrin and thiocyanate they contain. However, they do not seem to alter thyroid function in humans at realistic amounts in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiophenols
Thiophenol is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SH, sometimes abbreviated as PhSH. This foul-smelling colorless liquid is the simplest aromatic thiol. The chemical structures of thiophenol and its derivatives are analogous to phenols except the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the aromatic ring is replaced by a sulfur atom. The prefix thio- implies a sulfur-containing compound and when used before a root word name for a compound which would normally contain an oxygen atom, in the case of 'thiol' that the alcohol oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom. Thiophenols also describes a class of compounds formally derived from thiophenol itself. All have a sulfhydryl group (-SH) covalently bonded to an aromatic ring. The organosulfur ligand in the medicine thiomersal is a thiophenol. Synthesis There are several methods of synthesis for thiophenol and related compounds, although thiophenol itself is usually purchased for laboratory operations. Methods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Naphthalenethiol
2-Naphthalenethiol is an organosulfur compound with the formula C10H7SH. It is a white solid. It is one of two monothiols of naphthalene, the other being 1-naphthalenethiol. Synthesis and reactions 2-Naphthalenethiol is prepared from 2-naphthol by the Newman–Kwart rearrangement starting from a thiocarbamate In organic chemistry, thiocarbamates (thiourethanes) are a family of organosulfur compounds. As the prefix ''thio-'' suggests, they are sulfur analogues of carbamates. There are two isomeric forms of thiocarbamates: ''O''-thiocarbamates, (ester .... It undergoes lithiation at the 1 and 3-position. It can be used as a flavouring agent. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Naphthalenethiol, 2- Thiols 2-Naphthyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonyl Sulfide
Carbonyl sulfide is the chemical compound with the linear formula OCS. It is a colorless flammable gas with an unpleasant odor. It is a linear molecule consisting of a carbonyl group double bonded to a sulfur atom. Carbonyl sulfide can be considered to be intermediate between carbon dioxide and carbon disulfide, both of which are valence isoelectronic with it. Occurrence Carbonyl sulfide is the most abundant sulfur compound naturally present in the atmosphere, at , because it is emitted from oceans, volcanoes and deep sea vents. As such, it is a significant compound in the global sulfur cycle. Measurements on the Antarctica ice cores and from air trapped in snow above glaciers ( firn air) have provided a detailed picture of OCS concentrations from 1640 to the present day and allow an understanding of the relative importance of anthropogenic and non-anthropogenic sources of this gas to the atmosphere. Some carbonyl sulfide that is transported into the stratospheric sulfate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols (that is, sulfur takes the place of oxygen in the hydroxyl () group of an alcohol), and the word is a blend of "''thio-''" with "alcohol". Many thiols have strong odors resembling that of garlic or rotten eggs. Thiols are used as odorants to assist in the detection of natural gas (which in pure form is odorless), and the "smell of natural gas" is due to the smell of the thiol used as the odorant. Thiols are sometimes referred to as mercaptans () or mercapto compounds, a term introduced in 1832 by William Christopher Zeise and is derived from the Latin ('capturing mercury')''Oxford American Dictionaries'' ( Mac OS X Leopard). because the thiolate group () bonds very stro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |