|
Thermal Transmittance
Thermal transmittance is the rate of transfer of heat through matter. The thermal transmittance of a material (such as insulation or concrete) or an assembly (such as a wall or window) is expressed as a U-value. The thermal insulance of a structure is the reciprocal of its thermal transmittance. U-value Although the concept of U-value (or U-factor) is universal, U-values can be expressed in different units. In most countries, U-value is expressed in SI units, as watts per square metre-kelvin: :W/(m2⋅K) In the United States, U-value is expressed as British thermal units (Btu) per hour-square feet-degrees Fahrenheit: :Btu/(h⋅ft2⋅°F) Within this article, U-values are expressed in SI unless otherwise noted. To convert from SI to US customary values, divide by 5.678. Well-insulated parts of a building have a low thermal transmittance whereas poorly insulated parts of a building have a high thermal transmittance. Losses due to thermal radiation, thermal convection and ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-value (insulation)
In the context of construction, the R-value is a measure of how well a two-dimensional barrier, such as a layer of insulation, a window or a complete wall or ceiling, resists the conductive flow of heat. R-value is the temperature difference per unit of heat flux needed to sustain one unit of heat flux between the warmer surface and colder surface of a barrier under steady-state conditions. The ''R-value'' is the building industry term for thermal resistance "per unit area." It is sometimes denoted RSI-value if the SI units are used. An R-value can be given for a material (e.g. for polyethylene foam), or for an assembly of materials (e.g. a wall or a window). In the case of materials, it is often expressed in terms of R-value per metre. R-values are additive for layers of materials, and the higher the R-value the better the performance. The U-factor or U-value is the overall heat transfer coefficient and can be found by taking the inverse of the R-value. It is a property ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavity Wall
A cavity wall is a type of wall that has a hollow center. They can be described as consisting of two "skins" separated by a hollow space (cavity). The skins typically are masonry, such as brick or cinder block. Masonry is an absorbent material that can slowly draw rainwater or even humidity into the wall. One function of the cavity is to drain water through weep holes at the base of the wall system or above windows. The weep holes allow wind to create an air stream through the cavity that exports evaporated water from the cavity to the outside. Usually, weep holes are created by separating several vertical joints approximately two meters apart at the base of each story. Weep holes are also placed above windows to prevent dry rot of wooden window frames. A cavity wall with masonry as both inner and outer skins is more commonly referred to as a double wythe masonry wall. History Cavity wall construction was introduced in the United Kingdom during the 19th century and gained wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermographic Camera
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermographic cameras usually detect radiation in the long-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum (roughly 9,000–14,000 nanometers or 9–14 μm) and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms. Since infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero according to the black body radiation law, thermography makes it possible to see one's environment with or without visible illumination. The amount of radiation emitted by an object increases with temperature; therefore, thermography allows one to see variations in temperature. When viewed through a thermal imaging camera, warm objects stand out well against cooler backgrounds; humans and other warm-blooded animals become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
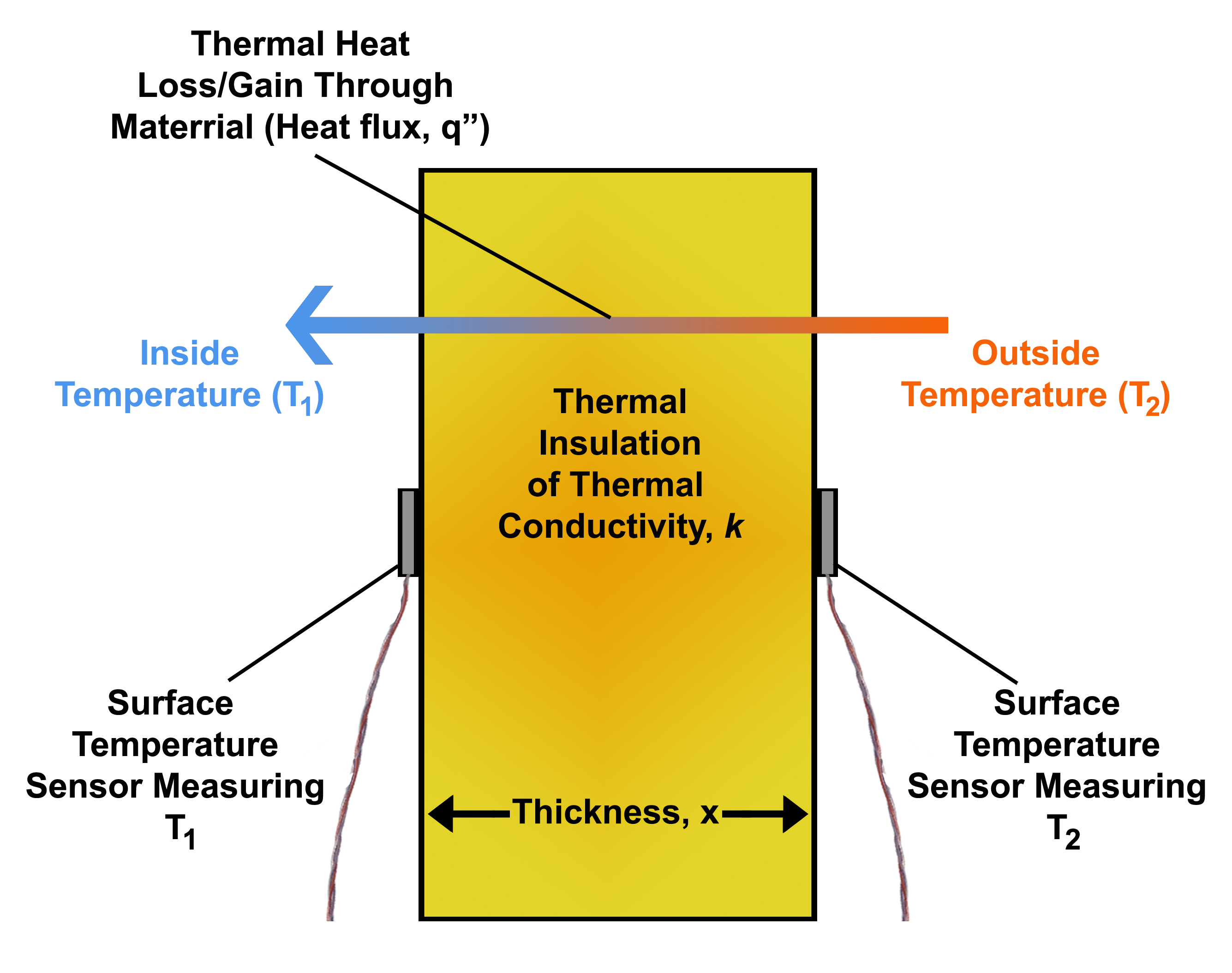
Heat Flux
Heat flux or thermal flux, sometimes also referred to as ''heat flux density'', heat-flow density or ''heat flow rate intensity'' is a flow of energy per unit area per unit time. In SI its units are watts per square metre (W/m2). It has both a direction and a magnitude, and so it is a vector quantity. To define the heat flux at a certain point in space, one takes the limiting case where the size of the surface becomes infinitesimally small. Heat flux is often denoted \vec_\mathrm, the subscript specifying ''heat'' flux, as opposed to ''mass'' or ''momentum'' flux. Fourier's law is an important application of these concepts. Fourier's law For most solids in usual conditions, heat is transported mainly by conduction and the heat flux is adequately described by Fourier's law. Fourier's law in one dimension \phi_\text = -k \frac where k is the thermal conductivity. The negative sign shows that heat flux moves from higher temperature regions to lower temperature regions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Flux Sensor
A heat flux sensor is a transducer that generates an electrical signal proportional to the total heat rate applied to the surface of the sensor. The measured heat rate is divided by the surface area of the sensor to determine the heat flux. The heat flux can have different origins; in principle convective, radiative as well as conductive heat can be measured. Heat flux sensors are known under different names, such as heat flux transducers, heat flux gauges, heat flux plates. Some instruments are actually single-purpose heat flux sensors, like pyranometers for solar radiation measurement. Other heat flux sensors include Gardon gauges (also known as a circular-foil gauge), thin-film thermopiles, and Schmidt-Boelter gauges. In SI units, the heat rate is measured in Watts, and the heat flux is computed in Watts per meter squared. Usage Heat flux sensors are used for a variety of applications. Common applications are studies of building envelope thermal resistance, studies of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaster
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for Molding (decorative), moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "render" commonly refers to external applications. Another imprecise term used for the material is stucco, which is also often used for plasterwork that is worked in some way to produce relief decoration, rather than flat surfaces. The most common types of plaster mainly contain either gypsum, lime plaster, lime, or cement plaster, cement,Franz Wirsching "Calcium Sulfate" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2012 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. but all work in a similar way. The plaster is manufactured as a dry powder and is mixed with water to form a stiff but workable paste immediately before it is applied to the surface. The reaction with water liberates heat through crystallization and the hydrated plaster then ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortar (masonry)
Mortar is a workable paste which hardens to bind building blocks such as stones, bricks, and concrete masonry units, to fill and seal the irregular gaps between them, spread the weight of them evenly, and sometimes to add decorative colors or patterns to masonry walls. In its broadest sense, mortar includes pitch, asphalt, and soft mud or clay, as those used between mud bricks, as well as cement mortar. The word "mortar" comes from Old French ''mortier'', "builder's mortar, plaster; bowl for mixing." (13c.). Cement mortar becomes hard when it cures, resulting in a rigid aggregate structure; however, the mortar functions as a weaker component than the building blocks and serves as the sacrificial element in the masonry, because mortar is easier and less expensive to repair than the building blocks. Bricklayers typically make mortars using a mixture of sand, a binder, and water. The most common binder since the early 20th century is Portland cement, but the ancient binder lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most widely used building material. Its usage worldwide, ton for ton, is twice that of steel, wood, plastics, and aluminum combined. Globally, the ready-mix concrete industry, the largest segment of the concrete market, is projected to exceed $600 billion in revenue by 2025. This widespread use results in a number of environmental impacts. Most notably, the production process for cement produces large volumes of greenhouse gas emissions, leading to net 8% of global emissions. Other environmental concerns include widespread illegal sand mining, impacts on the surrounding environment such as increased surface runoff or urban heat island effect, and potential public health implications from toxic ingredients. Significant research and development is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortar Joint
In masonry, mortar joints are the spaces between bricks, concrete blocks, or glass blocks, that are filled with mortar or grout. If the surface of the masonry remains unplastered, the joints contribute significantly to the appearance of the masonry.Joint. In: Mortar joints can be made in a series of different fashions, but the most common ones are raked, grapevine, extruded, concave, V, struck, flush, weathered and beaded. In order to produce a mortar joint, the mason must use one of several types of jointers (slickers), rakes, or beaders. These tools are run through the grout in between the building material before the grout is solid and create the desired outcome the mason seeks. Repointing Although good-quality bricks may outlast civilizations, the mortar that bonds them can crack and crumble after a number of years. Water penetration is the greatest degrader of mortar, and different mortar joints allow for varying degrees of water-resistance. For maintenance, degraded mort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplicative Inverse
In mathematics, a multiplicative inverse or reciprocal for a number ''x'', denoted by 1/''x'' or ''x''−1, is a number which when Multiplication, multiplied by ''x'' yields the multiplicative identity, 1. The multiplicative inverse of a rational number, fraction ''a''/''b'' is ''b''/''a''. For the multiplicative inverse of a real number, divide 1 by the number. For example, the reciprocal of 5 is one fifth (1/5 or 0.2), and the reciprocal of 0.25 is 1 divided by 0.25, or 4. The reciprocal function, the Function (mathematics), function ''f''(''x'') that maps ''x'' to 1/''x'', is one of the simplest examples of a function which is its own inverse (an Involution (mathematics), involution). Multiplying by a number is the same as Division (mathematics), dividing by its reciprocal and vice versa. For example, multiplication by 4/5 (or 0.8) will give the same result as division by 5/4 (or 1.25). Therefore, multiplication by a number followed by multiplication by its reciprocal yiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |