|
Tests Of Special Relativity
Special relativity is a physical theory that plays a fundamental role in the description of all physical phenomena, as long as gravitation is not significant. Many experiments played (and still play) an important role in its development and justification. The strength of the theory lies in its unique ability to correctly predict to high precision the outcome of an extremely diverse range of experiments. Repeats of many of those experiments are still being conducted with steadily increased precision, with modern experiments focusing on effects such as at the Planck scale and in the neutrino sector. Their results are consistent with the predictions of special relativity. Collections of various tests were given by Jakob Laub, Zhang, Mattingly, Clifford Will, and Roberts/Schleif. Special relativity is restricted to flat spacetime, ''i.e.'', to all phenomena without significant influence of gravitation. The latter lies in the domain of general relativity and the corresponding tests of ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two postulates: # The laws of physics are invariant (that is, identical) in all inertial frames of reference (that is, frames of reference with no acceleration). # The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of the light source or the observer. Origins and significance Special relativity was originally proposed by Albert Einstein in a paper published on 26 September 1905 titled "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".Albert Einstein (1905)''Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper'', ''Annalen der Physik'' 17: 891; English translatioOn the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodiesby George Barker Jeffery and Wilfrid Perrett (1923); Another English translation On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies by Megh Nad Saha (1920). The incompa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fizeau Experiment
The Fizeau experiment was carried out by Hippolyte Fizeau in 1851 to measure the relative speeds of light in moving water. Fizeau used a special interferometer arrangement to measure the effect of movement of a medium upon the speed of light. According to the theories prevailing at the time, light traveling through a moving medium would be dragged along by the medium, so that the measured speed of the light would be a simple sum of its speed ''through'' the medium plus the speed ''of'' the medium. Fizeau indeed detected a dragging effect, but the magnitude of the effect that he observed was far lower than expected. When he repeated the experiment with air in place of water he observed no effect. His results seemingly supported the partial aether-drag hypothesis of Fresnel, a situation that was disconcerting to most physicists. Over half a century passed before a satisfactory explanation of Fizeau's unexpected measurement was developed with the advent of Albert Einstein's theory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trouton–Rankine Experiment
The Trouton–Rankine experiment was an experiment designed to measure if the Lorentz–FitzGerald contraction of an object according to one frame (as defined by the luminiferous aether) produced a measurable effect in the rest frame of the object, so that the ether would act as a "preferred frame". The experiment was first performed by Frederick Thomas Trouton and Alexander Oliver Rankine in 1908. The outcome of the experiment was negative, which is in agreement with the principle of relativity (and thus special relativity as well), according to which observers at rest in a certain inertial reference frame, cannot measure their own translational motion by instruments at rest in the same frame. Consequently, also length contraction cannot be measured by co-moving observers. See also Tests of special relativity. Description The famous Michelson–Morley experiment of 1887 showed that the then-accepted aether theory needed to be modified. FitzGerald and Lorentz, independently of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress. Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. In the 19th century Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polariz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
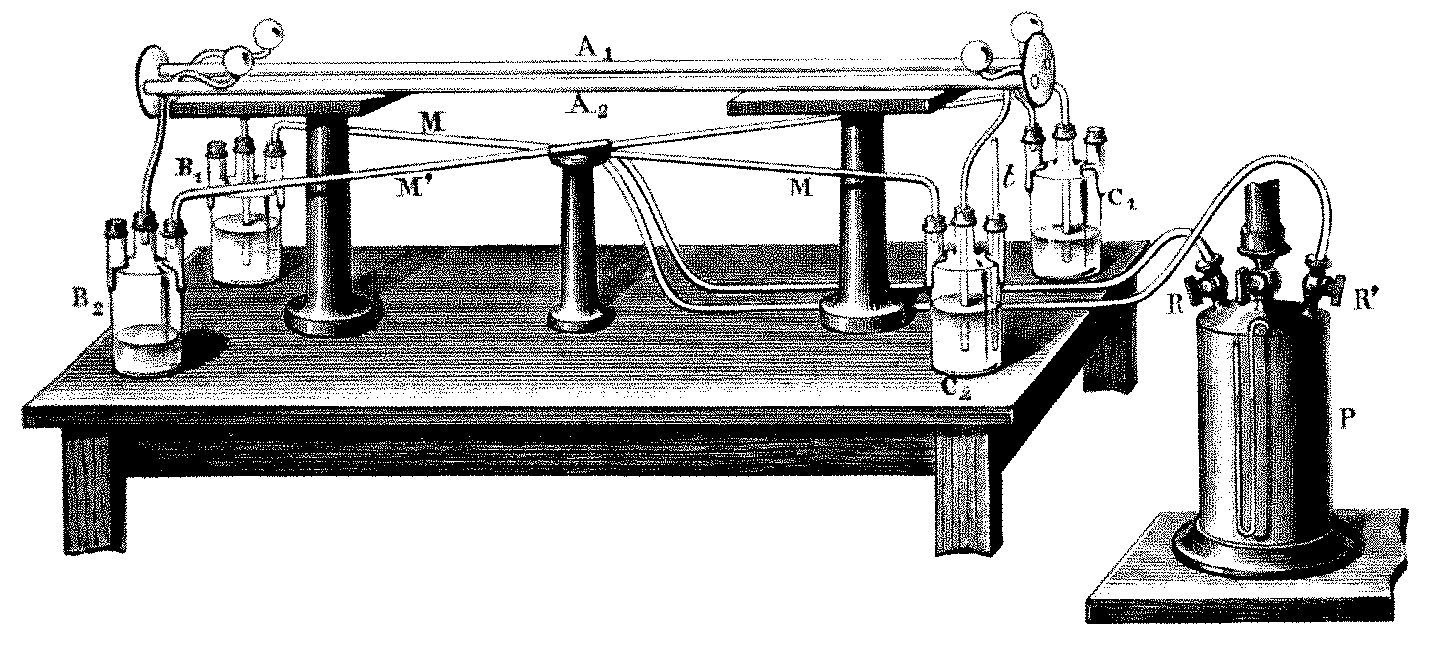
Experiments Of Rayleigh And Brace
The experiments of Rayleigh and Brace (1902, 1904) were aimed to show whether length contraction leads to birefringence or not. They were some of the first optical experiments measuring the relative motion of Earth and the luminiferous aether which were sufficiently precise to detect magnitudes of second order to v/c. The results were negative, which was of great importance for the development of the Lorentz transformation and consequently of the theory of relativity. See also Tests of special relativity. The experiments To explain the negative outcome of the Michelson–Morley experiment, George FitzGerald (1889) and Hendrik Lorentz (1892) introduced the contraction hypothesis, according to which a body is contracted during its motion through the stationary aether. Lord Rayleigh (1902) interpreted this contraction as a mechanical compression which should lead to optical anisotropy of materials, so the different refraction indices would cause birefringence. To measure this effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of the body. The concept originated with the studies by Archimedes of the usage of levers, which is reflected in his famous quote: "''Give me a lever and a place to stand and I will move the Earth''". Just as a linear force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist to an object around a specific axis. Torque is defined as the product of the magnitude of the perpendicular component of the force and the distance of the line of action of a force from the point around which it is being determined. The law of conservation of energy can also be used to understand torque. The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
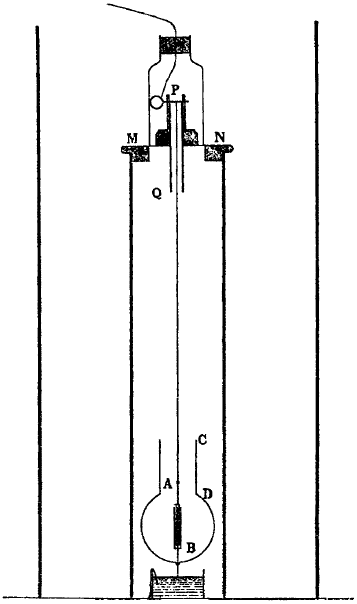
Trouton–Noble Experiment
The Trouton–Noble experiment was an attempt to detect motion of the Earth through the luminiferous aether, and was conducted in 1901–1903 by Frederick Thomas Trouton and H. R. Noble. It was based on a suggestion by George FitzGerald that a charged parallel-plate capacitor moving through the aether should orient itself perpendicular to the motion. Like the earlier Michelson–Morley experiment, Trouton and Noble obtained a null result: no motion relative to the aether could be detected.F. T. Trouton and H. R. Noble, "The mechanical forces acting on a charged electric condenser moving through space," ''Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. A'' 202, 165–181 (1903). This null result was reproduced, with increasing sensitivity, by Rudolf Tomaschek (1925, 1926), Chase (1926, 1927) and Hayden in 1994. Such experimental results are now seen, consistent with special relativity, to reflect the validity of the principle of relativity and the absence of any absolute rest frame (or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad Hoc
Ad hoc is a Latin phrase meaning literally 'to this'. In English, it typically signifies a solution for a specific purpose, problem, or task rather than a generalized solution adaptable to collateral instances. (Compare with ''a priori''.) Common examples are ad hoc committees and commissions created at the national or international level for a specific task. In other fields, the term could refer to, for example, a military unit created under special circumstances (see '' task force''), a handcrafted network protocol (e.g., ad hoc network), a temporary banding together of geographically-linked franchise locations (of a given national brand) to issue advertising coupons, or a purpose-specific equation. Ad hoc can also be an adjective describing the temporary, provisional, or improvised methods to deal with a particular problem, the tendency of which has given rise to the noun ''adhocism''. Styling Style guides disagree on whether Latin phrases like ad hoc should be italicized. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length Contraction
Length contraction is the phenomenon that a moving object's length is measured to be shorter than its proper length, which is the length as measured in the object's own rest frame. It is also known as Lorentz contraction or Lorentz–FitzGerald contraction (after Hendrik Lorentz and George Francis FitzGerald) and is usually only noticeable at a substantial fraction of the speed of light. Length contraction is only in the direction in which the body is travelling. For standard objects, this effect is negligible at everyday speeds, and can be ignored for all regular purposes, only becoming significant as the object approaches the speed of light relative to the observer. History Length contraction was postulated by George FitzGerald (1889) and Hendrik Antoon Lorentz (1892) to explain the negative outcome of the Michelson–Morley experiment and to rescue the hypothesis of the stationary aether ( Lorentz–FitzGerald contraction hypothesis). Although both FitzGerald and Lorentz a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Francis FitzGerald
Prof George Francis FitzGerald (3 August 1851 – 22 February 1901) was an Irish academic and physicist who served as Erasmus Smith's Professor of Natural and Experimental Philosophy at Trinity College Dublin (TCD) from 1881 to 1901. FitzGerald is known for his work in electromagnetic theory and for the Lorentz–FitzGerald contraction, which became an integral part of Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity. A crater on the far side of the Moon is named after him, as is a building at TCD. Life and work in physics FitzGerald was born at No. 19, Lower Mount Street in Dublin on 3 August 1851 to the Reverend William FitzGerald and his wife Anne Frances Stoney (sister of George Johnstone Stoney and Bindon Blood Stoney). Professor of Moral Philosophy in Trinity and vicar of St Anne's, Dawson Street, at the time of his son's birth, William FitzGerald was consecrated Bishop of Cork, Cloyne and Ross in 1857 and translated to Killaloe and Clonfert in 1862. George returne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interference Fringe
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two waves combine by adding their displacement together at every single point in space and time, to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude. Constructive and destructive interference result from the interaction of waves that are correlated or coherent with each other, either because they come from the same source or because they have the same or nearly the same frequency. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves, gravity waves, or matter waves. Etymology The word ''interference'' is derived from the Latin words ''inter'' which means "between" and ''fere'' which means "hit or strike", and was coined by Thomas Young in 1801. Mechanisms The principle of superposition of waves states that when two or more propagating waves of the same type are incident on the same point, the resultant amplitude at that point is equal to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michelson–Morley Experiment
The Michelson–Morley experiment was an attempt to detect the existence of the luminiferous aether, a supposed medium permeating space that was thought to be the carrier of light waves. The experiment was performed between April and July 1887 by American physicists Albert A. Michelson and Edward W. Morley at what is now Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio, and published in November of the same year. The experiment compared the speed of light in perpendicular directions in an attempt to detect the relative motion of matter through the stationary luminiferous aether ("aether wind"). The result was negative, in that Michelson and Morley found no significant difference between the speed of light in the direction of movement through the presumed aether, and the speed at right angles. This result is generally considered to be the first strong evidence against the then-prevalent aether theory, as well as initiating a line of research that eventually led to special r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |