|
Tax Wedge
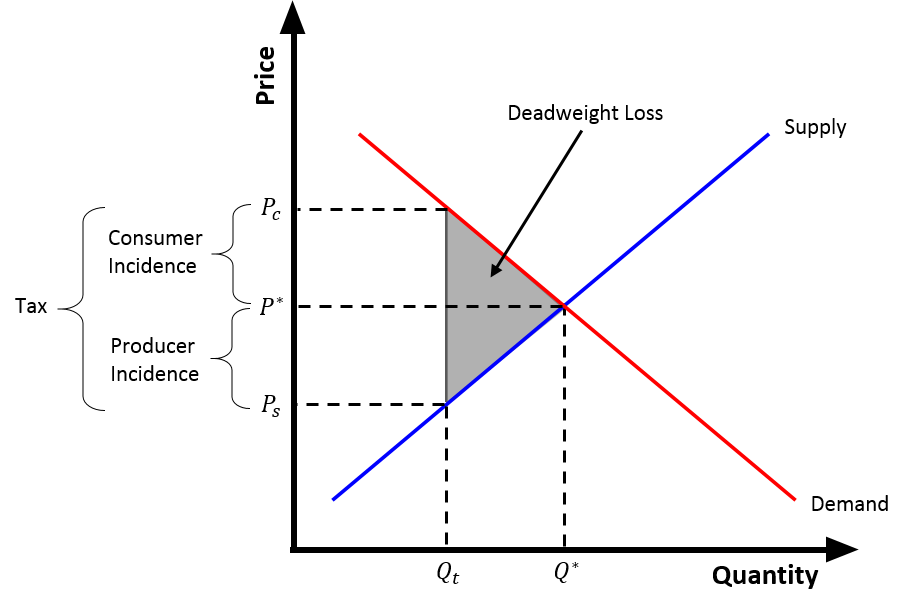
The tax wedge is the deviation from the equilibrium price and quantity (P^* and Q^*, respectively) as a result of the taxation of a good. Because of the tax, consumers pay more for the good (P_c) than they did before the tax, and Vendor (supply chain), suppliers receive less for the good (P_s) than they did before the tax . Put differently, the tax wedge is the difference between the price consumers pay and the value producers receive (net of tax) from a transaction. The tax effectively drives a "wedge" between the price consumers pay and the price producers receive for a product. Following the Law of Supply and Demand, as the price to consumers increases, and the price received by suppliers decreases, the quantity that each wishes to trade will decrease. After a tax is introduced, a new equilibrium is reached, where consumers pay more (P^* \rightarrow P_c), suppliers receive less (P^* \rightarrow P_s), and the quantity exchanged falls (Q^* \rightarrow Q_t). The difference between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in the commercial exchange, the payment for this product will likely be called its "price". However, if the product is "service", there will be other possible names for this product's name. For example, the graph on the bottom will show some situations A good's price is influenced by production costs, supply of the desired item, and demand for the product. A price may be determined by a monopolist or may be imposed on the firm by market conditions. Price can be quoted to currency, quantities of goods or vouchers. * In modern economies, prices are generally expressed in units of some form of currency. (More specifically, for raw materials they are expressed as currency per unit weight, e.g. euros per kilogram or Rands per KG.) * Although prices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantity
Quantity or amount is a property that can exist as a Counting, multitude or Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude, which illustrate discontinuity (mathematics), discontinuity and continuum (theory), continuity. Quantities can be compared in terms of "more", "less", or "equal", or by assigning a numerical value multiple of a unit of measurement. Mass, time, distance, heat, and angle are among the familiar examples of quantitative properties. Quantity is among the basic Class (philosophy), classes of things along with Quality (philosophy), quality, Substance theory, substance, change, and relation. Some quantities are such by their inner nature (as number), while others function as states (properties, dimensions, attributes) of things such as heavy and light, long and short, broad and narrow, small and great, or much and little. Under the name of multitude comes what is discontinuous and discrete and divisible ultimately into indivisibles, such as: ''army, fleet, flock, government, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxation
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal person, legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, or national), and tax compliance refers to policy actions and individual behaviour aimed at ensuring that taxpayers are paying the right amount of tax at the right time and securing the correct tax allowances and tax reliefs. The first known taxation took place in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC. A failure to pay in a timely manner (Tax noncompliance, non-compliance), along with evasion of or resistance to taxation, is punishable by law. Taxes consist of direct tax, direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as its labor equivalent. Most countries have a tax system in place, in order to pay for public, common societal, or agreed national needs and for the functions of government. Some levy a flat tax, flat percentag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer
A consumer is a person or a group who intends to order, or uses purchased goods, products, or services primarily for personal, social, family, household and similar needs, who is not directly related to entrepreneurial or business activities. The term most commonly refers to a person who purchases goods and services for personal use. Consumer rights “Consumers, by definition, include us all," said President John F. Kennedy, offering his definition to the United States Congress on March 15, 1962. This speech became the basis for the creation of World Consumer Rights Day, now celebrated on March 15. In his speech : John Fitzgerald Kennedy outlined the integral responsibility to consumers from their respective governments to help exercise consumers' rights, including: *The right to safety: To be protected against the marketing of goods that are hazardous to health or life. *The right to be informed: To be protected against fraudulent, deceitful, or grossly misleading informatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vendor (supply Chain)
In a supply chain, a vendor, supplier, provider or a seller, is an enterprise that contributes goods or services. Generally, a supply chain vendor manufactures inventory/stock items and sells them to the next link in the chain. Today, these terms refer to a supplier of any goods or service. Description A vendor is a supply chain management term that means anyone can sell at events and provides goods or services of experience to another entity. Vendors may sell B2B ( business-to-business; i.e., to other companies), B2C (business to consumers or Direct-to-consumer), or B2G (business to government). Some vendors manufacture inventoriable items and then sell those items to customers, while other vendors offer services or experiences. The term vendor and the term supplier are often used indifferently. The difference is that the vendors ''sells'' the goods or services while the supplier ''provides'' the goods or services. In most of business context, except retail, this difference h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
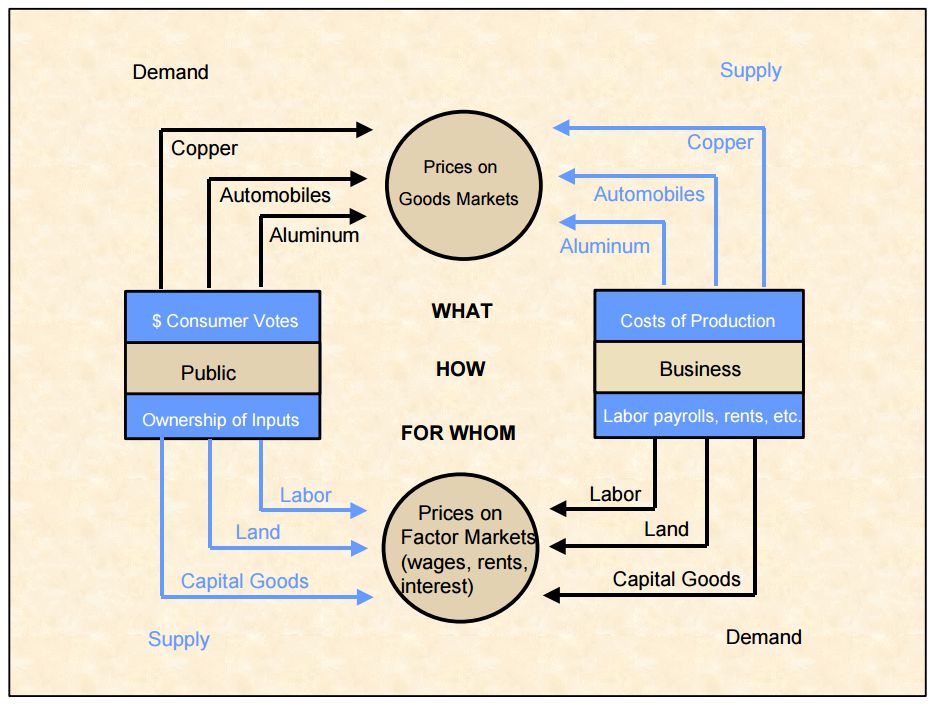
Supply And Demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a Market (economics), market. It postulates that, Ceteris paribus, holding all else equal, in a perfect competition, competitive market, the unit price for a particular Good (economics), good, or other traded item such as Labour supply, labor or Market liquidity, liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted. The concept of supply and demand forms the theoretical basis of modern economics. In macroeconomics, as well, the AD–AS model, aggregate demand-aggregate supply model has been used to depict how the quantity of real GDP, total output and the aggregate price level may be determined in equilibrium. Graphical representations Supply schedule A supply schedule, depicted graphically as a supply cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deadweight Loss
In economics, deadweight loss is the difference in production and consumption of any given product or service including government tax. The presence of deadweight loss is most commonly identified when the quantity produced ''relative'' to the amount consumed differs in regards to the optimal concentration of surplus. This difference in the amount reflects the quantity that is not being utilized or consumed and thus resulting in a ''loss''. This "deadweight loss" is therefore attributed to both, producers and consumers because neither one of them benefits from the surplus of the overall production. Deadweight loss can also be a measure of lost economic efficiency when the socially optimal quantity of a good or a service is not produced. Non-optimal production can be caused by monopoly pricing in the case of artificial scarcity, a positive or negative externality, a tax or subsidy, or a binding price ceiling or price floor such as a minimum wage. Examples Assume a market for na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Surplus
In mainstream economics, economic surplus, also known as total welfare or total social welfare or Marshallian surplus (after Alfred Marshall), is either of two related quantities: * Consumer surplus, or consumers' surplus, is the monetary gain obtained by consumers because they are able to purchase a product for a price that is less than the highest price that they would be willing to pay. * Producer surplus, or producers' surplus, is the amount that producers benefit by selling at a market price that is higher than the least that they would be willing to sell for; this is roughly equal to profit (since producers are not normally willing to sell at a loss and are normally indifferent to selling at a break-even price). Overview In the mid-19th century, engineer Jules Dupuit first propounded the concept of economic surplus, but it was the economist Alfred Marshall who gave the concept its fame in the field of economics. On a standard supply and demand diagram, consumer sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Wedge Inelastic Demand
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, or national), and tax compliance refers to policy actions and individual behaviour aimed at ensuring that taxpayers are paying the right amount of tax at the right time and securing the correct tax allowances and tax reliefs. The first known taxation took place in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC. A failure to pay in a timely manner ( non-compliance), along with evasion of or resistance to taxation, is punishable by law. Taxes consist of direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as its labor equivalent. Most countries have a tax system in place, in order to pay for public, common societal, or agreed national needs and for the functions of government. Some levy a flat percentage rate of taxation on personal annual income, but mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Wedge Inelastic Supply
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, or national), and tax compliance refers to policy actions and individual behaviour aimed at ensuring that taxpayers are paying the right amount of tax at the right time and securing the correct tax allowances and tax reliefs. The first known taxation took place in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC. A failure to pay in a timely manner ( non-compliance), along with evasion of or resistance to taxation, is punishable by law. Taxes consist of direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as its labor equivalent. Most countries have a tax system in place, in order to pay for public, common societal, or agreed national needs and for the functions of government. Some levy a flat percentage rate of taxation on personal annual income, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Incidence
In economics, tax incidence or tax burden is the effect of a particular tax on the distribution of economic welfare. Economists distinguish between the entities who ultimately bear the tax burden and those on whom tax is initially imposed. The tax burden measures the true economic weight of the tax, measured by the difference between real incomes or utilities before and after imposing the tax, taking into account how the tax leads prices to change. If a 10% tax is imposed on sellers of butter, for example, but the market price rises 8% as a result, most of the burden is on buyers, not sellers. The concept of tax incidence was initially brought to economists' attention by the French Physiocrats, in particular François Quesnay, who argued that the incidence of all taxation falls ultimately on landowners and is at the expense of land rent. Tax incidence is said to "fall" upon the group that ultimately bears the burden of, or ultimately suffers a loss from, the tax. The key concept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(14597240757).jpg)
.jpg)
'_oil_on_panel%2C_1620-1640._USC_Fisher_Museum_of_Art.jpg)