|
Tanks In France
French development into tanks began during World War I as an effort to overcome the stalemate of trench warfare, and largely at the initiative of the manufacturers. The Schneider CA1 was the first tank produced by France, and 400 units were built. The French also experimented with various tank designs, such as the Frot-Laffly landship, Boirault machine and Souain experiment. Another 400 Saint-Chamond tanks were manufactured from April 1917 to July 1918 but they were underpowered and were of limited utility because the caterpillar tracks were too short for the tank's length and weight. The most significant French tank development during the war was the Renault FT light tank, which set the general layout for future tank designs and was used or redesigned by various military forces, including those of the United States. History World War I While the British began the design and use of tanks in World War I, France at the same time developed its own tracked AFVs, but the situation t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FCM F1
The FCM F1 was a French super-heavy tank developed during the late Interbellum by the ''Forges et Chantiers de la Méditerranée'' (FCM) company. Twelve were ordered in 1940 to replace the Char 2C, but France was defeated before construction could begin, a wooden mock-up being all that was finished. The FCM F1 was large and elongated, and had two turrets: one in front and one in the back, with a single high-velocity gun in each turret. The rear turret was higher so it could Superfiring, shoot over the first one. The vehicle was intended to be heavily armoured. Its size and protection level made it by 1940, at about 140 tons the heaviest tank ever to have actually been ordered for production. Despite two engines its speed would have been low. The primary purpose of the tank was to breach German fortification lines, not to fight enemy tanks. The development path of the FCM F1 was extremely complex, due to the existence of a number of parallel super-heavy tank projects with overlappi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
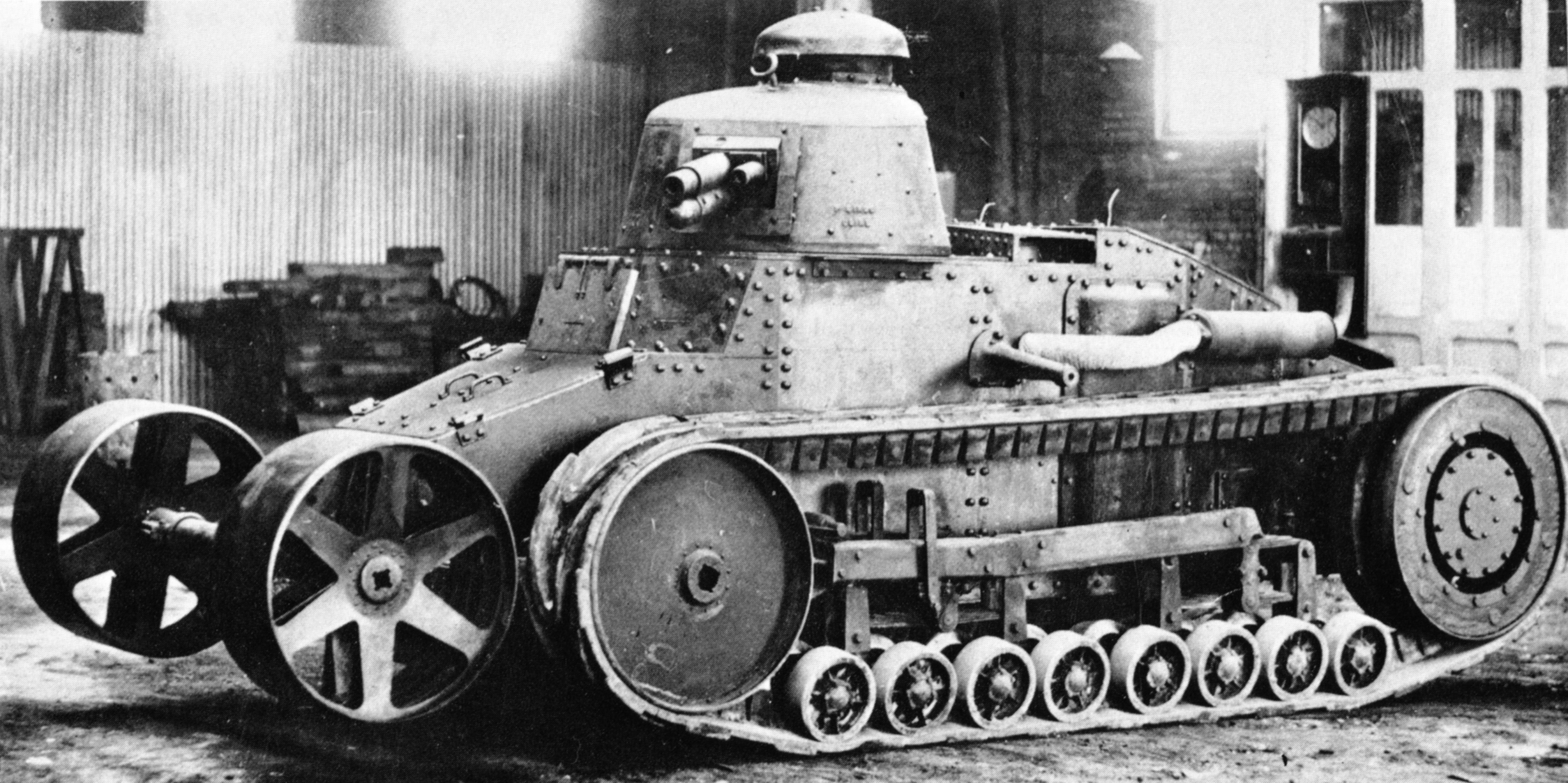
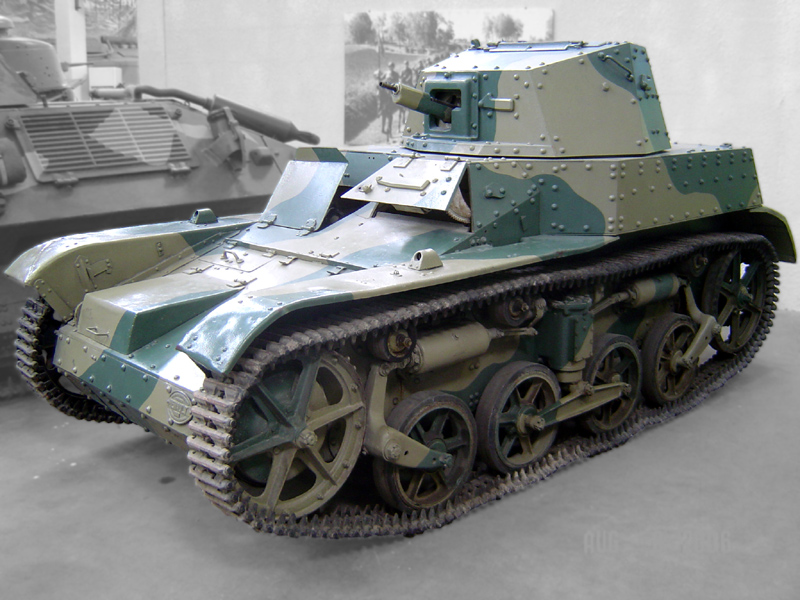
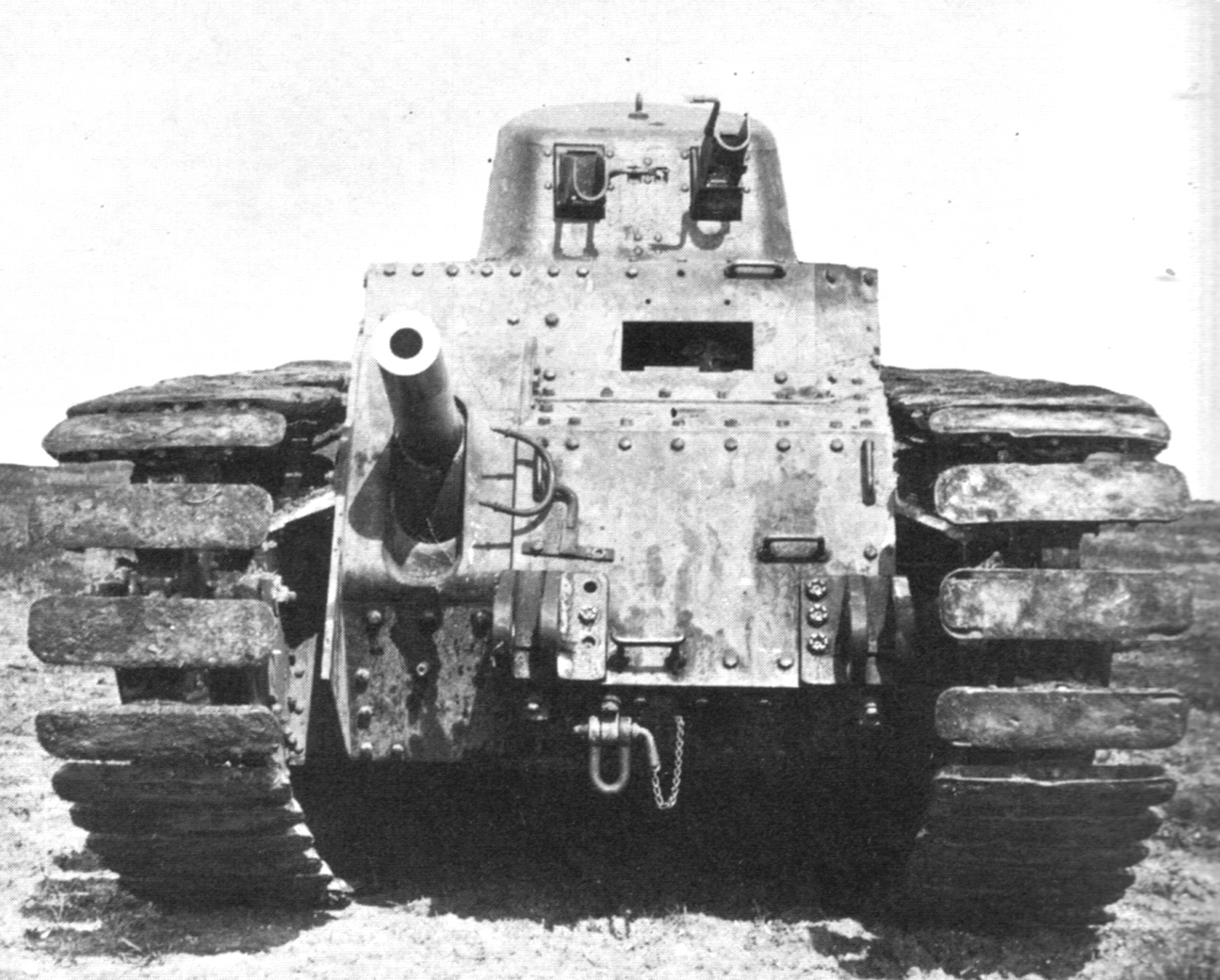
AMR 33
The Automitrailleuse de Reconnaissance Renault Modèle 1933 (AMR 33 or Renault VM) was a French cavalry light tank developed during the Interbellum and used in the Second World War. Developed by Renault from 1932, the type was ordered by the French Cavalry in 1933; a total of 123 would be built until 1935. The AMR 33 was lightly armed and armoured; though it was very fast for its day, it proved to be a mechanically unreliable vehicle, especially its suspension elements being too weak. It was therefore succeeded by an improved type, the AMR 35. Though its name might suggest otherwise, the AMR 33 was not a scout vehicle and mostly was not equipped with a radio set. The AMR 33s were intended to form a large mass of light tanks, preceding the medium types into battle. In reality they never served as such; by the time enough medium tanks were produced to form armoured divisions, the AMR 33 had already been replaced by the AMR 35 and was limited to the Cavalry Divisions and in 1940 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somua S35
The SOMUA S35 was a French cavalry tank of the Second World War. Built from 1936 until 1940 to equip the armoured divisions of the Cavalry, it was for its time a relatively agile medium-weight tank, superior in armour and armament to its French and foreign competitors, such as the contemporary versions of the German Panzer III medium tank. It was constructed from well-sloped, mainly cast, armour sections, that however made it expensive to produce and time-consuming to maintain. During the German invasion of May 1940, the SOMUA S35 proved itself to be a tactically effective type, but this was negated by the French command's strategic mistakes in deploying their Cavalry armoured divisions. After the defeat of France in June 1940, limiting production to a total of about 440, captured SOMUA S35s were used by the Axis powers, some of them on the Eastern Front. A derived type, the SOMUA S40, with an improved suspension, lowered hull cast and welded turret armour, had been planned to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMC 35
The AMC 35 (from ''Automitrailleuse de Combat Renault modèle 1935''), also known under a manufacturer's designation Renault ACG-1, was a French medium cavalry tank of the later Interwar era that served in the Second World War. It was developed as a result of the change of the specification that had led to the design of the AMC 34, calling for a vehicle that was not only well-armed and mobile but also well-armoured. Due to technological and financial problems production was delayed and limited. The AMC 35 was one of the few French tanks of the period featuring a two-man turret. Development Renault had developed the AMC 34 according to the specifications of the Plan 1931. On 26 June 1934 these were changed: it was now demanded that the vehicle attain a maximum speed of and be immune to anti-tank guns. On 7 March 1936 a changed prototype was delivered by Renault, who requested that the vehicle would be accepted if it met the new specifications; after all the AMC 34 had already been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMC 34
The AMC 34 was a French tank built originally for the French Army cavalry units. Its production was cut short, and the few vehicles produced were out of service by the time of the Battle of France in the Second World War. Development Alarmed by the rapid build-up of the Red Army the French Army on 24 December 1931 conceived a preliminary plan for the mechanisation of the Cavalry. This foresaw the development of several types of ''automitrailleuses'' — the official term for cavalry tanks because ''chars'' ("tanks") were by law part of the infantry arm — among which an ''Automitrailleuse de Combat'' (AMC), a lightly armoured (weighing no more than nine tons) but swift (30 km/h cruise speed) and strongly armed (47 mm gun) combat tank, capable of fighting enemy armour. The plan was affirmed by the French Supreme Command on 23 January 1932 and approved by the ministry of defence on 9 December. Even before Plan 1931 was put on paper Louis Renault was informed of its probab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotchkiss H35
The Hotchkiss H35 or was a French cavalry tank developed prior to World War II. Despite having been designed from 1933 as a rather slow but well-armoured light infantry support tank, the type was initially rejected by the French Infantry because it proved difficult to steer while driving cross-country, and was instead adopted in 1936 by the French Cavalry arm. From 1938 an improved version was produced with a more powerful engine, the ''Char léger modèle 1935 H modifié 39'', which from 1940 was also fitted with a longer, more powerful 37 mm gun. It was intended to make this improved variant the standard light tank, with at least four thousand produced to equip new armoured divisions of both the Cavalry and the Infantry arms, but due to the defeat of France in June 1940, total production of both subtypes was limited to about 1200 vehicles. For the remainder of the war Germany and its allies used captured Hotchkiss tanks in several modifications. Development In 1926, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-personnel
An anti-personnel weapon is a weapon primarily used to maim or kill infantry and other personnel not behind armor, as opposed to attacking structures or vehicles, or hunting game. The development of defensive fortification and combat vehicles gave rise to weapons designed specifically to attack them, and thus a need to distinguish between those systems and ones intended to attack people. For instance, an anti-personnel landmine will explode into small and sharp splinters that tear flesh but have little effect on metal surfaces, while anti-tank mines have considerably different design, using much more explosive power to effect damage to armored fighting vehicles, or use explosively formed penetrators to punch through armor plating. Many modern weapons systems can be employed in different roles. For example, a tank's main gun can fire armor-piercing ammunition in the anti-tank role, high-explosive ammunition in the anti-structure role and fragmentation shells in the anti-person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
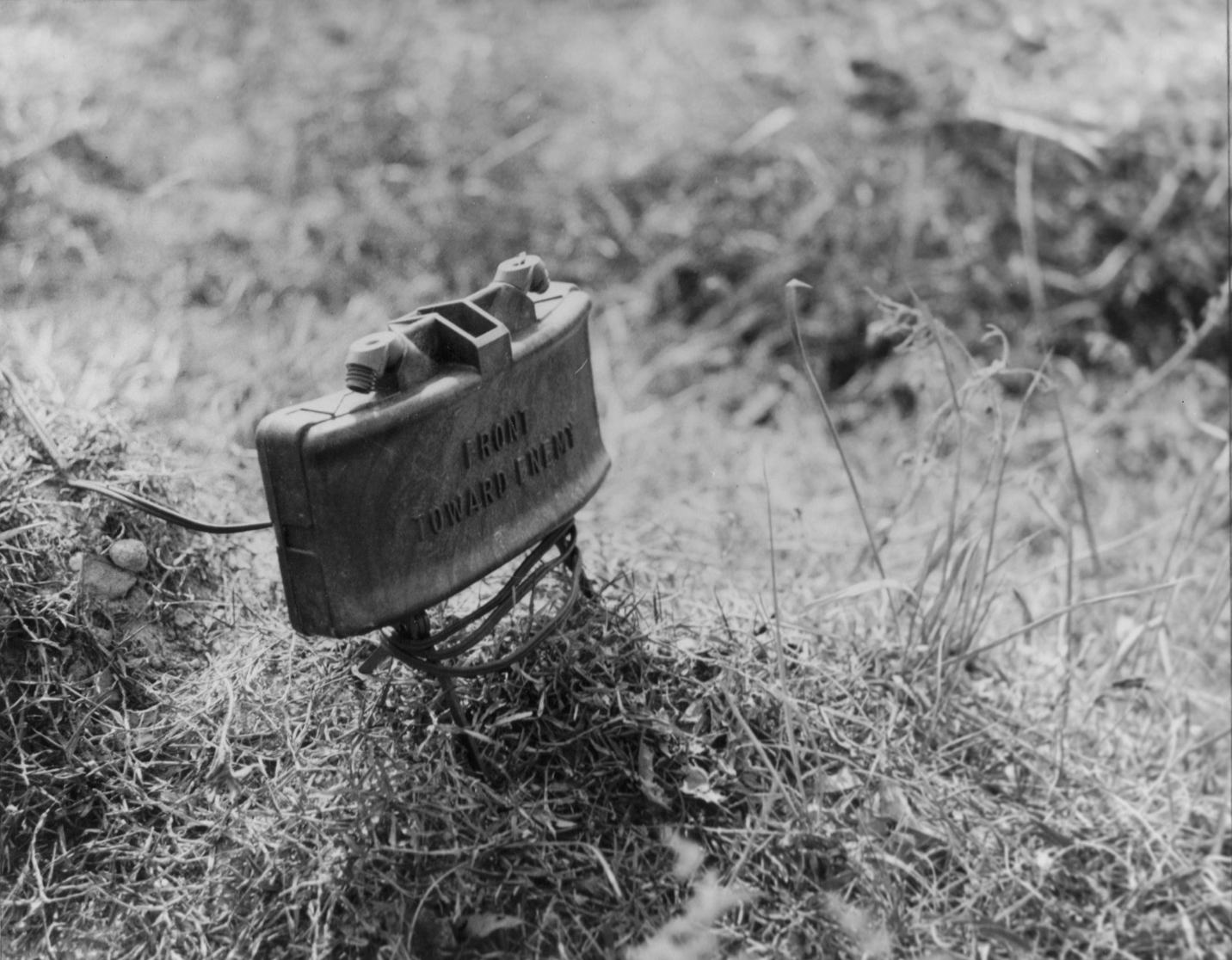
Anti-tank
Anti-tank warfare originated from the need to develop technology and tactics to destroy tanks during World War I. Since the Triple Entente deployed the first tanks in 1916, the German Empire developed the first anti-tank weapons. The first developed anti-tank weapon was a scaled-up bolt-action rifle, the Mauser 1918 T-Gewehr, that fired a 13mm cartridge with a solid bullet that could penetrate the thin armor of tanks of the time and destroy the engine or ricochet inside, killing occupants. Because tanks represent an enemy's strong force projection on land, military strategists have incorporated anti-tank warfare into the doctrine of nearly every combat service since. The most predominant anti-tank weapons at the start of World War II in 1939 included the tank-mounted gun, anti-tank guns and anti-tank grenades used by the infantry, and ground-attack aircraft. Anti-tank warfare evolved rapidly during World War II, leading to the inclusion of infantry-portable weapons such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Char B1
The Char B1 was a French heavy tank manufactured before World War II. The Char B1 was a specialised break-through vehicle, originally conceived as a self-propelled gun with a 75 mm howitzer in the hull; later a 47 mm gun in a turret was added, to allow it to function also as a , a "battle tank" fighting enemy armour, equipping the armoured divisions of the Infantry Arm. Starting in the early twenties, its development and production were repeatedly delayed, resulting in a vehicle that was both technologically complex and expensive, and already obsolescent when real mass-production of a derived version, the Char B1 "bis", started in the late 1930s. A further up-armoured version, the Char B1 "ter", was only built in two prototypes. Among the most powerfully armed and armoured tanks of its day, the type was very effective in direct confrontations with German armour in 1940 during the Battle of France, but low speed and high fuel consumption made it ill-adapted to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Char D2
The Char D2 was a French medium tank of the interwar period. In 1930, at a time the Char D1 had not even entered production, the Renault company agreed to build a better armoured version called the Char D2. By not using old-fashioned rivets, it was hoped to save weight. The tank should have the potential to serve as an alternative in the role of battle tank for the heavier Char B1, should the latter be forbidden by treaty. The failure of the armament limitation talks resulted in a severe reduction of the projected manufacture, now in the form of an interim tank. Organisational difficulties with Renault caused the actual production of a first series of fifty to be delayed to the years 1936 and 1937. A second series of fifty was ordered in 1938, despite indications that the type was mechanically unreliable, as a possible cheaper addition to the expensive Char B1. With the latter type, in case of war, only a limited number of armoured divisions for the Infantry Arm could be raised; t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Char D1
The Char D1 was an Interwar French light tank. The French plan of 1926, calling for the creation of a Light Infantry Support Tank, led to the development of the existing Renault NC1 prototype into the Char D1. One hundred and sixty vehicles of this type were produced between 1931 and 1935. There was a pre-series of ten vehicles and later 150 standard vehicles were built. Until 1936 the vehicles were fitted with Renault FT turrets because the intended cast ST2 turrets were not yet ready. The ST2 turret was armed with a short 47mm SA34 tank gun with a coaxial 7.5mm machine gun. The hull carried a 7.5mm MG in the bow. The type did not serve as an infantry support tank as originally intended, but as France's major battle tank of the early 1930s; it was quickly phased out in 1937 because of its mechanical unreliability and relegated to colonial units in North Africa. Development After World War I, France possessed a very large fleet of Renault FT light infantry support tanks. Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_tank.jpg)