|
Tafenoquine
Tafenoquine, sold under the brand name Krintafel among others, is a medication used to prevent and to treat malaria. With respect to acute malaria, it is used together with other medications to prevent relapse by ''Plasmodium vivax''. It may be used to prevent all types of malaria. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include vomiting, headache, and dizziness. Other side effects may include methemoglobinemia, trouble sleeping, and anaphylaxis. In people with G6PD deficiency, red blood cell breakdown may occur. Use in pregnancy is not recommended. Tafenoquine is in the 8-aminoquinoline family of medications. How it works is unclear but it is effective both in the liver and bloodstream. A possible mechanism of action and other novel perspectives have been published. Tafenoquine was approved for medical use in Australia and in the United States in 2018. Tafenoquine is related to primaquine. Medical use Prevention Tafenoquine may be used to prevent all types of malaria. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primaquine
Primaquine is a medication used to treat and prevent malaria and to treat ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia. Specifically it is used for malaria due to ''Plasmodium vivax'' and ''Plasmodium ovale'' along with other medications and for prevention if other options cannot be used. It is an alternative treatment for ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia together with clindamycin. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and stomach cramps. Primaquine should not be given to people with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency due to the risk of red blood cell breakdown. It is often recommended that primaquine not be used during pregnancy. It may be used while breastfeeding if the baby is known not to have G6PD deficiency. The mechanisms of action is not entirely clear but is believed to involve effects on the malaria parasites' DNA. Primaquine was first made in 1946. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primaquine
Primaquine is a medication used to treat and prevent malaria and to treat ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia. Specifically it is used for malaria due to ''Plasmodium vivax'' and ''Plasmodium ovale'' along with other medications and for prevention if other options cannot be used. It is an alternative treatment for ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia together with clindamycin. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and stomach cramps. Primaquine should not be given to people with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency due to the risk of red blood cell breakdown. It is often recommended that primaquine not be used during pregnancy. It may be used while breastfeeding if the baby is known not to have G6PD deficiency. The mechanisms of action is not entirely clear but is believed to involve effects on the malaria parasites' DNA. Primaquine was first made in 1946. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
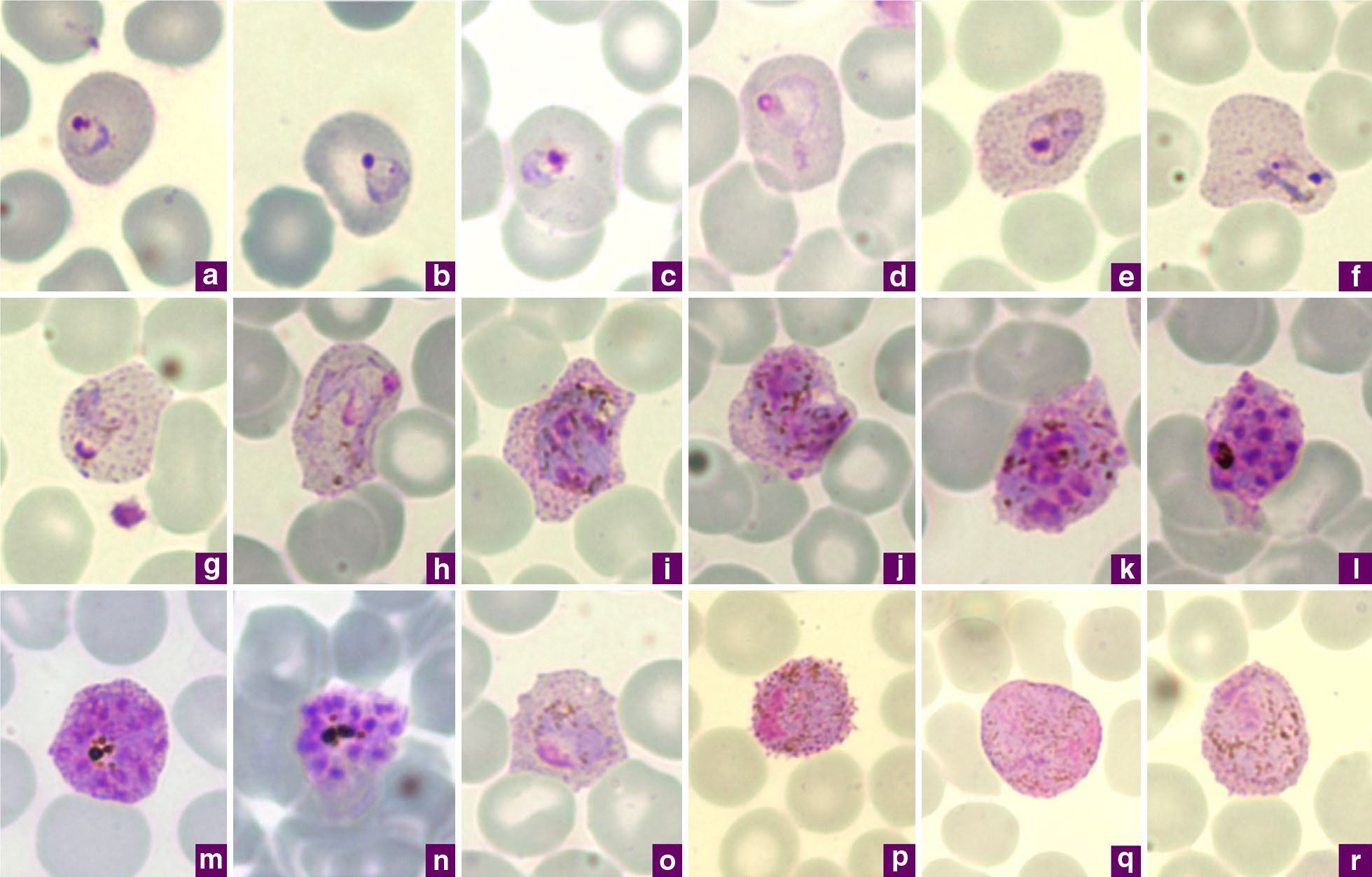
Plasmodium Vivax
''Plasmodium vivax'' is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than ''Plasmodium falciparum'', the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, ''P. vivax'' malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly (a pathologically enlarged spleen). ''P. vivax'' is carried by the female ''Anopheles'' mosquito; the males do not bite. Health Epidemiology ''Plasmodium vivax'' is found mainly in Asia, Latin America, and in some parts of Africa. ''P. vivax'' is believed to have originated in Asia, but recent studies have shown that wild chimpanzees and gorillas throughout central Africa are endemically infected with parasites that are closely related to human ''P. vivax.'' These findings indicate that human P. vivax is of African origin. ''Plasmodium vivax'' accounts for 65% of malaria cases in Asia and South America. Unlike ''Pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the ''Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spread by h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8-aminoquinoline
8-Aminoquinoline is the 8-amino derivative of quinoline. Often abbreviated AQ, it is a pale yellow solid. It is structurally analogous to 8-hydroxyquinoline. Drug derivatives The derivatives primaquine, tafenoquine and pamaquine have been tested for anti-malaria activity. Primaquine is still used routinely worldwide as part of the treatment of ''Plasmodium vivax'' and ''Plasmodium ovale'' malaria, although how it prevents malarial recurrences is not, at present, clear. Tafenoquine was approved for medical use in Australia and in the United States in 2018. Image:Primaquine.svg, Primaquine Image:Pamaquine.svg, Pamaquine Image:Tafenoquine.svg, Tafenoquine Directing group The amine functional group is amenable to formation of amide In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimalarial Agents
Antimalarial medications or simply antimalarials are a type of antiparasitic chemical agent, often naturally derived, that can be used to treat or to prevent malaria, in the latter case, most often aiming at two susceptible target groups, young children and pregnant women. As of 2018, modern treatments, including for severe malaria, continued to depend on therapies deriving historically from quinine and artesunate, both parenteral (injectable) drugs, expanding from there into the many classes of available modern drugs. Incidence and distribution of the disease ("malaria burden") is expected to remain high, globally, for many years to come; moreover, known antimalarial drugs have repeatedly been observed to elicit resistance in the malaria parasite—including for combination therapies featuring artemisinin, a drug of last resort, where resistance has now been observed in Southeast Asia. As such, the needs for new antimalarial agents and new strategies of treatment (e.g., new combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodium Ovale
''Plasmodium ovale'' is a species of parasitic protozoon that causes tertian malaria in humans. It is one of several species of ''Plasmodium'' parasites that infect humans, including ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and ''Plasmodium vivax'' which are responsible for most cases of malaria in the world. ''P. ovale'' is rare compared to these two parasites, and substantially less dangerous than ''P. falciparum''. ''P. ovale'' has recently been shown by genetic methods to consist of what is considered to be two species (despite having been given subspecies names), namely '' P. ovale curtisi'' and '' P. ovale wallikeri''. History This species was first described in 1914 by Stephens in a blood sample taken in the autumn of 1913 from a patient in the sanitarium of Pachmari in central India and sent by Major W. H. Kenrick to Stephens (who was working in Liverpool). Epidemiology ''P. ovale'' is primarily concentrated in sub-Saharan Africa and islands in the western Pacific. However ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakthrough Therapy
Breakthrough therapy is a United States Food and Drug Administration designation that expedites drug development that was created by Congress under Section 902 of the 9 July 2012 Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act. The FDA's "breakthrough therapy" designation is not intended to imply that a drug is actually a "breakthrough" or that there is high-quality evidence of treatment efficacy for a particular condition; rather, it allows the FDA to grant priority review to drug candidates if preliminary clinical trials indicate that the therapy may offer substantial treatment advantages over existing options for patients with serious or life-threatening diseases. The FDA has other mechanisms for expediting the review and approval process for promising drugs, including fast track designation, accelerated approval, and priority review. Requirements A breakthrough therapy designation can be assigned to a drug if "it is a drug which is intended alone or in combination with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDER
The Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER, pronounced "see'-der") is a division of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that monitors most drugs as defined in the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Some biological products are also legally considered drugs, but they are covered by the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. The center reviews applications for brand name, generic, and over the counter pharmaceuticals, manages US current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations for pharmaceutical manufacturing, determines which medications require a medical prescription, monitors advertising of approved medications, and collects and analyzes safety data about pharmaceuticals that are already on the market. CDER receives considerable public scrutiny, and thus implements processes that tend toward objectivity and tend to isolate decisions from being attributed to specific individuals. The decisions on approval will often make or break a small company's stock pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSK Plc Brands , a rendering pipeline
{{disambiguation ...
GSK may refer to: * Galatasaray S.K., a Turkish sports club based in Istanbul * Glycogen synthase kinase * Golden State Killer, a California serial rapist and murderer * GSK plc, formerly GlaxoSmithKline, a multinational pharmaceutical corporation * GTK Scene Graph Kit GTK Scene Graph Kit (GSK) is the rendering and scene graph API for GTK introduced with version 3.90. GSK lies between the graphical control elements (widgets) and the rendering. Like GDK, GSK is part of GTK and licensed under the GNU Lesser Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GlaxoSmithKline
GSK plc, formerly GlaxoSmithKline plc, is a British multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with global headquarters in London, England. Established in 2000 by a merger of Glaxo Wellcome and SmithKline Beecham. GSK is the tenth largest pharmaceutical company and #294 on the 2022 ''Fortune'' Global 500, ranked behind other pharmaceutical companies China Resources, Sinopharm, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, Roche, AbbVie, Novartis, Bayer, and Merck. The company has a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. , it had a market capitalisation of £70 billion, the eighth largest on the London Stock Exchange. It has a secondary listing on the New York Stock Exchange. The company developed the first malaria vaccine, RTS,S, which it said in 2014 it would make available for five percent above cost. Legacy products developed at GSK include several listed in the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
