|
Tung Oil
Tung oil or China wood oil is a drying oil obtained by pressing the seed from the nut of the tung tree (''Vernicia fordii''). The oil and its use are believed to have originated in ancient China and appear in the writings of Confucius from about 400 BC. Tung oil hardens upon exposure to air (through polymerization), and the resulting coating is transparent and has a deep, almost wet look. Used mostly for finishing and protecting wood, after numerous coats, the finish can even look plastic-like. Related drying oils include linseed, safflower, poppy, and soybean oils. Raw tung oil tends to dry to a fine, wrinkled finish (the English name for this is gas checking); this property was used to make wrinkle finishes, usually by adding excess cobalt drier. To prevent wrinkling, the oil is heated to gas-proof it (also known as "boiled"). 'Tung oil' is often used by paint and varnish manufacturers as a generic name for any wood-finishing product that contains the real tung oil or provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tung Tree Leaf And Berries
Tung may refer to: People * Madison Tung, a U.S. Air Force Officer, wrestler, and Rhodes Scholar * Ho-Pin Tung, a dutch race car driver of Chinese descent. * The_Summer_I_Turned_Pretty_(TV_series), Lola Tung, an actress known for her acting debut on drama series The Summer I Turned Pretty Places * Tung Fort, a hill fort in Maharashtra, India * Tung, a village in Bar Kham, Cambodia * Tung (Mawal), a village in Maharashtra, India * Tung, Sikkim, a village in India * Tung, West Bengal, India, on the Darjeeling Himalayan Railway Other uses * ''Vernicia fordii'' or Tung tree, a deciduous tree native to China ** Tung oil, a furniture finish made from the seeds of the tung tree * Tung (surname), a Cantonese Romanization of Chinese family names 董, commonly used in Hong Kong * Tung, the original Webster spelling of tongue * Tunng, an experimental folk band from the United Kingdom * Lê Quang Tung (1923–1963), Vietnamese military leader under Ngô Đình Diệm See also * {{Disa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oleic Acid
Oleic acid is a fatty acid that occurs naturally in various animal and vegetable fats and oils. It is an odorless, colorless oil, although commercial samples may be yellowish. In chemical terms, oleic acid is classified as a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid, abbreviated with a lipid number of 18:1 ''cis''-9, and a main product of Δ9 desaturase. It has the formula CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH. The name derives from the Latin word ''oleum'', which means oil. It is the most common fatty acid in nature. The salts and esters of oleic acid are called oleates. Occurrence Fatty acids (or their salts) often do not occur as such in biological systems. Instead fatty acids such as oleic acid occur as their esters, commonly triglycerides, which are the greasy materials in many natural oils. Oleic acid is the most common monounsaturated fatty acid in nature. It is found in fats (triglycerides), the phospholipids that make membranes, cholesterol esters, and wax esters. Triglycerides of oleic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the Eastern world, East and Western world, West. The name "Silk Road", first coined in the late 19th century, has fallen into disuse among some modern historians in favor of Silk Routes, on the grounds that it more accurately describes the intricate web of land and sea routes connecting East Asia, East and Southeast Asia, the South Asia, Indian subcontinent, Central Asia, the Middle East, East Africa and Southern Europe, Europe. The Silk Road derives its name from the highly lucrative trade of silk, silk textiles that were Silk industry in China, produced almost exclusively in China. The network began with the Han dynasty, Han dynasty's expansion into Central Asia around 114 BCE, Protectorate of the Western Regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asian Cultural Sphere
The East Asian cultural sphere, also known as the Sinosphere, the Sinic world, the Sinitic world, the Chinese cultural sphere, the Chinese character sphere encompasses multiple countries in East Asia and Southeast Asia that were historically influenced by Chinese culture. According to academic consensus, the East Asian cultural sphere is made up of four entities: Greater China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam. Other definitions sometimes include Mongolia and Singapore, because of limited historical Chinese influences or increasing modern-day Chinese diaspora. The East Asian cultural sphere is not to be confused with the Sinophone world, which includes countries where the Chinese-speaking population is dominant. Imperial China was a regional power and exerted influence on tributary states and neighboring states, among which were Japan, Korea, and Vietnam. These interactions brought ideological and cultural influences rooted in Confucianism, Buddhism, and Taoism. During classical h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limonene
Limonene is a colorless liquid aliphatic hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic monoterpene, and is the major component in the oil of citrus fruit peels. The -isomer, occurring more commonly in nature as the fragrance of oranges, is a flavoring agent in food manufacturing. It is also used in chemical synthesis as a precursor to carvone and as a renewables-based solvent in cleaning products. The less common -isomer has a piny, turpentine-like odor, and is found in the edible parts of such plants as caraway, dill, and bergamot orange plants. Limonene takes its name from Italian ''limone'' ("lemon"). Limonene is a chiral molecule, and biological sources produce one enantiomer: the principal industrial source, citrus fruit, contains -limonene ((+)-limonene), which is the (''R'')-enantiomer. Racemic limonene is known as dipentene. -Limonene is obtained commercially from citrus fruits through two primary methods: centrifugal separation or steam distillation. Chemical reactions Limon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity quantifies the internal frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's axis than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube with a constant rate of flow, the strength of the compensating force is proportional to the fluid's viscosity. In general, viscosity depends on a fluid's state, such as its temperature, pressure, and rate of deformation. However, the dependence on some of these properties is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alder With And Without Tung Oil
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few species extending into Central America, as well as the northern and southern Andes. Description With a few exceptions, alders are deciduous, and the leaves are alternate, simple, and serrated. The flowers are catkins with elongate male catkins on the same plant as shorter female catkins, often before leaves appear; they are mainly wind-pollinated, but also visited by bees to a small extent. These trees differ from the birches (''Betula'', another genus in the family) in that the female catkins are woody and do not disintegrate at maturity, opening to release the seeds in a similar manner to many conifer cones. The largest species are red alder (''A. rubra'') on the west coast of North America, and black alder (''A. glutinosa''), native to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
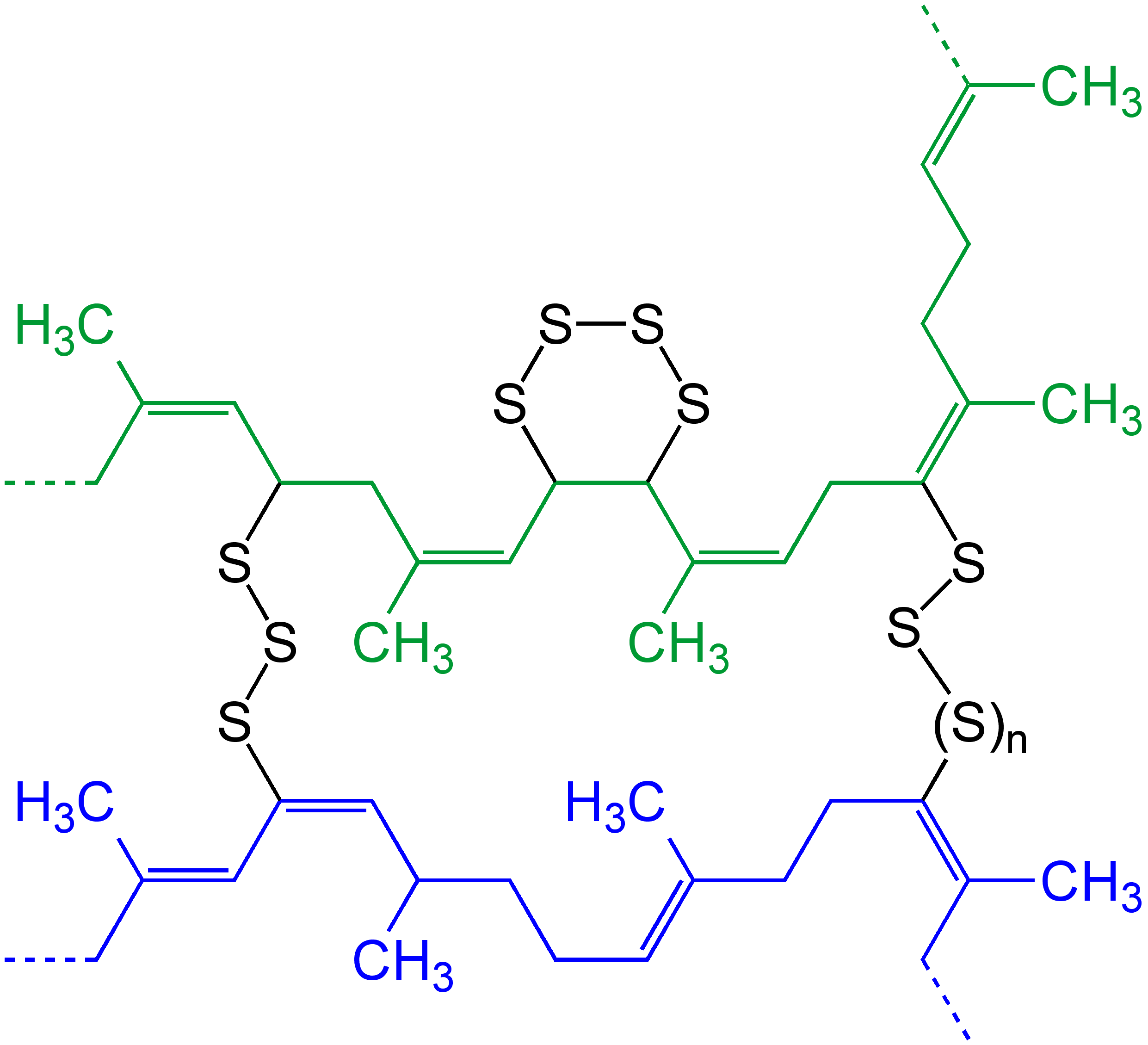
Cross Linking
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers (such as proteins). In polymer chemistry "cross-linking" usually refers to the use of cross-links to promote a change in the polymers' physical properties. When "crosslinking" is used in the biological field, it refers to the use of a probe to link proteins together to check for protein–protein interactions, as well as other creative cross-linking methodologies. Although the term is used to refer to the "linking of polymer chains" for both sciences, the extent of crosslinking and specificities of the crosslinking agents vary greatly. As with all science, there are overlaps, and the following delineations are a starting point to understanding the subtleties. Polymer chemistry Crosslinking is the general term for the process of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoxidation
Autoxidation (sometimes auto-oxidation) refers to oxidations brought about by reactions with oxygen at normal temperatures, without the intervention of flame or electric spark. The term is usually used to describe the gradual degradation of organic compounds in air at ambient temperatures. Many common phenomena can be attributed to autoxidation, such as food going rancid, the 'drying' of varnishes and paints, and the perishing of rubber. It is also an important concept in both industrial chemistry and biology. Autoxidation is therefore a fairly broad term and can encompass examples of photooxygenation and catalytic oxidation. The common mechanism is a free radical chain reaction, where the addition of oxygen gives rise to hydroperoxides and their associated peroxy radicals (ROO•). Typically, an induction period is seen at the start where there is little activity; this is followed by a gradually accelerating take-up of oxygen, giving an autocatalytic reaction which can only be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Bonds
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist between two different elements: for example, in a carbonyl group between a carbon atom and an oxygen atom. Other common double bonds are found in azo compounds (N=N), imines (C=N), and sulfoxides (S=O). In a skeletal formula, a double bond is drawn as two parallel lines (=) between the two connected atoms; typographically, the equals sign is used for this. Double bonds were first introduced in chemical notation by Russian chemist Alexander Butlerov. Double bonds involving carbon are stronger and shorter than single bonds. The bond order is two. Double bonds are also electron-rich, which makes them potentially more reactive in the presence of a strong electron acceptor (as in addition reactions of the halogens). File:Ethene structural.svg, Eth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |