|
Tubular Heart
The tubular heart or primitive heart tube is the earliest stage of heart development. From the inflow to the outflow, it consists of sinus venosus, primitive atrium, the primitive ventricle, the bulbus cordis, and truncus arteriosus The truncus arteriosus is a structure that is present during embryonic development. It is an arterial trunk that originates from both ventricles of the heart that later divides into the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. Structure The truncus arterio .... It forms primarily from splanchnic mesoderm. More specifically, they form from endocardial tubes, starting at day 21. References External links * * Embryology of cardiovascular system {{developmental-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splanchnic Mesoderm
The lateral plate mesoderm is the mesoderm that is found at the periphery of the embryo. It is to the side of the paraxial mesoderm, and further to the axial mesoderm. The lateral plate mesoderm is separated from the paraxial mesoderm by a narrow region of intermediate mesoderm. The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers, between the outer ectoderm and inner endoderm. During the third week of embryonic development the lateral plate mesoderm splits into two layers forming the intraembryonic coelom. The outer layer of lateral plate mesoderm adheres to the ectoderm to become the somatic or parietal layer known as the somatopleure. The inner layer adheres to the endoderm to become the splanchnic or visceral layer known as the splanchnopleure. Development The lateral plate mesoderm will split into two layers, the somatopleuric mesenchyme, and the splanchnopleuric mesenchyme. * The ''somatopleuric layer'' forms the future body wall. * The ''splanchnopleuric layer'' form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
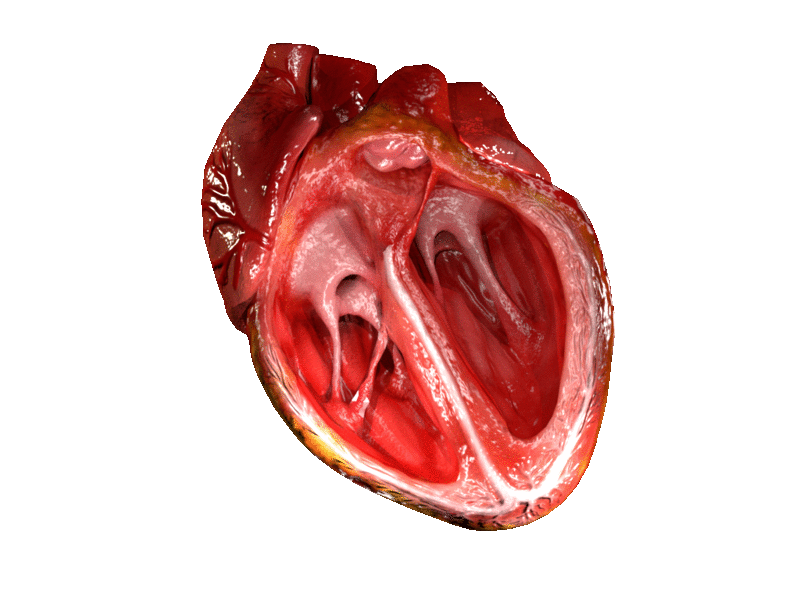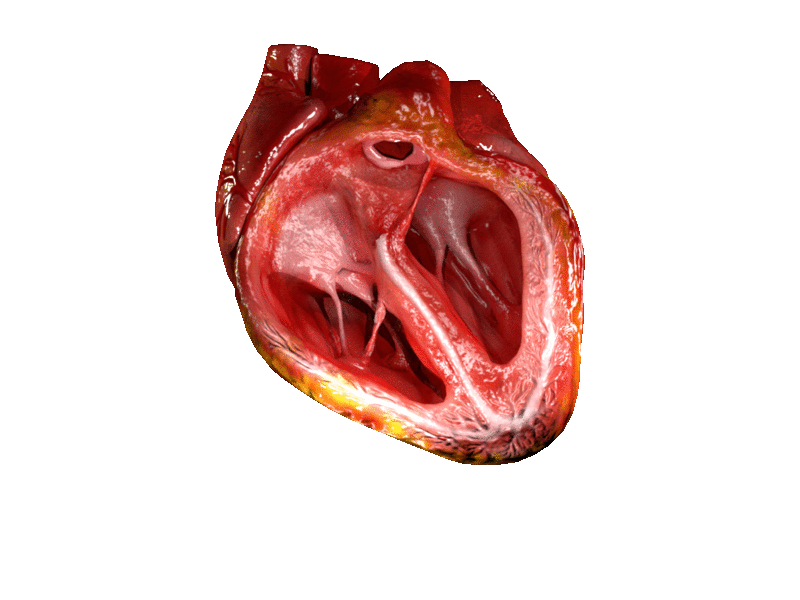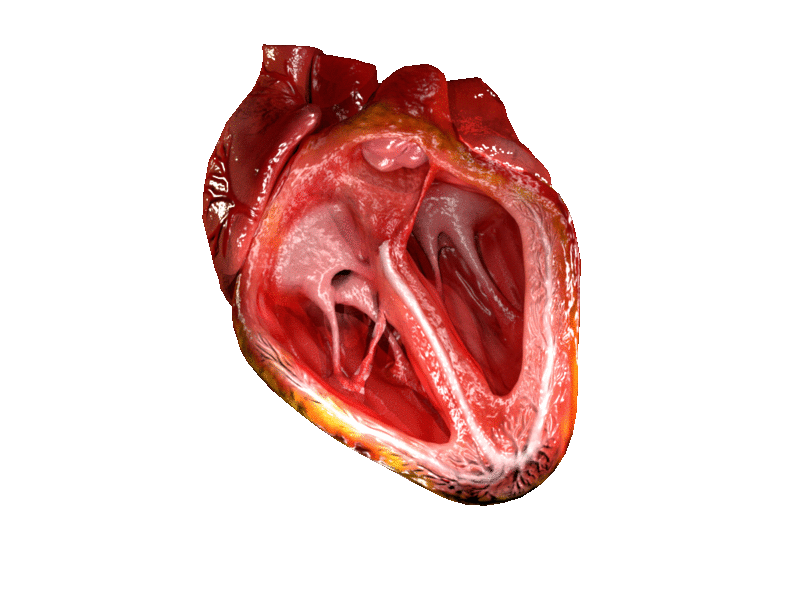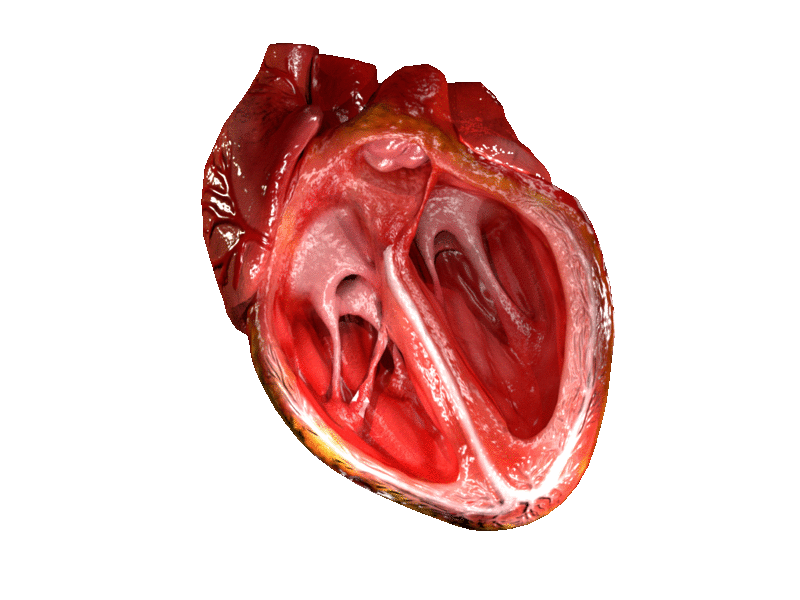
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus Venosus
The sinus venosus is a large quadrangular cavity which precedes the atrium on the venous side of the chordate heart. In mammals, it exists distinctly only in the embryonic heart, where it is found between the two venae cavae. However, the sinus venosus persists in the adult. In the adult, it is incorporated into the wall of the right atrium to form a smooth part called the sinus venarum, which is separated from the rest of the atrium by a ridge of fibres called the crista terminalis. The sinus venosus also forms the sinoatrial node and the coronary sinus; in (most) mammals only. In the embryo, the thin walls of the sinus venosus are connected below with the right ventricle, and medially with the left atrium, but are free in the rest of their extent. It receives blood from the vitelline vein, umbilical vein and common cardinal vein. The sinus venosus originally starts as a paired structure but shifts towards associating only with the right atrium as the embryonic heart develops. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primitive Atrium
The primitive atrium is a stage in the embryonic development of the human heart. It grows rapidly and partially encircles the bulbus cordis; the groove against which the bulbus cordis lies is the first indication of a division into right and left atria. The cavity of the primitive atrium becomes subdivided into right and left chambers by a septum, the septum primum, which grows downward into the cavity. For a time the atria communicate with each other by an opening, the primary interatrial foramen, below the free margin of the septum. This opening is closed by the union of the septum primum with the septum intermedium, and the communication between the atria is re-established through an opening which is developed in the upper part of the septum primum; this opening is known as the foramen ovale (ostium secundum of Born) and persists until birth. A second septum, the septum secundum, semilunar in shape, grows downward from the upper wall of the atrium immediately to the right of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primitive Ventricle
The primitive ventricle or embryonic ventricle of the developing heart, together with the bulbus cordis that lies in front of it, gives rise to the left and right ventricles. The primitive ventricle provides the trabeculated parts of the walls, and the bulbus cordis the smooth parts. The primitive ventricle becomes divided by the septum inferius which develops into the interventricular septum. The septum grows upward from the lower part of the ventricle, at a position marked on the heart's surface by a furrow. Its dorsal part increases more rapidly than its ventral portion, and fuses with the dorsal part of the septum intermedium. For a time an interventricular foramen exists above its ventral portion, but this foramen is ultimately closed by the fusion of the aortic septum The aorticopulmonary septum is developmentally formed from neural crest, specifically the cardiac neural crest, and actively separates the aorta and pulmonary arteries and fuses with the interventricular se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulbus Cordis
The bulbus cordis (the bulb of the heart) is a part of the developing heart that lies ventral to the primitive ventricle after the heart assumes its S-shaped form. The superior end of the bulbus cordis is also called the conotruncus. Structure In the early tubular heart, the bulbus cordis is the major outflow pathway. It receives blood from the primitive ventricle, and passes it to the truncus arteriosus. After heart looping, it is located slightly to the left of the ventricle. Development The early bulbus cordis is formed by the fifth week of development. The truncus arteriosus is derived from it later. The adjacent walls of the bulbus cordis and ventricle approximate, fuse, and finally disappear, and the bulbus cordis now communicates freely with the right ventricle, while the junction of the bulbus with the truncus arteriosus is brought directly ventral to and applied to the atrial canal. By the upgrowth of the ventricular septum the bulbus cordis is separated from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truncus Arteriosus
The truncus arteriosus is a structure that is present during embryonic development. It is an arterial trunk that originates from both ventricles of the heart that later divides into the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. Structure The truncus arteriosus and bulbus cordis are divided by the aorticopulmonary septum. The truncus arteriosus gives rise to the ascending aorta and the pulmonary trunk. The caudal end of the bulbus cordis gives rise to the smooth parts (outflow tract) of the left and right ventricles (aortic vestibule & conus arteriosus respectively). The cranial end of the bulbus cordis (also known as the conus cordis) gives rise to the aorta and pulmonary trunk with the truncus arteriosus. This makes its appearance in three portions. # Two distal ridge-like thickenings project into the lumen of the tube: the truncal and bulbar ridges. These increase in size, and ultimately meet and fuse to form a septum ( aorticopulmonary septum), which takes a spiral course toward the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splanchnic Mesoderm
The lateral plate mesoderm is the mesoderm that is found at the periphery of the embryo. It is to the side of the paraxial mesoderm, and further to the axial mesoderm. The lateral plate mesoderm is separated from the paraxial mesoderm by a narrow region of intermediate mesoderm. The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers, between the outer ectoderm and inner endoderm. During the third week of embryonic development the lateral plate mesoderm splits into two layers forming the intraembryonic coelom. The outer layer of lateral plate mesoderm adheres to the ectoderm to become the somatic or parietal layer known as the somatopleure. The inner layer adheres to the endoderm to become the splanchnic or visceral layer known as the splanchnopleure. Development The lateral plate mesoderm will split into two layers, the somatopleuric mesenchyme, and the splanchnopleuric mesenchyme. * The ''somatopleuric layer'' forms the future body wall. * The ''splanchnopleuric layer'' form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocardial Tubes
The endocardial tubes are paired regions in the embryo that appear in its ventral pole by the middle of the third week of gestation and consist of precursor cells for the development of the embryonic heart. The endocardial heart tubes derive from the visceral mesoderm and initially are formed by a confluence of angioblastic blood vessels on either side of the embryonic midline. The endocardial tubes have an intimate proximity to the foregut or pharyngeal endoderm. As folding of the embryo in the horizontal plane initiates in the 4th week of gestation, the endocardial tubes meet in the midline to form the primitive heart tube, which will eventually develop into the histologically definitive endocardium. The myocardium forms from mesoderm cells surrounding the heart tube, while the epicardium develops from other cells, most likely from neural crest Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to vertebrates that arise from the embryonic ectoderm germ layer, and in turn g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |