|
Trusses
A truss is an assembly of ''members'' such as beams, connected by ''nodes'', that creates a rigid structure. In engineering, a truss is a structure that "consists of two-force members only, where the members are organized so that the assemblage as a whole behaves as a single object". A ''two-force member'' is a structural component where force is applied to only two points. Although this rigorous definition allows the members to have any shape connected in any stable configuration, architectural trusses typically comprise five or more triangular units constructed with straight members whose ends are connected at joints referred to as '' nodes''. In this typical context, external forces and reactions to those forces are considered to act only at the nodes and result in forces in the members that are either tensile or compressive. For straight members, moments (torques) are explicitly excluded because, and only because, all the joints in a truss are treated as revolutes, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truss Bridge
A truss bridge is a bridge whose load-bearing superstructure is composed of a truss, a structure of connected elements, usually forming triangular units. The connected elements, typically straight, may be stressed from tension, compression, or sometimes both in response to dynamic loads. There are several types of truss bridges, including some with simple designs that were among the first bridges designed in the 19th and early 20th centuries. A truss bridge is economical to construct primarily because it uses materials efficiently. Design The nature of a truss allows the analysis of its structure using a few assumptions and the application of Newton's laws of motion according to the branch of physics known as statics. For purposes of analysis, trusses are assumed to be pin-jointed where the straight components meet, meaning that taken alone, every joint on the structure is functionally considered to be a flexible joint as opposed to a rigid joint with the strength to mainta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Framing (construction)
Framing, in construction, is the fitting together of pieces to give a structure, particularly a building, support and shape. Framing materials are usually wood, engineered wood, or structural steel. The alternative to framed construction is generally called ''mass wall'' construction, where horizontal layers of stacked materials such as log building, masonry, rammed earth, adobe, etc. are used without framing. Building framing is divided into two broad categories, heavy-frame construction (heavy framing) if the vertical supports are few and heavy such as in timber framing, pole building framing, or steel framing; or light-frame construction (light-framing) if the supports are more numerous and smaller, such as balloon, platform, light-steel framing and pre-built framing. Light-frame construction using standardized dimensional lumber has become the dominant construction method in North America and Australia due to the economy of the method; use of minimal structural m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
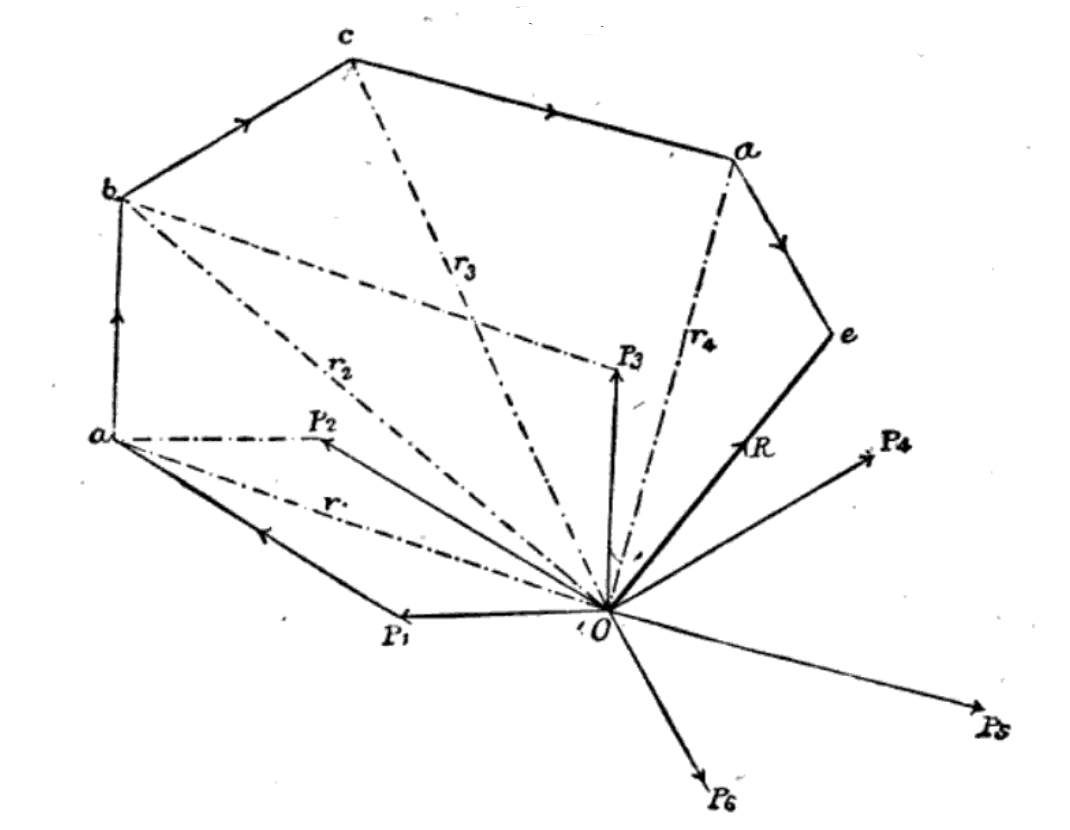
Graphic Statics
In a broad sense, the term graphic statics is used to describe the technique of solving particular practical problems of statics using graphical means. Actively used in the architecture of the 19th century, the methods of graphic statics were largely abandoned in the second half of the 20th century, primarily due to widespread use of frame structures of steel and reinforced concrete that facilitated analysis based on linear algebra. The beginning of the 21st century was marked by a "renaissance" of the technique driven by its addition to the computer-aided design tools thus enabling engineers to instantly visualize form and forces. History Markou and Ruan trace the origins of the graphic statics to da Vinci and Galileo who used the graphical means to calculate the sum of forces, Simon Stevin's parallelogram of forces and the 1725 introduction of the force polygon and funicular polygon by Pierre Varignon. Giovanni Poleni used the graphical calculations (and Robert Hooke's anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wells Egyptian Ship Red Sea
Wells most commonly refers to: * Wells, Somerset, a cathedral city in Somerset, England * Well, an excavation or structure created in the ground * Wells (name) Wells may also refer to: Places Canada * Wells, British Columbia England * Wells (Priory Road) railway station was a railway station in Wells, Somerset * Wells (Tucker Street) railway station was a railway station in Wells, Somerset * Wells (UK Parliament constituency), the UK parliamentary constituency in which the city of Wells, Somerset, is located * Wells-next-the-Sea, town and port in Norfolk ** Wells-on-Sea railway station was a railway station in Wells-next-the-Sea Scotland * Wells, Roxburghshire, a Scottish barony United States *Wells, California, former name of Keene, California * Wells Peak * Wells, Indiana * Wells, Kansas * Wells, Maine * Wells, Minnesota * Wells, Mississippi * Wells, Nevada * Wells, New York, a town ** Wells (CDP), New York, a census-designated place in the town * Wells, Texas * We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electricity Pylon
A transmission tower (also electricity pylon, hydro tower, or pylon) is a tall structure, usually a lattice tower made of steel that is used to support an overhead power line. In electrical grids, transmission towers carry high voltage, high-voltage transmission lines that transport bulk electric power from generating stations to electrical substations, from which electricity is delivered to end consumers; moreover, utility poles are used to support low voltage, lower-voltage electric power transmission, sub-transmission and distribution lines that transport electricity from substation, substations to electricity customers. There are four categories of transmission towers: (i) the suspension tower, (ii) the Dead-end tower#Termination pylon, dead-end terminal tower, (iii) the Dead-end tower, tension tower, and (iv) the transposition tower. The heights of transmission towers typically range from , although when longer spans are needed, such as for crossing water, taller towers are s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular Face (geometry), faces, six straight Edge (geometry), edges, and four vertex (geometry), vertices. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polytope, convex polyhedra. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean geometry, Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid (geometry), pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron, the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such net (polyhedron), nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Span (engineering)
In engineering, span is the distance between two adjacent structural supports (e.g., two piers) of a structural member (e.g., a beam). Span is measured in the horizontal direction either between the faces of the supports (clear span) or between the centers of the bearing surfaces (effective span): A span can be closed by a solid beam or by a rope. The first kind is used for bridges, the second one for power lines, overhead telecommunication lines, some type of antennas or for aerial tramway An aerial tramway, aerial tram, sky tram, cable car or aerial cablecar, aerial cableway, ropeway, téléphérique (French), or Seilbahn (German) is a type of aerial lift which uses one or two stationary cables for support, with a third movin ...s. Span is a significant factor in finding the strength and size of a beam as it determines the maximum bending moment and deflection. The maximum bending moment M_ and deflection \delta_in the pictured beam is found using: :M_ = \fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girder
A girder () is a Beam (structure), beam used in construction. It is the main horizontal support of a structure which supports smaller beams. Girders often have an I-beam cross section composed of two load-bearing ''flanges'' separated by a stabilizing ''web'', but may also have a box girder, box shape, Z shape, or other forms. Girders are commonly used to build bridges. A girt is a vertically aligned girder placed to resist shear loads. Small steel girders are Rolling (metalworking), rolled into shape. Larger girders (1 m/3 feet deep or more) are made as plate girders, welded or bolted together from separate pieces of steel plate. The Warren truss, Warren type girder replaces the solid web with an open latticework truss between the flanges. This arrangement combines strength with economy of materials, minimizing weight and thereby reducing loads and expense. Patented in 1848 by its designers James Warren (engineer), James Warren and Willoughby Theobald Monzani, its st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane (mathematics)
In mathematics, a plane is a two-dimensional space or flat surface that extends indefinitely. A plane is the two-dimensional analogue of a point (zero dimensions), a line (one dimension) and three-dimensional space. When working exclusively in two-dimensional Euclidean space, the definite article is used, so ''the'' Euclidean plane refers to the whole space. Several notions of a plane may be defined. The Euclidean plane follows Euclidean geometry Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to ancient Greek mathematics, Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry, ''Euclid's Elements, Elements''. Euclid's approach consists in assuming a small set ..., and in particular the parallel postulate. A projective plane may be constructed by adding "points at infinity" where two otherwise parallel lines would intersect, so that every pair of lines intersects in exactly one point. The elliptic plane may be further defined by adding a metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roof Truss 2
A roof (: roofs or rooves) is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of temperature, and wind. A roof is part of the building envelope. The characteristics of a roof are dependent upon the purpose of the building that it covers, the available roofing materials and the local traditions of construction and wider concepts of architectural design and practice, and may also be governed by local or national legislation. In most countries, a roof protects primarily against rain. A verandah may be roofed with material that protects against sunlight but admits the other elements. The roof of a garden conservatory protects plants from cold, wind, and rain, but admits light. A roof may also provide additional living space, for example, a roof garden. Etymology Old English 'roof, ceiling, top, summit; heaven, sky', also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |