|
Triangle Trade
Triangular trade or triangle trade is trade between three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. It has been used to offset trade imbalances between different regions. The most commonly cited example of a triangular trade is the Atlantic slave trade, but other examples existed. These include the seventeenth-century carriage of manufactured goods from England to History of New England, New England and History of Newfoundland and Labrador, Newfoundland, then dried cod from Newfoundland and New England to the Mediterranean and Iberian peninsula, followed by cargoes of gold, silver, olive oil, tobacco, dried fruit, and "sacks" of wine back to England. Maritime carriers referred to this Atlantic trade as the "sack trade." Another example was general cargo from Britain to Australia, Australian coal to China, then tea and silk back to Britain. The Atlantic slave trade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Trade2
A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called Vertex (geometry), ''vertices'', are zero-dimensional point (geometry), points while the sides connecting them, also called Edge (geometry), ''edges'', are one-dimensional line segments. A triangle has three internal angles, each one bounded by a pair of adjacent edges; the sum of angles of a triangle always equals a straight angle (180 degrees or π radians). The triangle is a plane figure and its interior is a planar region. Sometimes an arbitrary edge is chosen to be the base (geometry), ''base'', in which case the opposite vertex is called the apex (geometry), ''apex''; the shortest segment between the base and apex is the height (triangle), ''height''. The area of a triangle equals one-half the product of height and base length. In Euclidean geometry, any two points determine a unique line segment situated within a unique straight line, and any three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population, seventh-largest by population, with over 212 million people. The country is a federation composed of 26 Federative units of Brazil, states and a Federal District (Brazil), Federal District, which hosts the capital, Brasília. List of cities in Brazil by population, Its most populous city is São Paulo, followed by Rio de Janeiro. Brazil has the most Portuguese-speaking countries, Portuguese speakers in the world and is the only country in the Americas where Portuguese language, Portuguese is an Portuguese-speaking world, official language. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a Coastline of Brazil, coastline of . Covering roughly half of South America's land area, it Borders of Brazil, borders all other countries and ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atlantic Ocean, about west of Lisbon, about northwest of Morocco, about southeast of Newfoundland, Canada, and the same distance southwest of Cork, Ireland. Its main industries are agriculture, dairy farming, livestock, fishing, and tourism, which has become a major service activity in the region. In the 20th century and to some extent into the 21st, they have served as a waypoint for refueling aircraft flying between Europe and North America. The government of the Azores employs a large percentage of the population directly or indirectly in the service and tertiary sectors. The largest city of the Azores is Ponta Delgada. The culture, dialect, cuisine, and traditions of the Azorean islands vary considerably, because these remote island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the continent being 100 kilometres (62 miles) away. The islands have a population of 2.25 million people and are the most populous overseas Special member state territories and the European Union, special territory of the European Union. The seven main islands are from largest to smallest in area, Tenerife, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Lanzarote, La Palma, La Gomera, and El Hierro. The only other populated island is Graciosa, Canary Islands, La Graciosa, which administratively is dependent on Lanzarote. The archipelago includes many smaller islands and islets, including Alegranza, Islote de Lobos, Isla de Lobos, Montaña Clara, Roque del Oeste, and Roque del Este. It includes a number of rocks, including Roque de Garachico, Garachico and Roques de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volta Do Mar
, , or (the phrase in Portuguese means literally 'turn of the sea' but also 'return from the sea') is a navigational technique perfected by Portuguese navigators during the Age of Discovery in the late fifteenth century, using the dependable phenomenon of the great permanent wind circle, the North Atlantic Gyre. This was a major step in the history of navigation, when an understanding of winds in the age of sail was crucial to success: the European sea empires would not have been established without an understanding of the trade winds. History Portuguese discovery in the Atlantic Ocean The was a sailing technique discovered in successfully returning from the Atlantic islands, where the pilot first had to sail far to the west in order to catch usable following winds, and return to Europe. This was a counter-intuitive sailing direction, as it required the pilot to steer in a direction that was perpendicular to the ports of Portugal. Lack of this information may have d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyages Of Christopher Columbus
Between 1492 and 1504, the Italian explorer and navigator Christopher Columbus led four transatlantic maritime expeditions in the name of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain to the Caribbean and to Central and South America. These voyages led to the widespread knowledge of the New World. This breakthrough inaugurated the period known as the Age of Exploration, which saw the colonization of the Americas, a related biological exchange, and trans-Atlantic trade. These events, the effects and consequences of which persist to the present, are often cited as the beginning of the modern era. Born in the Republic of Genoa, Columbus was a navigator who sailed in search of a westward route to India, China, Japan and the Spice Islands thought to be the East Asian source of spices and other precious oriental goods obtainable only through arduous overland routes. Columbus was partly inspired by 13th-century Italian explorer Marco Polo in his ambition to explore Asia. His initial belief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes (about 30 degrees) and trend towards the poles and steer extratropical cyclones in this general manner. Tropical cyclones which cross the subtropical ridge axis into the westerlies recurve due to the increased westerly flow. The winds are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere. The westerlies are strongest in the winter hemisphere and times when the pressure is lower over the poles, while they are weakest in the summer hemisphere and when pressures are higher over the poles. The westerlies are particularly strong, especially in the Southern Hemisphere (called also 'Brave West winds' at striking Chile, Argentina, Tasmania and New Zealand), in areas where land is absent, bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
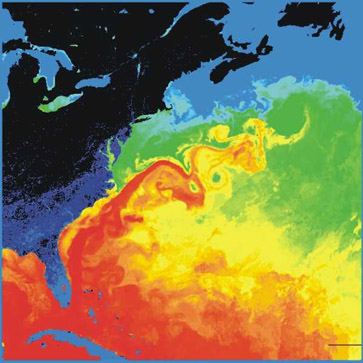
Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude (North Carolina) and moves toward Northwest Europe as the North Atlantic Current. The process of western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northward-accelerating current off the east coast of North America. Around , it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa. The Gulf Stream influences the climate of the coastal areas of the East Coast of the United States from Florida to southeast Virginia (near 36°N latitude), and to a greater degree, the climate of Northwest Europe. A consensus exists that the climate of Northwest Europe is warmer than other areas of similar latitude at least partially because of the stron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern America
Northern America is the northernmost subregion of North America, as well as the northernmost region in the Americas. The boundaries may be drawn significantly differently depending on the source of the definition. In one definition, it lies directly north of Middle America.Gonzalez, Joseph. 2004"Northern America: Land of Opportunity"(ch. 6). ''The Complete Idiot's Guide to Geography.'' () New York: Alpha Books; pp. 57–8 Northern America's land frontier with the rest of North America then coincides with the Mexico–United States border. Geopolitically, according to the United Nations' scheme of geographical regions and subregions, Northern America consists of Bermuda, Canada, Greenland, Saint Pierre and Miquelon and the United States (the contiguous United States and Alaska only, excluding Hawaii, Navassa Island, Puerto Rico, the United States Virgin Islands, and other minor U.S. Pacific territories). Definitions Maps using the term ''Northern America'' date back to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Winds
The trade winds or easterlies are permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere, strengthening during the winter and when the Arctic oscillation is in its warm phase. Trade winds have been used by captains of sailing ships to cross the world's oceans for centuries. They enabled European colonization of the Americas, and trade routes to become established across the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. In meteorology, they act as the steering flow for tropical storms that form over the Atlantic, Pacific, and southern Indian oceans and cause rainfall in North America, Southeast Asia, and Madagascar and East Africa. Shallow cumulus clouds are seen within trade wind regimes and are capped from becoming taller by a trade wind inversion, which is caused by descending air aloft from within the subtropical ridge. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
30th Parallel North
Following are circles of latitude between the 25th parallel north and the 30th parallel north: 26th parallel north The 26th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 26 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, Asia, the Indian Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean. A section of the border between Western Sahara and Mauritania is defined by the parallel. It is the most populous parallel on Earth, being home to between 247.2 million and 248.0 million people as of 2019. At this latitude the sun is visible for 13 hours, 46 minutes during the summer solstice and 10 hours, 31 minutes during the winter solstice. The sun is at 40.17 degrees in the sky during the winter solstice and 87.83 degrees in the sky during the summer solstice. Around the world Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the parallel 26° north passes through: : 27th parallel north The 27th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winds In The Age Of Sail
The captain of a steam ship naturally chooses the shortest route to nearby destinations. Since a sailing ship is usually pushed by winds and currents, its captain must find a route where the wind will probably blow in the right direction. Tacking, i.e. using contrary wind to pull (sic) the sails, was always possible but wasted time because of the zigzagging required, and significantly delayed long voyages. The early European explorers were not only looking for new lands. They also had to discover the pattern of winds and currents that would carry them where they wanted to go. During the Age of Sail, winds and currents determined trade routes and therefore influenced European imperialism and modern political geography. For an outline to the main wind systems see Global wind patterns. Pilotage or cabotage, in one sense, is the art of sailing along the coast using known landmarks. Navigation, in one sense, is the art of sailing long distances out of sight of land. Although the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |