|
Traveling Plane Wave
In mathematics and physics, a traveling plane wave is a special case of plane wave, namely a field (physics), field whose evolution in time can be described as simple translation of its values at a constant wave speed c, along a fixed direction of propagation \vec n. Such a field can be written as :F(\vec x, t)=G\left(\vec x \cdot \vec n - c t\right)\, where G(u) is a function of a single real parameter u = d - c t. The function G describes the profile of the wave, namely the value of the field at time t = 0, for each displacement d = \vec x \cdot \vec n. For each displacement d, the moving plane perpendicular to \vec n at distance d + c t from the origin is called a wavefront. This plane too travels along the direction of propagation \vec n with velocity c; and the value of the field is then the same, and constant in time, at every one of its points. The wave F may be a scalar field, scalar or vector field; its values are the values of G. A sinusoidal plane wave is a special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane Wave
In physics, a plane wave is a special case of wave or field: a physical quantity whose value, at any moment, is constant through any plane that is perpendicular to a fixed direction in space. For any position \vec x in space and any time t, the value of such a field can be written as :F(\vec x,t) = G(\vec x \cdot \vec n, t), where \vec n is a unit-length vector, and G(d,t) is a function that gives the field's value as dependent on only two real parameters: the time t, and the scalar-valued displacement d = \vec x \cdot \vec n of the point \vec x along the direction \vec n. The displacement is constant over each plane perpendicular to \vec n. The values of the field F may be scalars, vectors, or any other physical or mathematical quantity. They can be complex numbers, as in a complex exponential plane wave. When the values of F are vectors, the wave is said to be a longitudinal wave if the vectors are always collinear with the vector \vec n, and a transverse wave if they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field (physics)
In physics, a field is a physical quantity, represented by a scalar (mathematics), scalar, vector (mathematics and physics), vector, or tensor, that has a value for each Point (geometry), point in Spacetime, space and time. For example, on a weather map, the surface temperature is described by assigning a real number, number to each point on the map; the temperature can be considered at a certain point in time or over some interval of time, to study the dynamics of temperature change. A surface wind map, assigning an vector (mathematics and physics), arrow to each point on a map that describes the wind velocity, speed and direction at that point, is an example of a vector field, i.e. a 1-dimensional (rank-1) tensor field. Field theories, mathematical descriptions of how field values change in space and time, are ubiquitous in physics. For instance, the electric field is another rank-1 tensor field, while electrodynamics can be formulated in terms of Mathematical descriptions of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane Wave Wavefronts 3D
Plane(s) most often refers to: * Aero- or airplane, a powered, fixed-wing aircraft * Plane (geometry), a flat, 2-dimensional surface Plane or planes may also refer to: Biology * Plane (tree) or ''Platanus'', wetland native plant * ''Planes'' (genus), marsh crabs in Grapsidae * '' Bindahara phocides'', the plane butterfly of Asia Maritime transport * Planing (boat), where weight is predominantly supported by hydrodynamic lift * ''Plane'' (wherry), a Norfolk canal boat, in use 1931–1949 Music *"Planes", a 1976 song by Colin Blunstone *"Planes (Experimental Aircraft)", a 1989 song by Jefferson Airplane from ''Jefferson Airplane'' *" Planez", originally "Planes", a 2015 song by Jeremih *"The Plane", a 1987 song on the '' Empire of the Sun'' soundtrack *"The Plane", a 1997 song by Kinito Méndez Other entertainment * Plane (''Dungeons & Dragons''), any fictional realm of the D&D roleplaying game's multiverse * ''Planes'' (film), a 2013 animation **'' Planes: Fire & Resc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
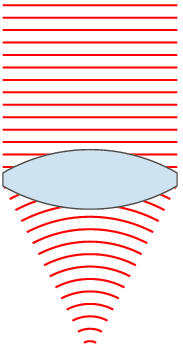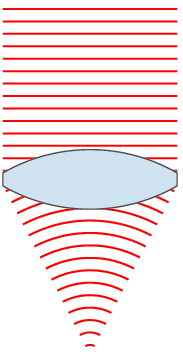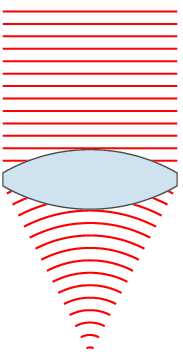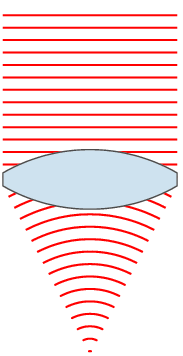
Wavefront
In physics, the wavefront of a time-varying ''wave field'' is the set (locus) of all points having the same ''phase''. The term is generally meaningful only for fields that, at each point, vary sinusoidally in time with a single temporal frequency (otherwise the phase is not well defined). Wavefronts usually move with time. For waves propagating in a unidimensional medium, the wavefronts are usually single points; they are curves in a two dimensional medium, and surfaces in a three-dimensional one. For a sinusoidal plane wave, the wavefronts are planes perpendicular to the direction of propagation, that move in that direction together with the wave. For a sinusoidal spherical wave, the wavefronts are spherical surfaces that expand with it. If the speed of propagation is different at different points of a wavefront, the shape and/or orientation of the wavefronts may change by refraction. In particular, lenses can change the shape of optical wavefronts from planar to spher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalar Field
In mathematics and physics, a scalar field is a function (mathematics), function associating a single number to every point (geometry), point in a space (mathematics), space – possibly physical space. The scalar may either be a pure Scalar (mathematics), mathematical number (dimensionless) or a scalar (physics), scalar physical quantity (with unit of measurement, units). In a physical context, scalar fields are required to be independent of the choice of reference frame, meaning that any two observers using the same units will agree on the value of the scalar field at the same absolute point in space (or spacetime) regardless of their respective points of origin. Examples used in physics include the temperature distribution throughout space, the pressure distribution in a fluid, and spin-zero quantum fields, such as the Higgs field. These fields are the subject of scalar field theory. Definition Mathematically, a scalar field on a Region (mathematical analysis), region ''U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinusoidal Plane Wave
In physics, a sinusoidal (or monochromatic) plane wave is a special case of plane wave: a field whose value varies as a sinusoidal function of time and of the distance from some fixed plane. For any position \vec x in space and any time t, the value of such a field can be written as :F(\vec x, t)=A \cos\left(2\pi \nu (\vec x \cdot \vec n - c t) + \varphi\right)\, where \vec n is a unit-length vector, the direction of propagation of the wave, and "\cdot" denotes the dot product of two vectors. The parameter A, which may be a scalar or a vector, is called the amplitude of the wave; the coefficient \nu, a positive scalar, its spatial frequency; and the adimensional scalar \varphi, an angle in radians, is its initial phase or phase shift. The scalar quantity d = \vec x \cdot \vec n gives the (signed) displacement of the point \vec x from the plane that is perpendicular to \vec n and goes through the origin of the coordinate system. This quantity is constant over each plane perpendic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinusoidal
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in mathematics, as well as in physics, engineering, signal processing and many other fields. Formulation Its most basic form as a function of time (''t'') is: y(t) = A\sin(2 \pi f t + \varphi) = A\sin(\omega t + \varphi) where: * ''A'', ''amplitude'', the peak deviation of the function from zero. * ''f'', ''ordinary frequency'', the ''number'' of oscillations (cycles) that occur each second of time. * ''ω'' = 2''f'', ''angular frequency'', the rate of change of the function argument in units of radians per second. * \varphi, ''phase'', specifies (in radians) where in its cycle the oscillation is at ''t'' = 0. When \varphi is non-zero, the entire waveform appears to be shifted in time by the amount ''φ''/''ω'' seconds. A negative value rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Differential Equation
In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation which imposes relations between the various partial derivatives of a Multivariable calculus, multivariable function. The function is often thought of as an "unknown" to be solved for, similarly to how is thought of as an unknown number to be solved for in an algebraic equation like . However, it is usually impossible to write down explicit formulas for solutions of partial differential equations. There is, correspondingly, a vast amount of modern mathematical and scientific research on methods to Numerical methods for partial differential equations, numerically approximate solutions of certain partial differential equations using computers. Partial differential equations also occupy a large sector of pure mathematics, pure mathematical research, in which the usual questions are, broadly speaking, on the identification of general qualitative features of solutions of various partial differential equations, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Equation
The (two-way) wave equation is a second-order linear partial differential equation for the description of waves or standing wave fields — as they occur in classical physics — such as mechanical waves (e.g. water waves, sound waves and seismic waves) or electromagnetic waves (including light waves). It arises in fields like acoustics, electromagnetism, and fluid dynamics. Single mechanical or electromagnetic waves propagating in a pre-defined direction can also be described with the first-order one-way wave equation which is much easier to solve and also valid for inhomogenious media. Introduction The (two-way) wave equation is a second-order partial differential equation describing waves, including traveling and standing waves; the latter can be considered as linear superpositions of waves traveling in opposite directions. This article mostly focuses on the scalar wave equation describing waves in scalars by scalar functions of a time variable (a variable repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |