|
Transplant Experiments
A transplant experiment, or common garden experiment, is an experiment to test the effect of environment by moving two species from their native environments into a common environment. The name was originally applied to experiments on plants but is now equally applied to animals such as lizards and ants, and other organisms. A reciprocal transplant experiment involves introducing organisms from each of two environments into the other; the approach can be extended to more than two environments if required. Transplant experiments are often used to test if there is a genetic component to differences in populations. Advances in molecular biology have provided researchers with the ability to study genetic variation more directly. However, transplant experiments still have the advantages of being simple and requiring little technology. On the other hand, they may require considerable time and labour, and the number of test organisms is often relatively limited. Common garden methods c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphagnum Cultivation At Universität Greifswald 2023-06-11 01
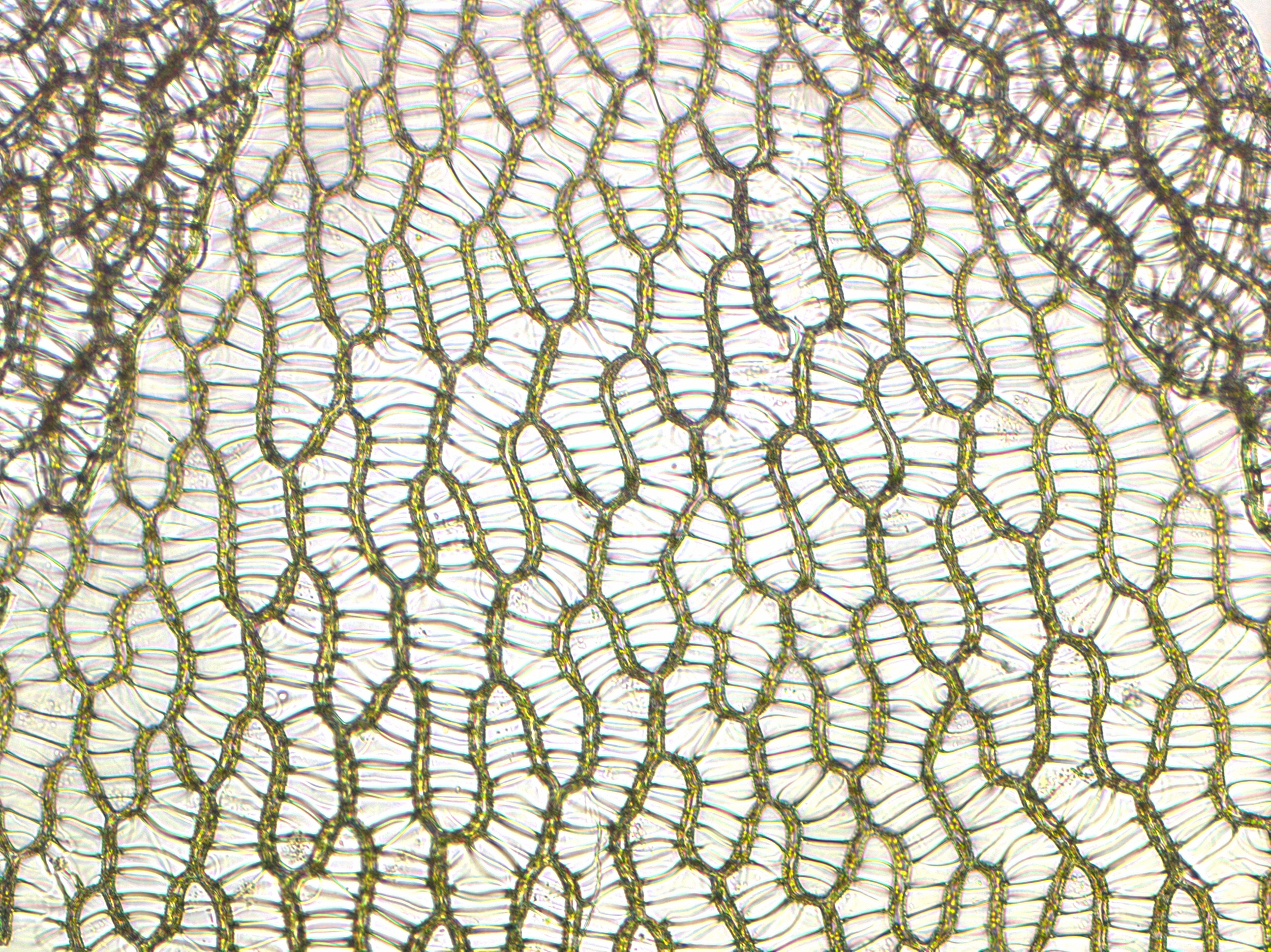
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225–229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As ''Sphagnum'' moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, ''Sphagnum'' can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing ''Sphagnum'' as 'habitat manipulators' or 'autogenic ecosystem engineers'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and ericaceous shrubs, as well as or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |