|
Transmembrane Domains
A transmembrane domain (TMD, TM domain) is a membrane-spanning protein domain. TMDs may consist of one or several alpha-helices or a transmembrane beta barrel. Because the interior of the lipid bilayer is hydrophobic, the amino acid residues in TMDs are often hydrophobic, although proteins such as membrane pumps and ion channels can contain polar residues. TMDs vary greatly in size and hydrophobicity; they may adopt organelle-specific properties. Functions of transmembrane domains Transmembrane domains are known to perform a variety of functions. These include: * Anchoring transmembrane proteins to the membrane. *Facilitating molecular transport of molecules such as ions and proteins across biological membranes; usually hydrophilic residues and binding sites in the TMDs help in this process. *Signal transduction across the membrane; many transmembrane proteins, such as G protein-coupled receptors, receive extracellular signals. TMDs then propagate those signals across the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's Peptide, polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that Protein folding, folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded Protein tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or Disulfide bond, disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF-hand, EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimera (protein), chimeric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophobicity Scales
Hydrophobicity scales are values that define the relative hydrophobicity or hydrophilicity of amino acid residues. The more positive the value, the more hydrophobic are the amino acids located in that region of the protein. These scales are commonly used to predict the Transmembrane domain, transmembrane alpha-helices of membrane proteins. When consecutively measuring amino acids of a protein, changes in value indicate attraction of specific protein regions towards the hydrophobic region inside lipid bilayer. The hydrophobic or hydrophilic character of a compound or amino acid is its hydropathic character, hydropathicity, or hydropathy. Hydrophobicity and the hydrophobic effect The hydrophobic effect represents the tendency of water#Properties, water to exclude non-polar molecules. The effect originates from the disruption of highly dynamic hydrogen bonds between molecules of liquid water. Polar chemical groups, such as OH group in methanol do not cause the hydrophobic effect. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SGTA
Small glutamine-rich tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SGTA'' gene. ''SGTA'' orthologs have also been identified in several mammals for which complete genome data are available. STGA belongs to a family of co-chaperone proteins that obtain a TPR motif. STGA was discovered just 15 years ago. Function The molecular function of the protein states that SGTA is a small glutamine-rich tetratricopeptide repeat (TRP)-containing protein, ubiquitously expressed, interacting with the NS1 protein of parvovirus H-1. The SGTA gene encodes a protein that is capable of interacting with the major nonstructural protein of parvovirus H-1 and 70-kDa heat shock cognate protein; however, its function is not known. Since this transcript is expressed ubiquitously in various tissues, this protein may serve a housekeeping function. Overview of main functions: * hormone signaling * viral assembly and release * cell cycle and apoptosis * int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Recognition Particle
The signal recognition particle (SRP) is an abundant, cytosolic, universally conserved ribonucleoprotein (protein-RNA complex) that recognizes and targets specific proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotes and the plasma membrane in prokaryotes. History The function of SRP was discovered by the study of processed and unprocessed secretory proteins, particularly immunoglobulin light chains; and bovine preprolactin. Newly synthesized proteins in eukaryotes carry N-terminal hydrophobic Signal peptide, signal sequences, which are bound by SRP when they emerge from the ribosome. Mechanism In eukaryotes, SRP binds to the Signal peptide, signal sequence of a newly synthesized peptide as it emerges from the ribosome. This binding leads to the slowing of protein synthesis known as "elongation arrest", a conserved function of SRP that facilitates the coupling of the protein Translation (genetics), translation and the protein translocation processes. SRP then targets this en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
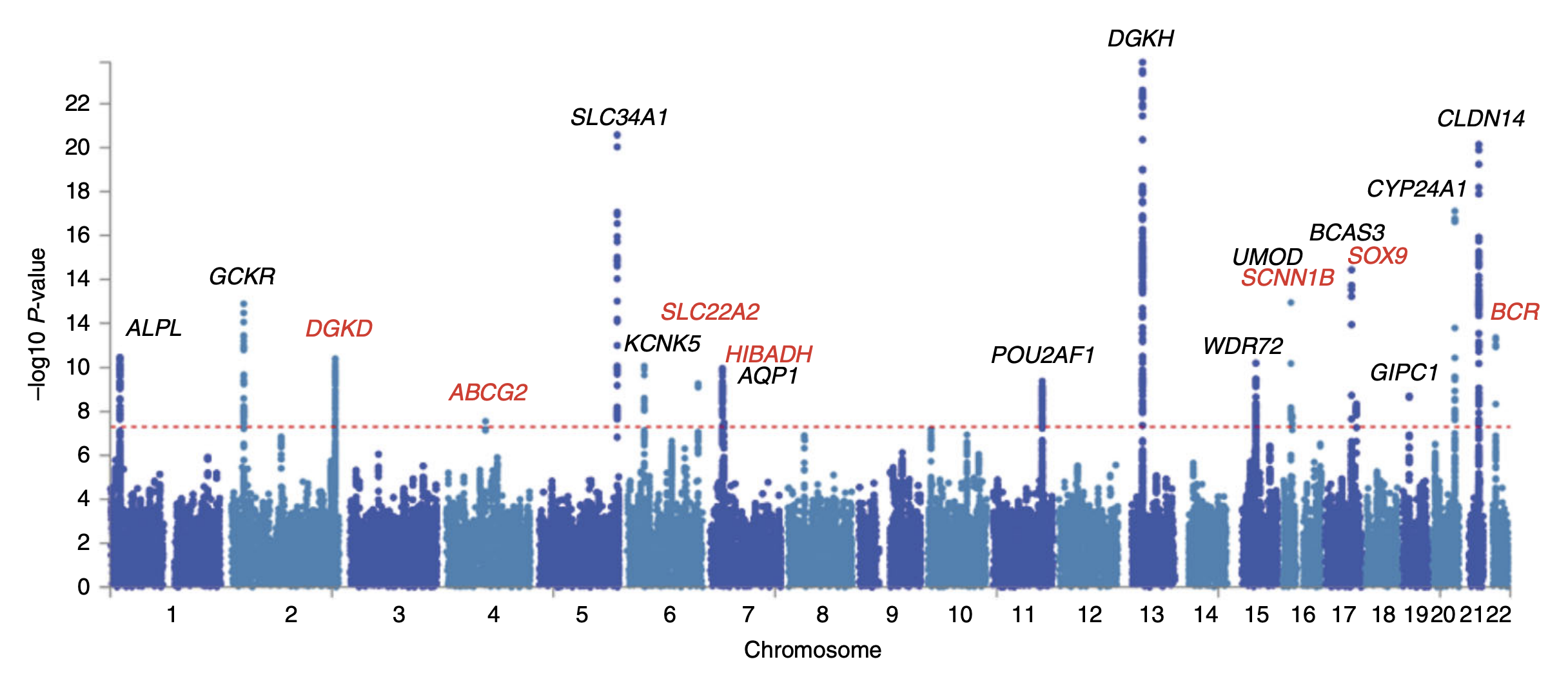
Genome-wide Association Study
In genomics, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), is an observational study of a genome-wide set of Single-nucleotide polymorphism, genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA studies typically focus on associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and traits like major human diseases, but can equally be applied to any other genetic variants and any other organisms. When applied to human data, GWA studies compare the DNA of participants having varying phenotypes for a particular trait or disease. These participants may be people with a disease (cases) and similar people without the disease (controls), or they may be people with different phenotypes for a particular trait, for example blood pressure. This approach is known as phenotype-first, in which the participants are classified first by their clinical manifestation(s), as opposed to Genotype-first approach, genotype-first. Each person gives a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
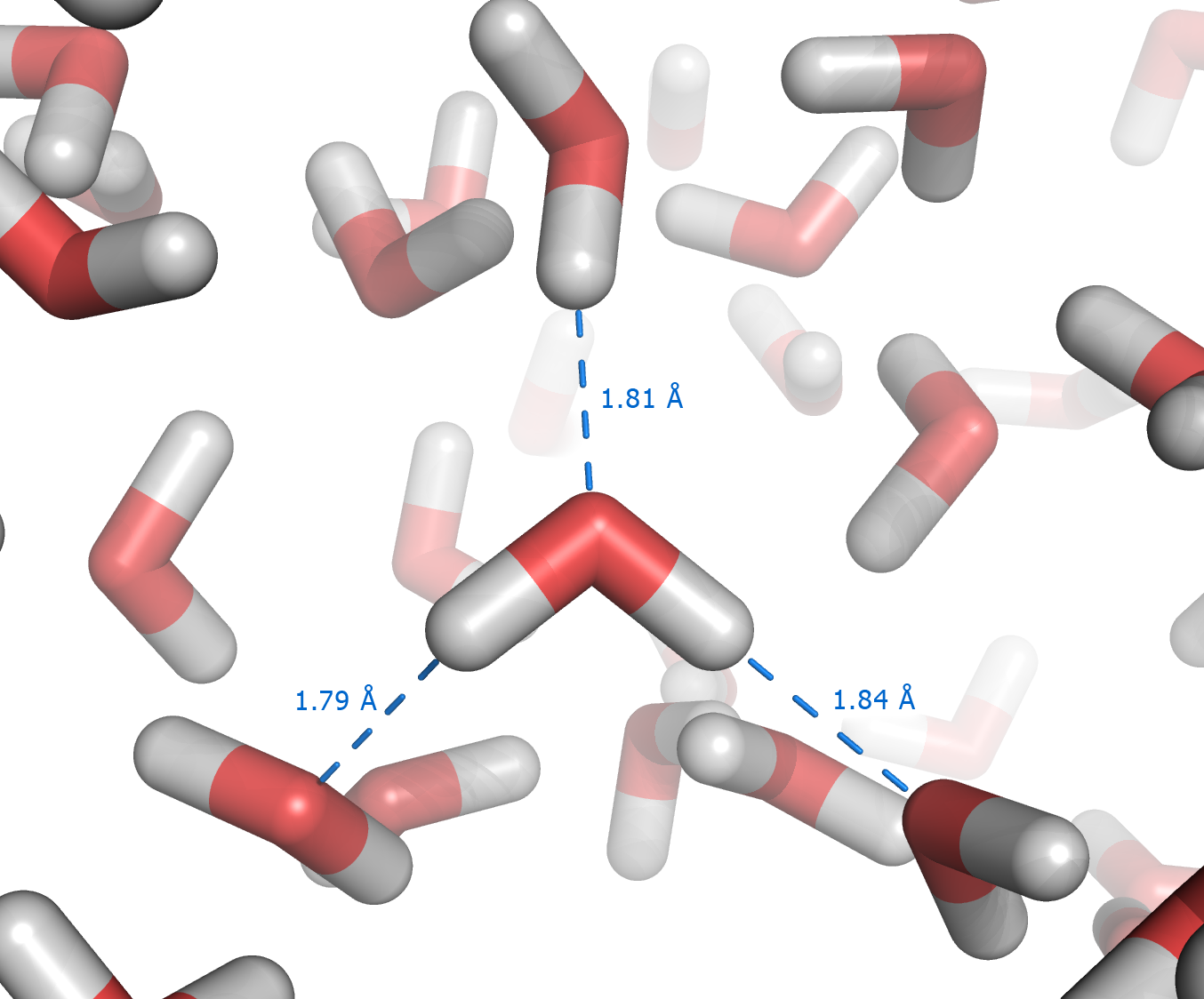
Aqueous Solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be represented as . The word ''aqueous'' (which comes from ''aqua'') means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in, water. As water is an excellent solvent and is also naturally abundant, it is a ubiquitous solvent in chemistry. Since water is frequently used as the solvent in experiments, the word solution refers to an aqueous solution, unless the solvent is specified. A ''non-aqueous solution'' is a solution in which the solvent is a liquid, but is not water. Characteristics Substances that are ''hydrophobic'' ('water-fearing') do not dissolve well in water, whereas those that are '' hydrophilic'' ('water-friendly') do. An example of a hydrophilic substance is sodium chloride. In an aqueous solution the hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments. In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is surrounded by the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. The cytosol is thus a liquid matrix around the organelles. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others take place within organelles. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (biology)
In biology, translation is the process in living Cell (biology), cells in which proteins are produced using RNA molecules as templates. The generated protein is a sequence of amino acids. This sequence is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in the RNA. The nucleotides are considered three at a time. Each such triple results in the addition of one specific amino acid to the protein being generated. The matching from nucleotide triple to amino acid is called the genetic code. The translation is performed by a large complex of functional RNA and proteins called ribosomes. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later protein folding, folds into an Activation energy, active protein and performs its functions in the cell. The polypeptide can also start folding during protein synthesis. The ribosome facilitates decoding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and Bioinformatics software, software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, data science, computer programming, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret biological data. The process of analyzing and interpreting data can sometimes be referred to as computational biology, however this distinction between the two terms is often disputed. To some, the term ''computational biology'' refers to building and using models of biological systems. Computational, statistical, and computer programming techniques have been used for In silico, computer simulation analyses of biological queries. They include reused specific analysis "pipelines", particularly in the field of genomics, such as by the identification of genes and single nucleotide polymorphis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Silico
In biology and other experimental sciences, an ''in silico'' experiment is one performed on a computer or via computer simulation software. The phrase is pseudo-Latin for 'in silicon' (correct ), referring to silicon in computer chips. It was coined in 1987 as an allusion to the Latin phrases , , and , which are commonly used in biology (especially systems biology). The latter phrases refer, respectively, to experiments done in living organisms, outside living organisms, and where they are found in nature. History The earliest known use of the phrase was by Christopher Langton to describe artificial life, in the announcement of a workshop on that subject at the Center for Nonlinear Studies at the Los Alamos National Laboratory in 1987. The expression ''in silico'' was first used to characterize biological experiments carried out entirely in a computer in 1989, in the workshop "Cellular Automata: Theory and Applications" in Los Alamos, New Mexico, by Pedro Miramontes, a mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Topology
Topology of a transmembrane protein refers to locations of N- and C-termini of membrane-spanning polypeptide chain with respect to the inner or outer sides of the biological membrane occupied by the protein. Several databases provide experimentally determined topologies of membrane proteins. They include Uniprot, TOPDB, OPM, and ExTopoDB. There is also a database of domains located conservatively on a certain side of membranes, TOPDOM. Several computational methods were developed, with a limited success, for predicting transmembrane alpha-helices and their topology. Pioneer methods utilized the fact that membrane-spanning regions contain more hydrophobic residues than other parts of the protein, however applying different hydrophobic scales altered the prediction results. Later, several statistical methods were developed to improve the topography prediction and a special alignment method was introduced. According to the positive-inside rule, cytosolic loops near the lipid bilayer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophilicity Plot
A hydrophilicity plot is a quantitative analysis of the degree of hydrophobicity or hydrophilicity of amino acids of a protein. It is used to characterize or identify possible structure or domains of a protein. The plot has amino acid sequence of a protein on its x-axis, and degree of hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity on its y-axis. There are a number of methods to measure the degree of interaction of polar solvents such as water with specific amino acids. For instance, the Kyte-Doolittle scale indicates hydrophobic amino acids, whereas the Hopp-Woods scale measures hydrophilic residues. Analyzing the shape of the plot gives information about partial structure of the protein. For instance, if a stretch of about 20 amino acids shows positive for hydrophobicity, these amino acids may be part of alpha-helix spanning across a lipid bilayer The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes form a contin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |