|
Towboat
A pusher, pusher craft, pusher boat, pusher tug, or towboat, is a boat designed for pushing barges or car floats. In the United States, the industries that use these vessels refer to them as towboats. These vessels are characterized by a square bow, a shallow draft, and typically have knees, which are large plates mounted to the bow for pushing barges of various heights. These boats usually operate on rivers and inland waterways. Multiple barges lashed together, or a boat and any barges lashed to it, are referred to as a "tow" and can have dozens of barges. Many of these vessels, especially the long distances, or long haul boats, include living quarters for the crew. Size Towboat engine outputs range from less than up to . Most towboats are from long, and wide. Smaller boats are used in harbors, fleeting areas and around locks while larger boats operate in "line-haul" operations over long distances and between major ports. In the United States, south of the Chain of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barge
Barge nowadays generally refers to a flat-bottomed inland waterway vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but nowadays most are pushed by pusher boats, or other vessels. The term barge has a rich history, and therefore there are many other types of barges. History of the barge Etymology "Barge" is attested from 1300, from Old French ''barge'', from Vulgar Latin ''barga''. The word originally could refer to any small boat; the modern meaning arose around 1480. ''Bark'' "small ship" is attested from 1420, from Old French ''barque'', from Vulgar Latin ''barca'' (400 AD). The more precise meaning of Barque as "three-masted sailing vessel" arose in the 17th century, and often takes the French spelling for disambiguation. Both are probably derived from the Latin ''barica'', from Greek ''baris'' "Egyptian boat", from Coptic ''bari'' "small boat", hieroglyphic Egyptian D58-G29-M17-M17-D21-P1 and similar ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
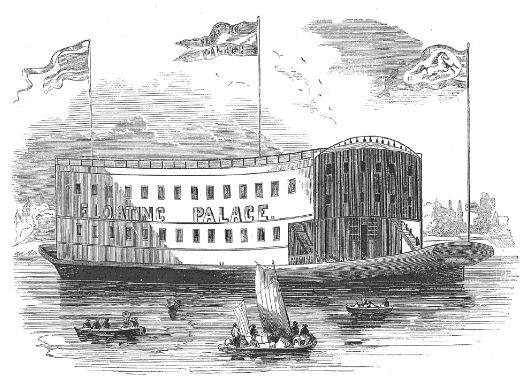
Showboat Majestic
''The Majestic'' is a historic riverboat that is moored on the Ohio River at Manchester, Ohio. Built in 1923, she was the last floating theater to be built in the United States, and one of its longest-lived. Declared a National Historic Landmark on December 20, 1989. Description ''Majestic'' is moored on the Ohio River at New Richmond, Ohio. She is long, with a beam of and a draft depth of . Her wooden hull has been sheathed inside a steel one, and is still visible from within the boat. Its superstructure housing the theater has been little altered since 1969. History The last of the original traveling showboats, ''Majestic'' was built in 1923 in Pittsburgh, and plied the Ohio River and other portions of its watershed for many years, offering shows at towns along the way. The showboat was not necessarily a "ship" at all. It has no motor and no means of movement. Therefore, she came as a pair with a tugboat the ''Attaboy'' which towed her from venue to venue. Tom Reynolds and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Car Float
A railroad car float or rail barge is a specialised form of lighter with railway tracks mounted on its deck used to move rolling stock across water obstacles, or to locations they could not otherwise go. An unpowered barge, it is towed by a tugboat or pushed by a towboat. This is distinguished from a train ferry, which is self-powered. Historical operations U.S. East Coast During the American Civil War, Civil War, Union general Herman Haupt, a civil engineer, used huge barges fitted with tracks to enable military trains to cross the Rappahannock River in support of the Army of the Potomac. Beginning in the 1830s, the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) operated Capital Subdivision#Alexandria Division, a car float across the Potomac River, just south of Washington, D.C., between Shepherds Landing on the east shore, and Alexandria, Virginia on the west. The ferry operation ended in 1906. The B&O operated a car float across the Baltimore Inner Harbor until the mid-1890 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Showboat
A showboat, or show boat, was a floating theater that traveled along the waterways of the United States, especially along the Mississippi and Ohio rivers, to bring culture and entertainment to the inhabitants of river frontiers. Showboats were a special type of riverboat designed to carry passengers rather than cargo, and they had to be pushed by a small (and misleadingly labeled) towboat, also known as a pusher, which was attached to it. Showboats were rarely steam-powered because the steam engine had to be placed right in the auditorium for logistical reasons, therefore making it difficult to have a large theater. History During the American frontier era, populations of potential audiences were widely scattered about the area that is now the United States. Actors traveled to America from England, and theatre venues as well as touring companies were developed. Noah Ludlow, an early pioneer in travelling theater, purchased a keelboat in 1816 for $200 and named it ''Noah's Ark''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tugboat
A tugboat or tug is a marine vessel that manoeuvres other vessels by pushing or pulling them, with direct contact or a tow line. These boats typically tug ships in circumstances where they cannot or should not move under their own power, such as in crowded harbour or narrow canals, or cannot move at all, such as barges, disabled ships, log rafts, or oil platforms. Some are ocean-going, some are icebreakers or salvage tugs. Early models were powered by steam engines, long ago superseded by diesel engines. Many have deluge gun water jets, which help in firefighting, especially in harbours. Types Seagoing Seagoing tugs (deep-sea tugs or ocean tugboats) fall into four basic categories: #The standard seagoing tug with model bow that tows almost exclusively by way of a wire cable. In some rare cases, such as some USN fleet tugs, a synthetic rope hawser may be used for the tow in the belief that the line can be pulled aboard a disabled ship by the crew owing to its lightne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Waterways Operators
The American Waterways Operators, is the national trade association for the U.S. tugboat, towboat and barge industry. For more than 60 years AWO has promoted the contribution of the domestic waterways transportation industry to the U.S. economy. AWO acts as the principal advocate for the U.S. tugboat, towboat and barge industry in Washington, D.C. with key policymakers and federal officials. AWO maintains regional offices in Seattle, St. Louis, New Orleans, and Washington, D.C. These offices manage state legislative and regional regulatory issues and maintain an effective grassroots network for congressional advocacy. Organized in Washington, D.C. in 1944, AWO now has over 300 member companies that serve the diverse needs of U.S. shippers and consumers. AWO members operate throughout the United States on America's rivers, canals, in its ports and harbors, on the Great Lakes, and on the Atlantic, Pacific and Gulf coasts. AWO is governed by an elected body of 52 members who serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riverboat
A riverboat is a watercraft designed for inland navigation on lakes, rivers, and artificial waterways. They are generally equipped and outfitted as work boats in one of the carrying trades, for freight or people transport, including luxury units constructed for entertainment enterprises, such as lake or harbour tour boats. As larger water craft, virtually all riverboats are especially designed and constructed, or alternatively, constructed with special-purpose features that optimize them as riverine or lake service craft, for instance, dredgers, survey boats, fisheries management craft, fireboats and law enforcement patrol craft. Design differences Riverboats are usually less sturdy than ships built for the open seas, with limited navigational and rescue equipment, as they do not have to withstand the high winds or large waves characteristic to large lakes, seas or oceans. They can thus be built from light composite materials. They are limited in size by width and depth of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steamboat
A steamboat is a boat that is propelled primarily by steam power, typically driving propellers or paddlewheels. Steamboats sometimes use the prefix designation SS, S.S. or S/S (for 'Screw Steamer') or PS (for 'Paddle Steamer'); however, these designations are most often used for steamships. The term ''steamboat'' is used to refer to smaller, insular, steam-powered boats working on lakes and rivers, particularly riverboats. As using steam became more reliable, steam power became applied to larger, ocean-going vessels. Background Limitations of the Newcomen steam engine Early steamboat designs used Newcomen steam engines. These engines were large, heavy, and produced little power, which resulted in an unfavorable power-to-weight ratio. The Newcomen engine also produced a reciprocating or rocking motion because it was designed for pumping. The piston stroke was caused by a water jet in the steam-filled cylinder, which condensed the steam, creating a vacuum, which in turn caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Of Rocks Lock
Chain of Rocks Lock and Dam, also known as Locks No. 27, is a lock situated at the southern end of Chouteau Island near St. Louis, Missouri on the Upper Mississippi River. Its associated dam is just downstream of the Chain of Rocks Bridge, and the lock is located over southeast on the Chain of Rocks canal. The canal and locks allow river traffic to bypass a portion of the river that is unnavigable in low water due to an anticlinal exposure of bedrock in the river—a "chain of rocks". The canal, main lock, and auxiliary lock were built in the late 1940s and early 1950s to allow a by-pass of the Chain of Rocks lying in the main channel of the Mississippi River. This stretch of river in low water seasons was treacherous for commercial tow boats and barges, often requiring them to wait several days for the river to rise. The dam for lock 27 is atypical for the Mississippi, being a weir made of tons of rock laid in the Mississippi to create a small pool elevation upstream from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it flows generally south for to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian mountains. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is , of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the thirteenth-largest river by discharge in the world. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana. Native Americans have lived along the Mississippi River and its tributaries for thousands of years. Most were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Holland
South Holland ( nl, Zuid-Holland ) is a province of the Netherlands with a population of over 3.7 million as of October 2021 and a population density of about , making it the country's most populous province and one of the world's most densely populated areas. Situated on the North Sea in the west of the Netherlands, South Holland covers an area of , of which is water. It borders North Holland to the north, Utrecht and Gelderland to the east, and North Brabant and Zeeland to the south. The provincial capital is the Dutch seat of government The Hague, while its largest city is Rotterdam. The Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt delta drains through South Holland into the North Sea. Europe's busiest seaport, the Port of Rotterdam, is located in South Holland. History Early history Archaeological discoveries in Hardinxveld-Giessendam indicate that the area of South Holland has been inhabited since at least c. 7,500 years before present, probably by nomadic hunter-gatherers. Agriculture and per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)