|
Tip Speed Ratio
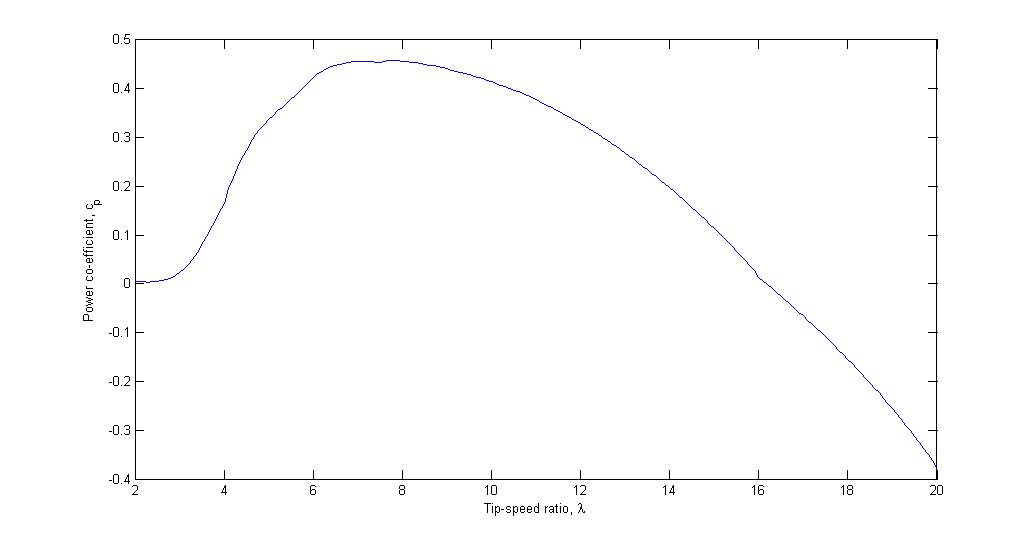
The tip-speed ratio, λ, or TSR for wind turbines is the ratio between the tangential speed of the tip of a blade and the actual speed of the wind, v. The tip-speed ratio is related to efficiency, with the optimum varying with blade design. Higher tip speeds result in higher noise levels and require stronger blades due to larger centrifugal forces. :: \lambda = \frac The tip speed of the blade can be calculated as \omega times R, where \omega is the rotational speed of the rotor in radians/second, and R is the rotor radius in metres. Therefore, we can also write: :: \lambda = \frac where v is the wind speed in metres/second at the height of the blade hub. Cp–λ curves The power coefficient, C_p is a quantity that expresses what fraction of the power in the wind is being extracted by the wind turbine. It is generally assumed to be a function of both tip-speed ratio and pitch angle. Below is a plot of the variation of the power coefficient with variations in the tip-speed ratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. Wind turbines are an increasingly important source of intermittent renewable energy, and are used in many countries to lower energy costs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. One study claimed that, wind had the "lowest relative greenhouse gas emissions, the least water consumption demands and the most favorable social impacts" compared to photovoltaic, hydro, geothermal, coal and gas energy sources. Smaller wind turbines are used for applications such as battery charging for auxiliary power for boats or caravans, and to power traffic warning signs. Larger turbines can contribute to a domestic power supply while selling unused power back to the utility supplier via the electrical grid. Wind turbines are manufactured in a wide ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed
In everyday use and in kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a scalar quantity. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance travelled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as the duration of the time interval approaches zero. Speed is not the same as velocity. Speed has the dimensions of distance divided by time. The SI unit of speed is the metre per second (m/s), but the most common unit of speed in everyday usage is the kilometre per hour (km/h) or, in the US and the UK, miles per hour (mph). For air and marine travel, the knot is commonly used. The fastest possible speed at which energy or information can travel, according to special relativity, is the speed of light in a vacuum ''c'' = metres per seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifugal Force
In Newtonian mechanics, the centrifugal force is an inertial force (also called a "fictitious" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It is directed away from an axis which is parallel to the axis of rotation and passing through the coordinate system's origin. If the axis of rotation passes through the coordinate system's origin, the centrifugal force is directed radially outwards from that axis. The magnitude of centrifugal force ''F'' on an object of mass ''m'' at the distance ''r'' from the origin of a frame of reference rotating with angular velocity is: F = m\omega^2 r The concept of centrifugal force can be applied in rotating devices, such as centrifuges, centrifugal pumps, centrifugal governors, and centrifugal clutches, and in centrifugal railways, planetary orbits and banked curves, when they are analyzed in a rotating coordinate system. Confusingly, the term has sometimes also been used for the rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Speed Wind Turbine
A variable speed wind turbine is one which is specifically designed to operate over a wide range of rotor speeds. It is in direct contrast to fixed speed wind turbine where the rotor speed is approximately constant. The reason to vary the rotor speed is to capture the maximum aerodynamic power in the wind, as the wind speed varies. The aerodynamic efficiency, or coefficient of power, C_p for a fixed blade pitch angle is obtained by operating the wind turbine at the optimal tip-speed ratio as shown in the following graph. Tip-speed ratio is given by the following expression, \lambda = \frac where \omega is the rotor speed (in radians per second), R is the radius of the rotor, and v is the wind speed. As the wind speed varies, the rotor speed must be varied to maintain peak efficiency. Background Before the need to connect wind turbines to the grid, turbines were fixed-speed. This was not a problem because turbines did not have to be synchronized with the frequency of the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternator
An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature.Gordon R. Selmon, ''Magnetoelectric Devices'', John Wiley and Sons, 1966 no ISBN pp. 391-393 Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. In principle, any AC electrical generator can be called an alternator, but usually the term refers to small rotating machines driven by automotive and other internal combustion engines. An alternator that uses a permanent magnet for its magnetic field is called a magneto. Alternators in power stations driven by steam turbines are called turbo-alternators. Large 50 or 60 Hz three-phase alternators in power plants generate most of the world's electric power, which is distributed by electric power grids. History Alternating current generat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Power Transmission
Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines that facilitate this movement form a ''transmission network''. This is distinct from the local wiring between high-voltage substations and customers, which is typically referred to as electric power distribution. The combined transmission and distribution network is part of electricity delivery, known as the electrical grid. Efficient long-distance transmission of electric power requires high voltages. This reduces the losses produced by strong currents. Transmission lines use either alternating current (HVAC) or direct current (HVDC). The voltage level is changed with transformers. The voltage is stepped up for transmission, then reduced for local distribution. A wide area synchronous grid, known as an "interconnection" in North America, directly connects generators delivering AC power with the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Turbines
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. Wind turbines are an increasingly important source of intermittent renewable energy, and are used in many countries to lower energy costs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. One study claimed that, wind had the "lowest relative greenhouse gas emissions, the least water consumption demands and the most favorable social impacts" compared to photovoltaic, hydro, geothermal, coal and gas energy sources. Smaller wind turbines are used for applications such as battery charging for auxiliary power for boats or caravans, and to power traffic warning signs. Larger turbines can contribute to a domestic power supply while selling unused power back to the utility supplier via the electrical grid. Wind turbines are manufactured in a wide range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



