|
Tint
In color theory, a tint is a mixture of a color with white, which increases lightness, while a shade is a mixture with black, which increases darkness. Both processes affect the resulting color mixture's relative saturation. A tone is produced either by mixing a color with gray, or by both tinting and shading. Mixing a color with any neutral color (including black, gray, and white) reduces the chroma, or colorfulness, while the hue (the relative mixture of red, green, blue, etc. depending on the colorspace) remains unchanged. In the graphic arts, especially printmaking and drawing, "tone" has a different meaning, referring to areas of continuous color, produced by various means, as opposed to the linear marks made by an engraved or drawn line. In common language, the term ''shade'' can be generalized to encompass any varieties of a particular color, whether technically they are shades, tints, tones, or slightly different hues. Meanwhile, the term ''tint'' can be gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinted Window
Window film (tint) is a thin laminate film that can be installed to the interior or exterior of glass surfaces in automobiles and boats and also to the interior or exterior of glass in homes and buildings. It is usually made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family, due to its clarity, tensile strength, dimensional stability, and ability to accept a variety of surface-applied or embedded treatments. Window films are generically categorised by their construction components (dyed, pigmented, metallized, ceramic or nano), by their intended use (automotive, marine or architectural), by substrate type (glass or polycarbonate), and/or by their technical performance (privacy, solar control, safety and security). Window film is normally installed by professional service companies but there are also DIY kits widely available. The International Window Film Association, founded in 1991, provides unbranded information about window films. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed technique, rather than a photographic reproduction of a visual artwork which would be printed using an electronic machine ( a printer); however, there is some cross-over between traditional and digital printmaking, including risograph. Except in the case of monotyping, all printmaking processes have the capacity to produce identical multiples of the same artwork, which is called a print. Each print produced is considered an "original" work of art, and is correctly referred to as an "impression", not a "copy" (that means a different print copying the first, common in early printmaking). However, impressions can vary considerably, whether intentionally or not. Master printmakers are technicians who are capable of printing identical "impressions" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engraving
Engraving is the practice of incising a design onto a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or glass are engraved, or may provide an intaglio printing plate, of copper or another metal, for printing images on paper as prints or illustrations; these images are also called "engravings". Engraving is one of the oldest and most important techniques in printmaking. Wood engraving is a form of relief printing and is not covered in this article, same with rock engravings like petroglyphs. Engraving was a historically important method of producing images on paper in artistic printmaking, in mapmaking, and also for commercial reproductions and illustrations for books and magazines. It has long been replaced by various photographic processes in its commercial applications and, partly because of the difficulty of learning the technique, is much less common in printmaking, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Tints And Shades
Blue is one of the three primary colours in the RYB colour model (traditional colour theory), as well as in the RGB (additive) colour model. It lies between violet and cyan on the spectrum of visible light. The eye perceives blue when observing light with a dominant wavelength between approximately 450 and 495 nanometres. Most blues contain a slight mixture of other colours; azure contains some green, while ultramarine contains some violet. The clear daytime sky and the deep sea appear blue because of an optical effect known as Rayleigh scattering. An optical effect called Tyndall effect explains blue eyes. Distant objects appear more blue because of another optical effect called aerial perspective. Blue has been an important colour in art and decoration since ancient times. The semi-precious stone lapis lazuli was used in ancient Egypt for jewellery and ornament and later, in the Renaissance, to make the pigment ultramarine, the most expensive of all pigments. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
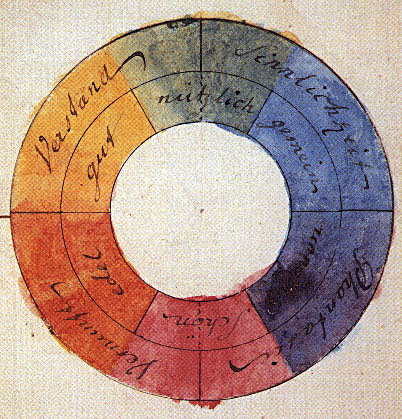
Color Theory
In the visual arts, color theory is the body of practical guidance for color mixing and the visual effects of a specific color combination. Color terminology based on the color wheel and its geometry separates colors into primary color, secondary color, and tertiary color. The understanding of color theory dates to antiquity. Aristotle (d. 322 BCE) and Claudius Ptolemy (d. 168 CE) already discussed which and how colors can be produced by mixing other colors. The influence of light on color was investigated and revealed further by al-Kindi (d. 873) and Ibn al-Haytham (d.1039). Ibn Sina (d. 1037), Nasir al-Din al-Tusi (d. 1274), and Robert Grosseteste (d. 1253) discovered that contrary to the teachings of Aristotle, there are multiple color paths to get from black to white. More modern approaches to color theory principles can be found in the writings of Leone Battista Alberti (c. 1435) and the notebooks of Leonardo da Vinci (c. 1490). A formalization of "color theory" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphic Arts
A category of fine art, graphic art covers a broad range of visual artistic expression, typically two-dimensional, i.e. produced on a flat surface.Graphic art " ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Britannica.com. Retrieved 21 February 2016. The term usually refers to the arts that rely more on line, color or tone, especially drawing and the various forms of ;"Graphic art." ''The Oxford Dictionary of Art''. 3rd ed. Ed. Ian Chilvers. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2004. p. 309. it is sometimes understood to refer specifically to processes, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastel (color)
Pastels or pastel colors belong to a pale family of colors, which, when described in the HSV color space, have high value and low saturation. They are named after an artistic medium made from pigment and solid binding agents, similar to crayons. Pastel sticks historically tended to have lower saturation than paints of the same pigment, hence the name of the color family. The colors of this family are usually described as "soothing." Pastel colors are common in the kawaii aesthetic. Pink, mauve, and baby blue are commonly used pastel colors, as well as mint green, peach, periwinkle, and lavender. In fashion A form of goth style called ''pastel goth'' adds pastel colors to the usually monochrome palette of gothic fashion. Examples Gallery File:Gaiety pastels.jpg, Gaiety pastels File:Perles pastel.jpg, Pastel-colored bead A bead is a small, decorative object that is formed in a variety of shapes and sizes of a material such as stone, bone, shell, glass, pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abney Effect
The Abney effect or the purity-on-hue effect describes the perceived hue shift that occurs when white light is added to a monochromatic light source. The addition of white light will cause a desaturation of the monochromatic source, as perceived by the human observer. However, a less intuitive effect of the perceived white light addition is the change in the apparent hue. This hue shift is physiological rather than physical in nature. This variance of hue as a result of the addition of white light was first described by the English chemist and physicist Sir William de Wiveleslie Abney in 1909, although the date is commonly reported as 1910. A white light source can be created by the combination of red, blue, and green light. Abney demonstrated that the cause of the apparent change in hue was the red and green light that comprised this light source, and that the blue light component had no contribution to the Abney effect.W. de W. Abney. “On the Change in Hue of Spectrum C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compounds. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli. Economic impact In 2006, around 7.4 million tons of inorganic, organic, and special pigments were marketed worldwide. Estimated at around US$14.86 billion in 2018 and will rise at over 4.9% CAGR from 2019 to 2026. The global demand for pigments was roughly US$20.5 billion in 2009. According to an April 2018 report by '' Bloomberg Businessweek'', the estimated value of the pigment industry globally is $30 billion. The value of titanium dioxide – used to enhance the white brightness of many products – was placed at $13.2 billion per year, while the color Ferrari red is valued at $300 million each year. Physical princip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complementary Color
Complementary colors are pairs of colors which, when combined or mixed, cancel each other out (lose hue) by producing a grayscale color like white or black. When placed next to each other, they create the strongest contrast for those two colors. Complementary colors may also be called "opposite colors". Which pairs of colors are considered complementary depends on the color theory one uses: *Modern color theory uses either the RGB additive color model or the CMY subtractive color model, and in these, the complementary pairs are red–cyan, green–magenta, and blue–yellow. *In the traditional RYB color model, the complementary color pairs are red–green, yellow– purple, and blue– orange. * Opponent process theory suggests that the most contrasting color pairs are red–green and blue–yellow. *The black-white color pair is common to all the above theories. In different color models Traditional color model The traditional color wheel model dates to the 18th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darkness
Darkness, the direct opposite of lightness, is defined as a lack of illumination, an absence of visible light, or a surface that absorbs light, such as black or brown. Human vision is unable to distinguish colors in conditions of very low luminance. This is because the hue sensitive photoreceptor cells on the retina are inactive when light levels are insufficient, in the range of visual perception referred to as scotopic vision. The emotional response to darkness has generated metaphorical usages of the term in many cultures, often used to describe an unhappy or foreboding feeling. Referring to a time of day, night, complete darkness occurs when the Sun is more than 18° below the horizon, without the effects of twilight on the night sky. Scientific Perception The perception of darkness differs from the mere absence of light due to the effects of afterimage, after images on perception. In perceiving, the eye is active, and the part of the retina that is unstimulated prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightness
Lightness is a visual perception of the luminance (L) of an object. It is often judged relative to a similarly lit object. In colorimetry and color appearance models, lightness is a prediction of how an illuminated color will appear to a standard observer. While luminance is a linear measurement of light, lightness is a linear prediction of the human perception of that light. This is because human vision's lightness perception is non-linear relative to light. Doubling the quantity of light does not result in a doubling in perceived lightness, only a modest increase. The symbol for perceptual lightness is usually either J as used in CIECAM02 or L^* as used in CIELAB and CIELUV. L^* ("Lstar") is not to be confused with L as used for luminance. In some color ordering systems such as Munsell color system, Munsell, Lightness is referenced as value. Chiaroscuro and Tenebrism both take advantage of dramatic contrasts of value to heighten drama in art. Artists may also employ shading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |