|
Printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed technique, rather than a photographic reproduction of a visual artwork which would be printed using an electronic machine ( a printer); however, there is some cross-over between traditional and digital printmaking, including risograph. Except in the case of monotyping, all printmaking processes have the capacity to produce identical multiples of the same artwork, which is called a print. Each print produced is considered an "original" work of art, and is correctly referred to as an "impression", not a "copy" (that means a different print copying the first, common in early printmaking). However, impressions can vary considerably, whether intentionally or not. Master printmakers are technicians who are capable of printing identical "impressions" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etching
Etching is traditionally the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio (incised) in the metal. In modern manufacturing, other chemicals may be used on other types of material. As a method of printmaking, it is, along with engraving, the most important technique for old master prints, and remains in wide use today. In a number of modern variants such as microfabrication etching and photochemical milling it is a crucial technique in much modern technology, including circuit boards. In traditional pure etching, a metal plate (usually of copper, zinc or steel) is covered with a waxy ground which is resistant to acid. The artist then scratches off the ground with a pointed etching needle where the artist wants a line to appear in the finished piece, exposing the bare metal. The échoppe, a tool with a slanted oval section, is also used for "swelling" lines. The plate is then dipped in a bath of ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatint
Aquatint is an intaglio printmaking technique, a variant of etching that produces areas of tone rather than lines. For this reason it has mostly been used in conjunction with etching, to give both lines and shaded tone. It has also been used historically to print in colour, both by printing with multiple plates in different colours, and by making monochrome prints that were then hand-coloured with watercolour. It has been in regular use since the later 18th century, and was most widely used between about 1770 and 1830, when it was used both for artistic prints and decorative ones. After about 1830 it lost ground to lithography and other techniques. There have been periodic revivals among artists since then. An aquatint plate wears out relatively quickly, and is less easily reworked than other intaglio plates. Many of Goya's plates were reprinted too often posthumously, giving very poor impressions. Among the most famous prints using the aquatint technique are the major s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
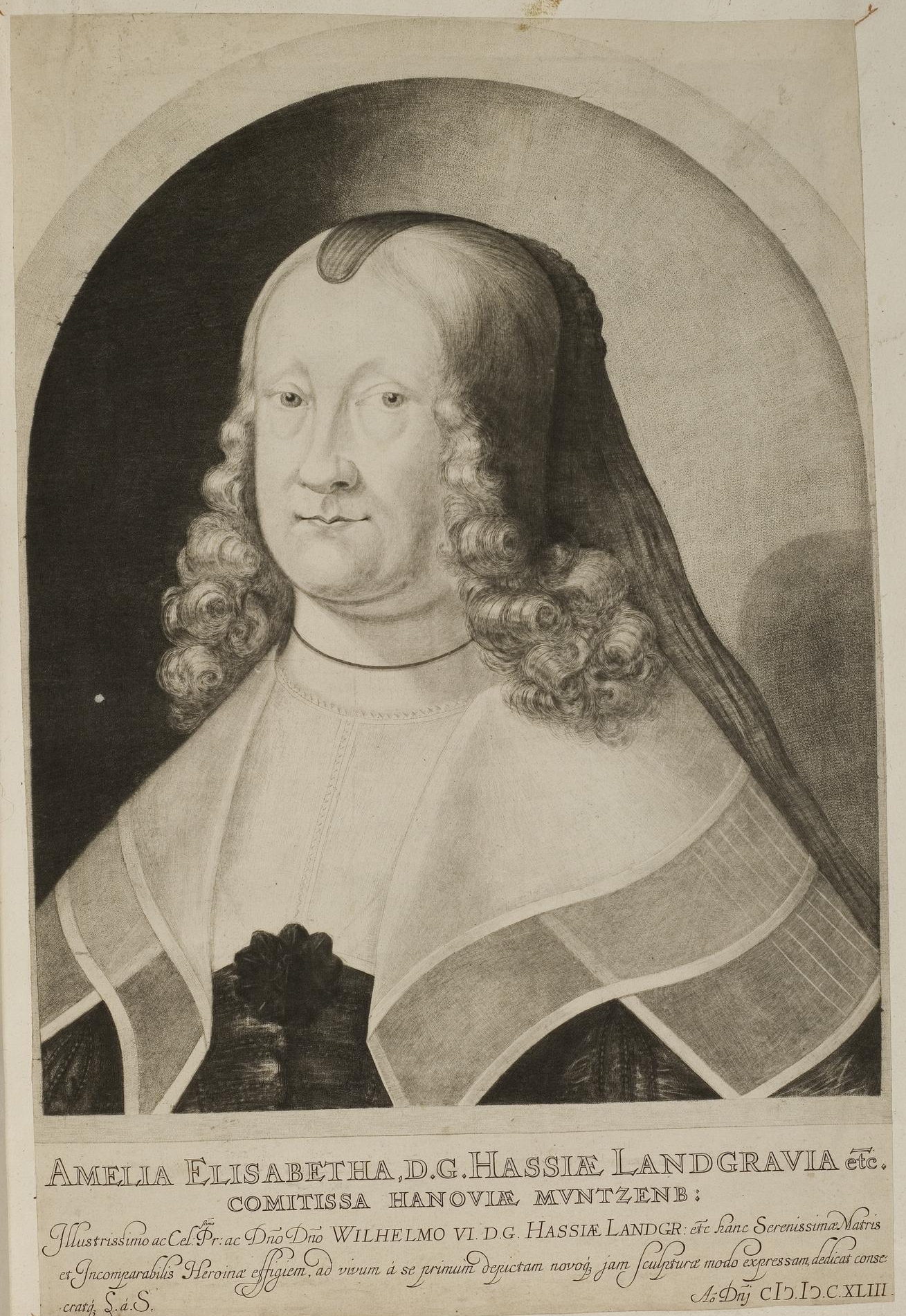
Engraving
Engraving is the practice of incising a design onto a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or glass are engraved, or may provide an intaglio printing plate, of copper or another metal, for printing images on paper as prints or illustrations; these images are also called "engravings". Engraving is one of the oldest and most important techniques in printmaking. Wood engraving is a form of relief printing and is not covered in this article, same with rock engravings like petroglyphs. Engraving was a historically important method of producing images on paper in artistic printmaking, in mapmaking, and also for commercial reproductions and illustrations for books and magazines. It has long been replaced by various photographic processes in its commercial applications and, partly because of the difficulty of learning the technique, is much less common in printmaking, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithography
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone ( lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German author and actor Alois Senefelder and was initially used mostly for musical scores and maps.Meggs, Philip B. A History of Graphic Design. (1998) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 146 Carter, Rob, Ben Day, Philip Meggs. Typographic Design: Form and Communication, Third Edition. (2002) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 11 Lithography can be used to print text or images onto paper or other suitable material. A lithograph is something printed by lithography, but this term is only used for fine art prints and some other, mostly older, types of printed matter, not for those made by modern commercial lithography. Originally, the image to be printed was drawn with a greasy substance, such as oil, fat, or wax onto the surface of a smooth and flat limestone pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intaglio (printmaking)
Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of printing and printmaking techniques in which the image is incised into a surface and the incised line or sunken area holds the ink. It is the direct opposite of a relief print where the parts of the matrix that make the image stand ''above'' the main surface. Normally, copper or in recent times zinc sheets, called plates, are used as a surface or matrix, and the incisions are created by etching, engraving, drypoint, aquatint or mezzotint, often in combination. Collagraphs may also be printed as intaglio plates. After the decline of the main relief technique of woodcut around 1550, the intaglio techniques dominated both artistic printmaking as well as most types of illustration and popular prints until the mid 19th century. Process In intaglio printing, the lines to be printed are cut into a metal (e.g. copper) plate by means either of a cutting tool called a burin, held in the hand – in which case the process is called ''engraving''; or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mezzotint
Mezzotint is a monochrome printmaking process of the '' intaglio'' family. It was the first printing process that yielded half-tones without using line- or dot-based techniques like hatching, cross-hatching or stipple. Mezzotint achieves tonality by roughening a metal plate with thousands of little dots made by a metal tool with small teeth, called a "rocker". In printing, the tiny pits in the plate retain the ink when the face of the plate is wiped clean. This technique can achieve a high level of quality and richness in the print. ''Mezzotint'' is often combined with other ''intaglio'' techniques, usually etching and engraving. The process was especially widely used in England from the eighteenth century, to reproduce portraits and other paintings. It was somewhat in competition with the other main tonal technique of the day, aquatint. Since the mid-nineteenth century it has been relatively little used, as lithography and other techniques produced comparable results more ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagraph
Collagraphy (sometimes spelled collography) is a printmaking process introduced in 1955 by Glen Alps in which materials are applied to a rigid substrate (such as paperboard or wood). The word is derived from the Greek word ''koll'' or ''kolla'', meaning glue, and ''graph'', meaning the activity of drawing. The plate can be intaglio-inked, inked with a roller or paintbrush or some combination thereof. Ink or pigment is applied to the resulting collage and the board is used to print onto paper or another material using either a printing press or various hand tools. The resulting print is termed a collagraph. Substances such as carborundum, acrylic texture mediums, sandpapers, textiles, bubble wrap, string or other fibres, cut card, leaves and grass can all be used in creating the collagraph plate. In some instances, leaves can be used as a source of pigment by rubbing them onto the surface of the plate. Different tonal effects and vibrant colours can be achieved with the techni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edition (printmaking)
In printmaking, an edition is a number of prints struck from one plate, usually at the same time. This may be a '' limited edition'', with a fixed number of impressions produced on the understanding that no further impressions (copies) will be produced later, or an ''open edition'' limited only by the number that can be sold or produced before the plate wears. Most modern artists produce only limited editions, normally signed by the artist in pencil, and numbered as say 67/100 to show the unique number of that impression and the total edition size. Original or reproduction? An important and often confused distinction is that between editions of original prints, produced in the same medium as the artist worked (e.g., etching, or lithography), and reproduction prints (or paintings), which are photographic reproductions of the original work, essentially in the same category as a picture in a book or magazine, though better printed and on better paper. These may be marketed as "limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodcut
Woodcut is a relief printing technique in printmaking Printmaking is the process of creating artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed techniq .... An artist carves an image into the surface of a block of wood—typically with Chisel#Gouge, gouges—leaving the printing parts level with the surface while removing the non-printing parts. Areas that the artist cuts away carry no ink, while characters or images at surface level carry the ink to produce the print. The block is cut along the wood grain (unlike wood engraving, where the block is cut in the end-grain). The surface is covered with ink by rolling over the surface with an ink-covered roller (brayer), leaving ink upon the flat surface but not in the non-printing areas. Multiple colors can be printed by keying the paper to a frame around the woodblocks (using a dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Engraving
Wood engraving is a printmaking technique, in which an artist works an image or ''matrix'' of images into a block of wood. Functionally a variety of woodcut, it uses relief printing, where the artist applies ink to the face of the block and prints using relatively low pressure. By contrast, ordinary engraving, like etching, uses a metal plate for the matrix, and is printed by the intaglio method, where the ink fills the ''valleys'', the removed areas. As a result, wood engravings deteriorate less quickly than copper-plate engravings, and have a distinctive white-on-black character. Thomas Bewick developed the wood engraving technique in Great Britain at the end of the 18th century. His work differed from earlier woodcuts in two key ways. First, rather than using woodcarving tools such as knives, Bewick used an engraver's burin (graver). With this, he could create thin delicate lines, often creating large dark areas in the composition. Second, wood engraving traditionally uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The earliest known form of printing as applied to paper was woodblock printing, which appeared in China before 220 AD for cloth printing. However, it would not be applied to paper until the seventh century.Shelagh Vainker in Anne Farrer (ed), "Caves of the Thousand Buddhas", 1990, British Museum publications, Later developments in printing technology include the movable type invented by Bi Sheng around 1040 AD and the printing press invented by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century. The technology of printing played a key role in the development of the Renaissance and the Scientific Revolution and laid the material basis for the modern knowledge-based economy and the spread of learning to the masses. History Woodblock printing Wood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relief Print
Relief printing is a family of printing methods where a printing block, plate or matrix, which has had ink applied to its non-recessed surface, is brought into contact with paper. The non-recessed surface will leave ink on the paper, whereas the recessed areas will not. A printing press may not be needed, as the back of the paper can be rubbed or pressed by hand with a simple tool such as a brayer or roller. In contrast, in intaglio printing, the ''recessed'' areas are printed. Relief printing is one of the traditional families of printmaking techniques, along with the intaglio and planographic families, though modern developments have created others. In the relief family of printing, the matrix was historically made subtractively, by removing material from the surface of areas not intended to be printed. The remaining surface would then receive ink. The relief family of techniques includes woodcut, metalcut, wood engraving, relief etching, linocut, rubber stamp, foam pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)