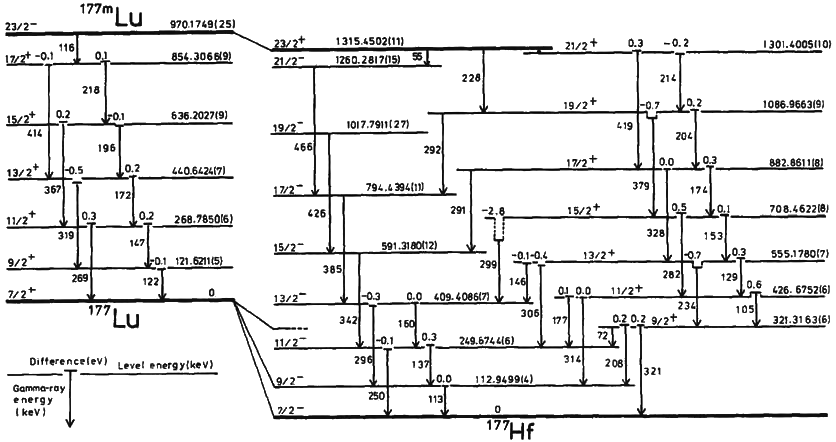
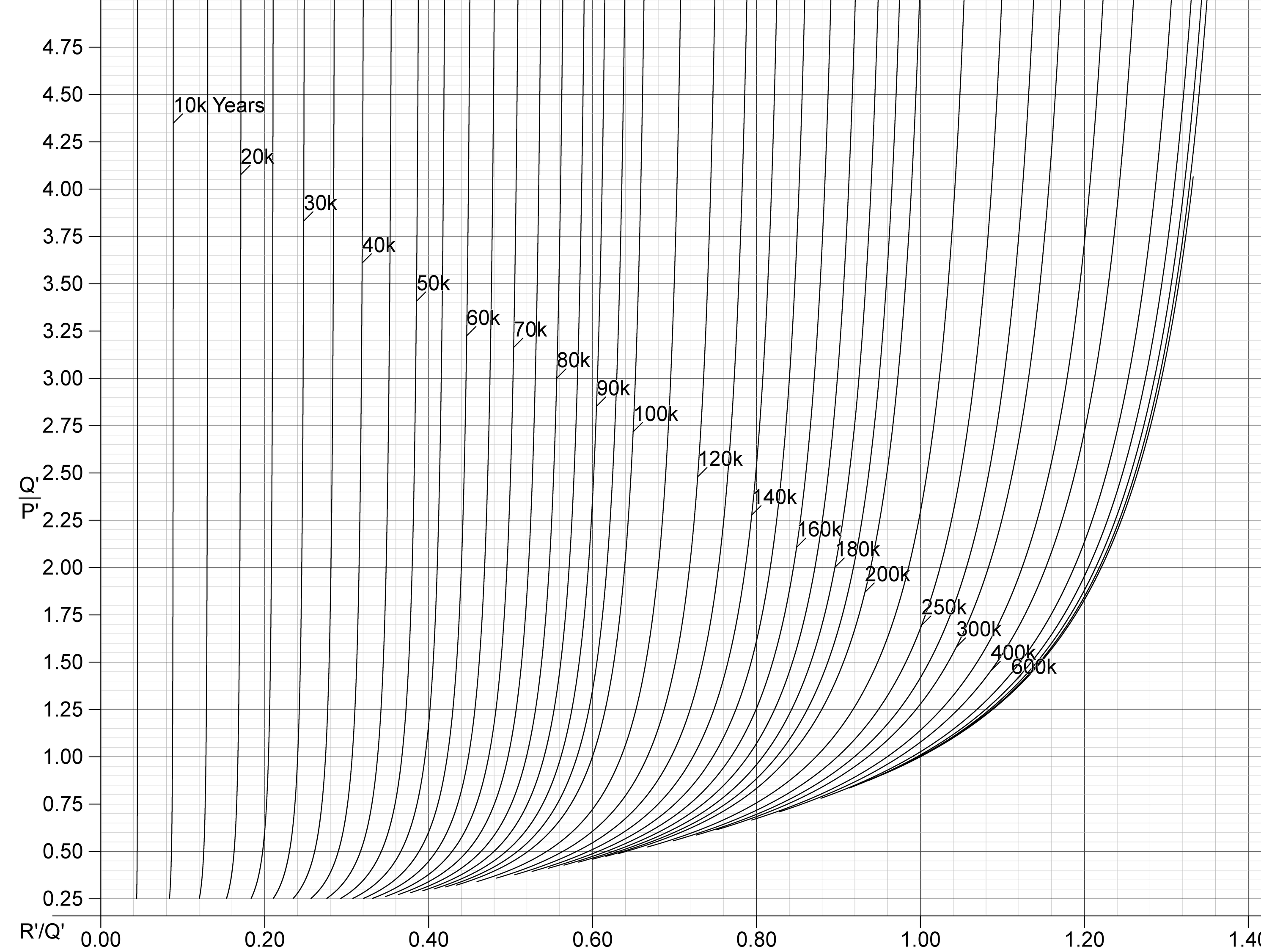
|
Thorium-234
Thorium (90Th) has seven naturally occurring isotopes but none are stable. One isotope, 232Th, is ''relatively'' stable, with a half-life of 1.405×1010 years, considerably longer than the age of the Earth, and even slightly longer than the generally accepted age of the universe. This isotope makes up nearly all natural thorium, so thorium was considered to be mononuclidic. However, in 2013, IUPAC reclassified thorium as binuclidic, due to large amounts of 230Th in deep seawater. Thorium has a characteristic terrestrial isotopic composition and thus a standard atomic weight can be given. Thirty-one radioisotopes have been characterized, with the most stable being 232Th, 230Th with a half-life of 75,380 years, 229Th with a half-life of 7,917 years, and 228Th with a half-life of 1.92 years. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than thirty days and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than ten minutes. One isotope, 229Th, has a nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium-238
Uranium-238 (238U or U-238) is the most common isotope of uranium found in nature, with a relative abundance of 99%. Unlike uranium-235, it is non-fissile, which means it cannot sustain a chain reaction in a thermal-neutron reactor. However, it is fissionable by fast neutrons, and is ''fertile'', meaning it can be transmuted to fissile plutonium-239. 238U cannot support a chain reaction because inelastic scattering reduces neutron energy below the range where fast fission of one or more next-generation nuclei is probable. Doppler broadening of 238U's neutron absorption resonances, increasing absorption as fuel temperature increases, is also an essential negative feedback mechanism for reactor control. Around 99.284% of natural uranium's mass is uranium-238, which has a half-life of 1.41 seconds (4.468 years, or 4.468 billion years). Due to its natural abundance and half-life relative to other radioactive elements, 238U produces ~40% of the radioactive heat produced within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha decay ( ), beta decay ( ), and gamma decay ( ), all of which involve emitting one or more particles. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetism and nuclear force. A fourth type of common decay is electron capture, in which an unstable nucleus captures an inner electron from one of the electron shells. The loss of that electron from the shell results in a cascade of electrons dropping down to that lower shell resulting in emission of discrete X-rays from the transitions. A common example is iodine-125 commonly used in medical settings. Radioactive decay is a stochastic (i.e. random) process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Decay
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus) and thereby transforms or 'decays' into a different atomic nucleus, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an atomic number that is reduced by two. An alpha particle is identical to the nucleus of a helium-4 atom, which consists of two protons and two neutrons. It has a charge of and a mass of . For example, uranium-238 decays to form thorium-234. While alpha particles have a charge , this is not usually shown because a nuclear equation describes a nuclear reaction without considering the electrons – a convention that does not imply that the nuclei necessarily occur in neutral atoms. Alpha decay typically occurs in the heaviest nuclides. Theoretically, it can occur only in nuclei somewhat heavier than nickel (element 28), where the overall binding energy per nucleon is no longer a maximum and the nuclides are therefore unstable toward spontaneou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Number
The mass number (symbol ''A'', from the German word ''Atomgewicht'' tomic weight, also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus. It is approximately equal to the ''atomic'' (also known as ''isotopic'') mass of the atom expressed in atomic mass units. Since protons and neutrons are both baryons, the mass number ''A'' is identical with the baryon number ''B'' of the nucleus (and also of the whole atom or ion). The mass number is different for each isotope of a given chemical element, and the difference between the mass number and the atomic number ''Z'' gives the number of neutrons (''N'') in the nucleus: . The mass number is written either after the element name or as a superscript to the left of an element's symbol. For example, the most common isotope of carbon is carbon-12, or , which has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. The full isotope symbol would also have the atomic number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spontaneous Fission
Spontaneous fission (SF) is a form of radioactive decay that is found only in very heavy chemical elements. The nuclear binding energy of the elements reaches its maximum at an atomic mass number of about 56 (e.g., iron-56); spontaneous breakdown into smaller nuclei and a few isolated nuclear particles becomes possible at greater atomic mass numbers. History By 1908, physicists understood that alpha decay involved ejection of helium nuclei from a decaying atom. Like cluster decay, alpha decay is not typically categorized as a process of fission. The first nuclear fission process discovered was fission induced by neutrons. Because cosmic rays produce some neutrons, it was difficult to distinguish between induced and spontaneous events. Cosmic rays can be reliably shielded by a thick layer of rock or water. Spontaneous fission was identified in 1940 by Soviet physicists Georgy Flyorov and Konstantin Petrzhak by their observations of uranium in the Moscow Metro Dinamo station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neptunium-237
Neptunium (93Np) is usually considered an artificial element, although trace quantities are found in nature, so a standard atomic weight cannot be given. Like all trace or artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized and identified was 239Np in 1940, produced by bombarding with neutrons to produce , which then underwent beta decay to . Trace quantities are found in nature from neutron capture reactions by uranium atoms, a fact not discovered until 1951. Twenty-five neptunium radioisotopes have been characterized, with the most stable being with a half-life of 2.14 million years, with a half-life of 154,000 years, and with a half-life of 396.1 days. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 4.5 days, and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than 50 minutes. This element also has five meta states, with the most stable being (t1/2 22.5 hours). The isotopes of neptunium range from to , th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomeric Transition
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have half-lives 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). The term "metastable" is usually restricted to isomers with half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer. Some references recommend 5 × 10−9 seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the nuclear isomer survives so long (at least 1015 years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can even exceed that of the ground state of the same nuclide, as shown by as well as , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium–thorium Dating
Uranium–thorium dating, also called thorium-230 dating, uranium-series disequilibrium dating or uranium-series dating, is a radiometric dating technique established in the 1960s which has been used since the 1970s to determine the age of calcium carbonate materials such as speleothem or coral. Unlike other commonly used radiometric dating techniques such as rubidium–strontium or uranium–lead dating, the uranium-thorium technique does not measure accumulation of a stable end-member decay product. Instead, it calculates an age from the degree to which secular equilibrium has been restored between the radioactive isotope thorium-230 and its radioactive parent uranium-234 within a sample. Background Thorium is not soluble in natural water under conditions found at or near the surface of the earth, so materials grown in or from this water do not usually contain thorium. In contrast, uranium is soluble to some extent in all natural water, so any material that precipitates or i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high melting point. Thorium is an electropositive actinide whose chemistry is dominated by the +4 oxidation state; it is quite reactive and can ignite in air when finely divided. All known thorium isotopes are unstable. The most stable isotope, 232Th, has a half-life of 14.05 billion years, or about the age of the universe; it decays very slowly via alpha decay, starting a decay chain named the thorium series that ends at stable 208 Pb. On Earth, thorium and uranium are the only significantly radioactive elements that still occur naturally in large quantities as primordial elements. Thorium is estimated to be over three times as abundant as uranium in the Earth's crust, and is chiefly refined from monazite sands as a by-product of extracti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium-235
Uranium-235 (235U or U-235) is an isotope of uranium making up about 0.72% of natural uranium. Unlike the predominant isotope uranium-238, it is fissile, i.e., it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is the only fissile isotope that exists in nature as a primordial nuclide. Uranium-235 has a half-life of 703.8 million years. It was discovered in 1935 by Arthur Jeffrey Dempster. Its fission cross section for slow thermal neutrons is about 584.3±1 barns. For fast neutrons it is on the order of 1 barn. Most but not all neutron absorptions result in fission; a minority result in neutron capture forming uranium-236. Natural decay chain :\begin \ce \begin \ce \\ \ce \end \ce \\ \ce \begin \ce \\ \ce \end \ce \end Fission properties The fission of one atom of uranium-235 releases () inside the reactor. That corresponds to 19.54 TJ/ mol, or 83.14 TJ/kg. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorium-232
Thorium-232 () is the main naturally occurring isotope of thorium, with a relative abundance of 99.98%. It has a half life of 14 billion years, which makes it the longest-lived isotope of thorium. It decays by alpha decay to radium-228; its decay chain terminates at stable lead-208. Thorium-232 is a fertile material; it can capture a neutron to form thorium-233, which subsequently undergoes two successive beta decays to uranium-233, which is fissile. As such, it has been used in the thorium fuel cycle in nuclear reactors; various prototype thorium-fueled reactors have been designed; however, as of 2022, thorium has not been used for large-scale commercial nuclear power. Natural occurrence The half-life of thorium-232 (14 billion years) is more than three times the age of the Earth; thorium-232 therefore occurs in nature as a primordial nuclide. Other thorium isotopes occur in nature in much smaller quantities as intermediate decay products of uranium-238, uranium-235, and thori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primordial Nuclide
In geochemistry, geophysics and nuclear physics, primordial nuclides, also known as primordial isotopes, are nuclides found on Earth that have existed in their current form since before Earth was formed. Primordial nuclides were present in the interstellar medium from which the solar system was formed, and were formed in, or after, the Big Bang, by nucleosynthesis in stars and supernovae followed by mass ejection, by cosmic ray spallation, and potentially from other processes. They are the stable nuclides plus the long-lived fraction of radionuclides surviving in the primordial solar nebula through planet accretion until the present; 286 such nuclides are known. Stability All of the known 251 stable nuclides, plus another 35 nuclides that have half-lives long enough to have survived from the formation of the Earth, occur as primordial nuclides. These 35 primordial radionuclides represent isotopes of 28 separate elements. Cadmium, tellurium, xenon, neodymium, samarium, osmium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Halflife_of_Radionulides_depending_on_Z²_to_A_ratio.png)