|
Thermal Reservoir
A thermal reservoir, also thermal energy reservoir or thermal bath, is a thermodynamic system with a heat capacity so large that the temperature of the reservoir changes relatively little when a significant amount of heat is added or extracted. As a conceptual simplification, it effectively functions as an infinite pool of thermal energy at a given, constant temperature. Since it can act as an inertial source and sink of heat, it is often also referred to as a heat reservoir or heat bath. Lakes, oceans and rivers often serve as thermal reservoirs in geophysical processes, such as the weather. In atmospheric science, large air masses in the atmosphere often function as thermal reservoirs. Since the temperature of a thermal reservoir does not change during the heat transfer, the change of entropy in the reservoir is: dS_\text=\frac The microcanonical partition sum Z(E) of a heat bath of temperature has the property: Z(E+\Delta E) = Z(E) e^ where k_\text is the Boltzmann consta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic System
A thermodynamic system is a body of matter and/or radiation separate from its surroundings that can be studied using the laws of thermodynamics. Thermodynamic systems can be passive and active according to internal processes. According to internal processes, passive systems and active systems are distinguished: passive, in which there is a redistribution of available energy, active, in which one type of energy is converted into another. Depending on its interaction with the environment, a thermodynamic system may be an isolated system, a Closed system#In thermodynamics, closed system, or an Open system (systems theory), open system. An isolated system does not exchange matter or energy with its surroundings. A closed system may exchange heat, experience forces, and exert forces, but does not exchange matter. An open system can interact with its surroundings by exchanging both matter and energy. The physical condition of a thermodynamic system at a given time is described by its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication. Entropy is central to the second law of thermodynamics, which states that the entropy of an isolated system left to spontaneous evolution cannot decrease with time. As a result, isolated systems evolve toward thermodynamic equilibrium, where the entropy is highest. A consequence of the second law of thermodynamics is that certain processes are irreversible. The thermodynami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Battery
Thermal energy storage (TES) is the storage of thermal energy for later reuse. Employing widely different technologies, it allows surplus thermal energy to be stored for hours, days, or months. Scale both of storage and use vary from small to large – from individual processes to district, town, or region. Usage examples are the balancing of energy demand between daytime and nighttime, storing summer heat for winter heating, or winter cold for summer cooling ( Seasonal thermal energy storage). Storage media include water or ice-slush tanks, masses of native earth or bedrock accessed with heat exchangers by means of boreholes, deep aquifers contained between impermeable strata; shallow, lined pits filled with gravel and water and insulated at the top, as well as eutectic solutions and phase-change materials. Other sources of thermal energy for storage include heat or cold produced with heat pumps from off-peak, lower cost electric power, a practice called peak shavin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Sink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is thermal management (electronics), dissipated away from the device, thereby allowing regulation of the device's temperature. In computers, heat sinks computer cooling, are used to cool central processing unit, CPUs, graphics processing unit, GPUs, and some chipsets and RAM modules. Heat sinks are used with other high-power semiconductor devices such as Transistor#Other transistor types, power transistors and optoelectronics such as lasers and light-emitting diodes (LEDs), where the heat dissipation ability of the component itself is insufficient to moderate its temperature. A heat sink is designed to maximize its surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Air velocity, choice of material, protrusion design and surface treatment are fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Heat Pump
A ground source heat pump (also geothermal heat pump) is a heating/cooling system for buildings that use a type of heat pump to transfer heat to or from the ground, taking advantage of the relative constancy of temperatures of the earth through the seasons. Ground-source heat pumps (GSHPs)or geothermal heat pumps (GHP), as they are commonly termed in North Americaare among the most energy-efficient technologies for providing HVAC and water heating, using less energy than can be achieved by use of resistive electric heaters. Efficiency is given as a coefficient of performance (CoP) which is typically in the range 3-6, meaning that the devices provide 3-6 units of heat for each unit of electricity used. Setup costs are higher than for other heating systems, due to the requirement of installing ground loops over large areas or of drilling bore holes, hence ground source is often installed when new blocks of flats are built. Air-source heat pumps have lower set-up costs but have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann Factor
Factor (Latin, ) may refer to: Commerce * Factor (agent), a person who acts for, notably a mercantile and colonial agent * Factor (Scotland), a person or firm managing a Scottish estate * Factors of production, such a factor is a resource used in the production of goods and services * Factor, a brand of HelloFresh meal-kit company Science and technology Biology * Coagulation factors, substances essential for blood coagulation * Environmental factor, any abiotic or biotic factor that affects life * Enzyme, proteins that catalyze chemical reactions * Factor B, and factor D, peptides involved in the alternate pathway of immune system complement activation * Transcription factor, a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences Computer science and information technology * Factor (programming language), a concatenative stack-oriented programming language * Factor (Unix), a utility for factoring an integer into its prime factors * Factor, a substring, a subsequence of conse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann Constant
The Boltzmann constant ( or ) is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative thermal energy of particles in a ideal gas, gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin (K) and the molar gas constant, in Planck's law of black-body radiation and Boltzmann's entropy formula, and is used in calculating Johnson–Nyquist noise, thermal noise in resistors. The Boltzmann constant has Dimensional analysis, dimensions of energy divided by temperature, the same as entropy and heat capacity. It is named after the Austrian scientist Ludwig Boltzmann. As part of the 2019 revision of the SI, the Boltzmann constant is one of the seven "Physical constant, defining constants" that have been defined so as to have exact finite decimal values in SI units. They are used in various combinations to define the seven SI base units. The Boltzmann constant is defined to be exactly joules per kelvin, with the effect of defining the SI unit ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcanonical Ensemble
In statistical mechanics, the microcanonical ensemble is a statistical ensemble that represents the possible states of a mechanical system whose total energy is exactly specified. The system is assumed to be isolated in the sense that it cannot exchange energy or particles with its environment, so that (by conservation of energy) the energy of the system does not change with time. The primary macroscopic variables of the microcanonical ensemble are the total number of particles in the system (symbol: ), the system's volume (symbol: ), as well as the total energy in the system (symbol: ). Each of these is assumed to be constant in the ensemble. For this reason, the microcanonical ensemble is sometimes called the ensemble. In simple terms, the microcanonical ensemble is defined by assigning an equal probability to every microstate whose energy falls within a range centered at . All other microstates are given a probability of zero. Since the probabilities must add up to 1, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, Convection (heat transfer), thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes. Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species (mass transfer in the form of advection), either cold or hot, to achieve heat transfer. While these mechanisms have distinct characteristics, they often occur simultaneously in the same system. Heat conduction, also called diffusion, is the direct microscopic exchanges of kinetic energy of particles (such as molecules) or quasiparticles (such as lattice waves) through the boundary between two systems. When an object is at a different temperature from another body or its surroundings, heat flows so that the body and the surroundings reach the same temperature, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
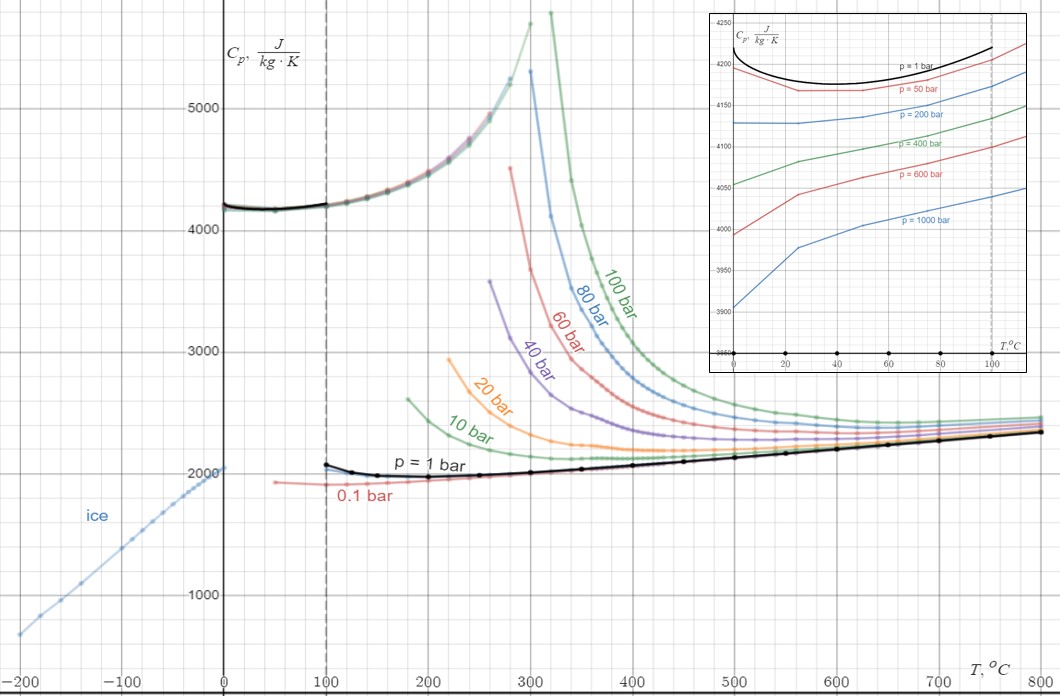
Heat Capacity
Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin (J/K). Heat capacity is an extensive property. The corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacity, found by dividing the heat capacity of an object by its mass. Dividing the heat capacity by the amount of substance in moles yields its molar heat capacity. The volumetric heat capacity measures the heat capacity per volume. In architecture and civil engineering, the heat capacity of a building is often referred to as its '' thermal mass''. Definition Basic definition The heat capacity of an object, denoted by C, is the limit C = \lim_\frac, where \Delta Q is the amount of heat that must be added to the object (of mass ''M'') in order to raise its temperature by \Delta T. The value of this parameter usually varies considerably depending o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Mass
In meteorology, an air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and humidity. Air masses cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles, and adapt to the characteristics of the surface below them. They are classified according to latitude and their continental or maritime source regions. Colder air masses are termed polar or arctic, while warmer air masses are deemed tropical. Continental and superior air masses are dry, while maritime and monsoon air masses are moist. Weather fronts separate air masses with different density (temperature or moisture) characteristics. Once an air mass moves away from its source region, underlying vegetation and body of water, water bodies can quickly modify its character. Classification schemes tackle an air mass's characteristics, as well as modification. Classification and notation The Tor Bergeron, Bergeron classification is the most widely accepted form of air mass classification, though others have produced more refined versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Science
Atmospheric science is the study of the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere and its various inner-working physical processes. Meteorology includes atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physics with a major focus on weather forecasting. Climatology is the study of atmospheric conditions over timescales longer than those of weather, weather, focusing on average climate conditions and their climate variability and change, variability over time. Aeronomy is the study of the upper layers of the atmosphere, where dissociation (chemistry), dissociation and ionization are important. Atmospheric science has been extended to the field of planetary science and the study of the atmospheres of the planets and natural satellites of the Solar System. Experimental instruments used in atmospheric science include satellites, rocketsondes, radiosondes, weather balloons, radars, and lasers. The term aerology (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἀήρ, ''aēr'', "air"; and -λογία, ''-logy, -logia'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |