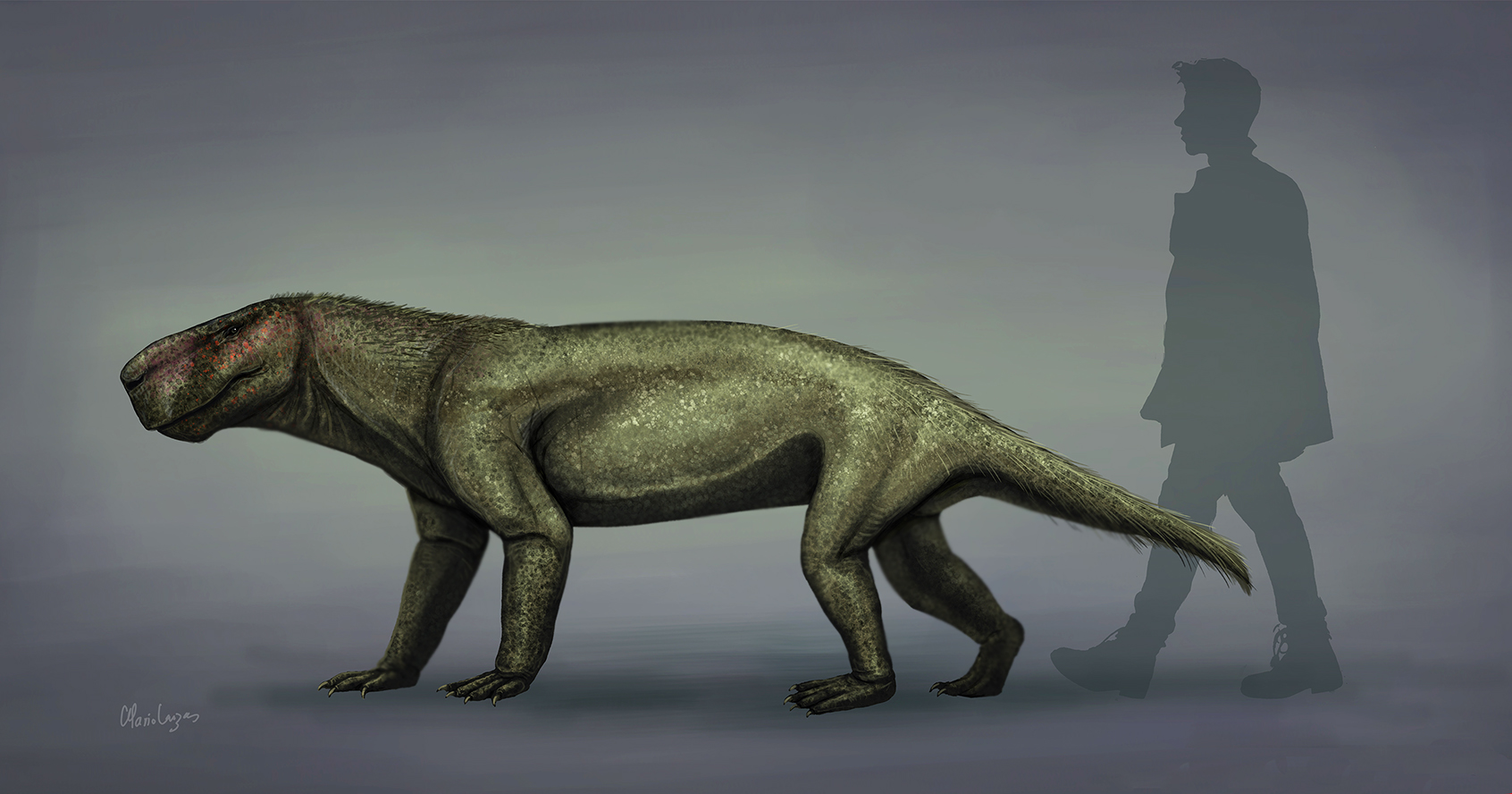|
Theriodonts
The theriodonts ( clade Theriodontia) are a major group of therapsids which appeared during the Middle Permian and which includes the gorgonopsians and the eutheriodonts, itself including the therocephalians and the cynodonts. Naming In 1876, Richard Owen named a suborder Theriodontia, which he divided into the Cynodontia and the Gomphodontia. The modern clade concept was devised by James Allen Hopson. In his system, Theriodontia fall into two main groups: the Gorgonopsia and the Eutheriodontia. The latter consist of the Therocephalia and Cynodontia.J.A. Hopson. 1999. "Therapsids". ''Encyclopedia of Paleontology'' 2: 1256-1266 Evolution Theriodonts appeared at the same time as their sister group within the Neotherapsida, the Anomodontia, about 270 million years ago, in the Middle Permian. Even these early theriodonts were more mammal-like than their anomodont and dinocephalian contemporaries. Early theriodonts may have been warm-blooded. Early forms were carnivorous, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgonopsians
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle to Upper Permian roughly 265 to 252 million years ago. They are characterised by a long and narrow skull, as well as elongated upper and sometimes lower canine teeth and incisors which were likely used as slashing and stabbing weapons. Postcanine teeth are generally reduced or absent. For hunting large prey, they possibly used a bite-and-retreat tactic, ambushing and taking a debilitating bite out of the target, and following it at a safe distance before its injuries exhausted it, whereupon the gorgonopsian would grapple the animal and deliver a killing bite. They would have had an exorbitant gape, possibly in excess of 90°, without having to unhinge the jaw. They markedly increased in size as time went on, growing from small skull lengths of in the Middle Permian to bear-like proportions of up to in the Upper Permian. The latest gorgonopsia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgonopsia
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle to Upper Permian roughly 265 to 252 million years ago. They are characterised by a long and narrow skull, as well as elongated upper and sometimes lower canine teeth and incisors which were likely used as slashing and stabbing weapons. Postcanine teeth are generally reduced or absent. For hunting large prey, they possibly used a bite-and-retreat tactic, ambushing and taking a debilitating bite out of the target, and following it at a safe distance before its injuries exhausted it, whereupon the gorgonopsian would grapple the animal and deliver a killing bite. They would have had an exorbitant gape, possibly in excess of 90°, without having to unhinge the jaw. They markedly increased in size as time went on, growing from small skull lengths of in the Middle Permian to bear-like proportions of up to in the Upper Permian. The latest gorgonopsia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapsid
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more underneath the body, as opposed to the sprawling posture of many reptiles and salamanders. Therapsids evolved from "pelycosaurs", specifically within the Sphenacodontia, more than 279.5 million years ago. They replaced the "pelycosaurs" as the dominant large land animals in the Middle Permian through to the Early Triassic. In the aftermath of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, therapsids declined in relative importance to the rapidly diversifying reptiles during the Middle Triassic. The therapsids include the cynodonts, the group that gave rise to mammals ( Mammaliaformes) in the Late Triassic, around 225 million years ago. Of the non-mammalian therapsids, only cynodonts survived beyond the end of the Triassic, with the only other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neotherapsida
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more underneath the body, as opposed to the sprawling posture of many reptiles and salamanders. Therapsids evolved from "pelycosaurs", specifically within the Sphenacodontia, more than 279.5 million years ago. They replaced the "pelycosaurs" as the dominant large land animals in the Middle Permian through to the Early Triassic. In the aftermath of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, therapsids declined in relative importance to the rapidly diversifying reptiles during the Middle Triassic. The therapsids include the cynodonts, the group that gave rise to mammals ( Mammaliaformes) in the Late Triassic, around 225 million years ago. Of the non-mammalian therapsids, only cynodonts survived beyond the end of the Triassic, with the only othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therocephalia
Therocephalia is an extinct suborder of eutheriodont therapsids (mammals and their close relatives) from the Permian and Triassic. The therocephalians ("beast-heads") are named after their large skulls, which, along with the structure of their teeth, suggest that they were carnivores. Like other non-mammalian synapsids, therocephalians were once described as "mammal-like reptiles". Therocephalia is the group most closely related to the cynodonts, which gave rise to the mammals. This relationship takes evidence in a variety of skeletal features. The fossils of therocephalians are numerous in the Karoo of South Africa, but have also been found in Russia, China, Tanzania, Zambia, and Antarctica. Early therocephalian fossils discovered in Middle Permian deposits of South Africa support a Gondwanan origin for the group, which seems to have spread quickly across Earth. Although almost every therocephalian lineage ended during the great Permian–Triassic extinction event, a few represe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutheriodontia
Eutheriodontia is a clade of therapsids which appear during the Middle Permian and which includes therocephalians and cynodonts, this latter group including mammals and related forms. With the dicynodonts, they form one of two lineages of therapsids that survived the Permian extinction and which diversified again during the Triassic, before the majority of them disappeared before or during the Triassic–Jurassic extinction, except for a lineage of cynodonts that would later give rise to mammals. Classification The clade was named in 1986 by James Allen Hopson and Herbert Richard Barghusen, the name meaning the "true Theriodontia". Within Hopson's system, the Eutheriodontia are the sister group of the Gorgonopsia within the Theriodontia. A close relationship between therocephalians and cynodonts had been recognized for many years. In 2001 the Eutheriodontia were defined as the least inclusive clade including Mammalia and ''Bauria''.James A. Hopson and James W. Kitching, 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutheriodont
Eutheriodontia is a clade of therapsids which appear during the Middle Permian and which includes therocephalians and cynodonts, this latter group including mammals and related forms. With the dicynodonts, they form one of two lineages of therapsids that survived the Permian extinction and which diversified again during the Triassic, before the majority of them disappeared before or during the Triassic–Jurassic extinction, except for a lineage of cynodonts that would later give rise to mammals. Classification The clade was named in 1986 by James Allen Hopson and Herbert Richard Barghusen, the name meaning the "true Theriodontia". Within Hopson's system, the Eutheriodontia are the sister group of the Gorgonopsia within the Theriodontia. A close relationship between therocephalians and cynodonts had been recognized for many years. In 2001 the Eutheriodontia were defined as the least inclusive clade including Mammalia and ''Bauria''.James A. Hopson and James W. Kitching, 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scylacosaurus
''Scylacosaurus'' is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsid Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more ...s. References Scylacosaurids Therocephalia genera Permian synapsids Lopingian synapsids of Africa Fossil taxa described in 1903 Taxa named by Robert Broom {{paleo-therapsid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therocephalia
Therocephalia is an extinct suborder of eutheriodont therapsids (mammals and their close relatives) from the Permian and Triassic. The therocephalians ("beast-heads") are named after their large skulls, which, along with the structure of their teeth, suggest that they were carnivores. Like other non-mammalian synapsids, therocephalians were once described as "mammal-like reptiles". Therocephalia is the group most closely related to the cynodonts, which gave rise to the mammals. This relationship takes evidence in a variety of skeletal features. The fossils of therocephalians are numerous in the Karoo of South Africa, but have also been found in Russia, China, Tanzania, Zambia, and Antarctica. Early therocephalian fossils discovered in Middle Permian deposits of South Africa support a Gondwanan origin for the group, which seems to have spread quickly across Earth. Although almost every therocephalian lineage ended during the great Permian–Triassic extinction event, a few represe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinocephalia
Dinocephalians (terrible heads) are a clade of large-bodied early therapsids that flourished in the Early and Middle Permian between 279.5 and 260 million years ago (Ma), but became extinct during the Capitanian mass extinction event. Dinocephalians included herbivorous, carnivorous, and omnivorous forms. Many species had thickened skulls with many knobs and bony projections. Dinocephalians were the first non-mammalian therapsids to be scientifically described and their fossils are known from Russia, China, Brazil, South Africa, Zimbabwe, and Tanzania. Description Apart from the Biarmosuchians, the dinocephalians are the least advanced therapsids, although still uniquely specialised in their own way. They retain a number of primitive characteristics (e.g. no secondary palate, small dentary) shared with their pelycosaur ancestors, although they are also more advanced in possessing therapsid adaptations like the expansion of the ilium and more erect limbs. They include carni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warm-blooded
Warm-blooded is an informal term referring to animal species which can maintain a body temperature higher than their environment. In particular, homeothermic species maintain a stable body temperature by regulating metabolic processes. The only known living homeotherms are birds and mammals, and the only living homeothermic lizard is the Argentine black and white tegu. Some extinct reptiles such as ichthyosaurs, pterosaurs, plesiosaurs and some non-avian dinosaurs are believed to have been homeotherms. Other species have various degrees of thermoregulation. Animal body temperature control varies by species, so the terms "warm-blooded" and " cold-blooded" (though still in everyday use) suggest a false idea of there being only two categories of body temperature control, and are no longer used scientifically. Terminology In general, warm-bloodedness refers to three separate categories of thermoregulation. *Endothermy is the ability of some creatures to control their body temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomodontia
Anomodontia is an extinct group of non-mammalian therapsids from the Permian and Triassic periods. By far the most speciose group are the dicynodonts, a clade of beaked, tusked herbivores.Chinsamy-Turan, A. (2011) ''Forerunners of Mammals: Radiation - Histology - Biology''p.39.Indiana University Press, . Retrieved May 2012 Anomodonts were very diverse during the Middle Permian, including primitive forms like ''Anomocephalus'' and ''Patranomodon'' and groups like Venyukovioidea and Dromasauria. Dicynodonts became the most successful and abundant of all herbivores in the Late Permian, filling ecological niches ranging from large browsers down to small burrowers. Few dicynodont families survived the Permian–Triassic extinction event, but one lineage (Kannemeyeriiformes) evolved into large, stocky forms that became dominant terrestrial herbivores right until the Late Triassic, when changing conditions caused them to decline, finally going extinct during the Triassic-Jurassic ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |