|
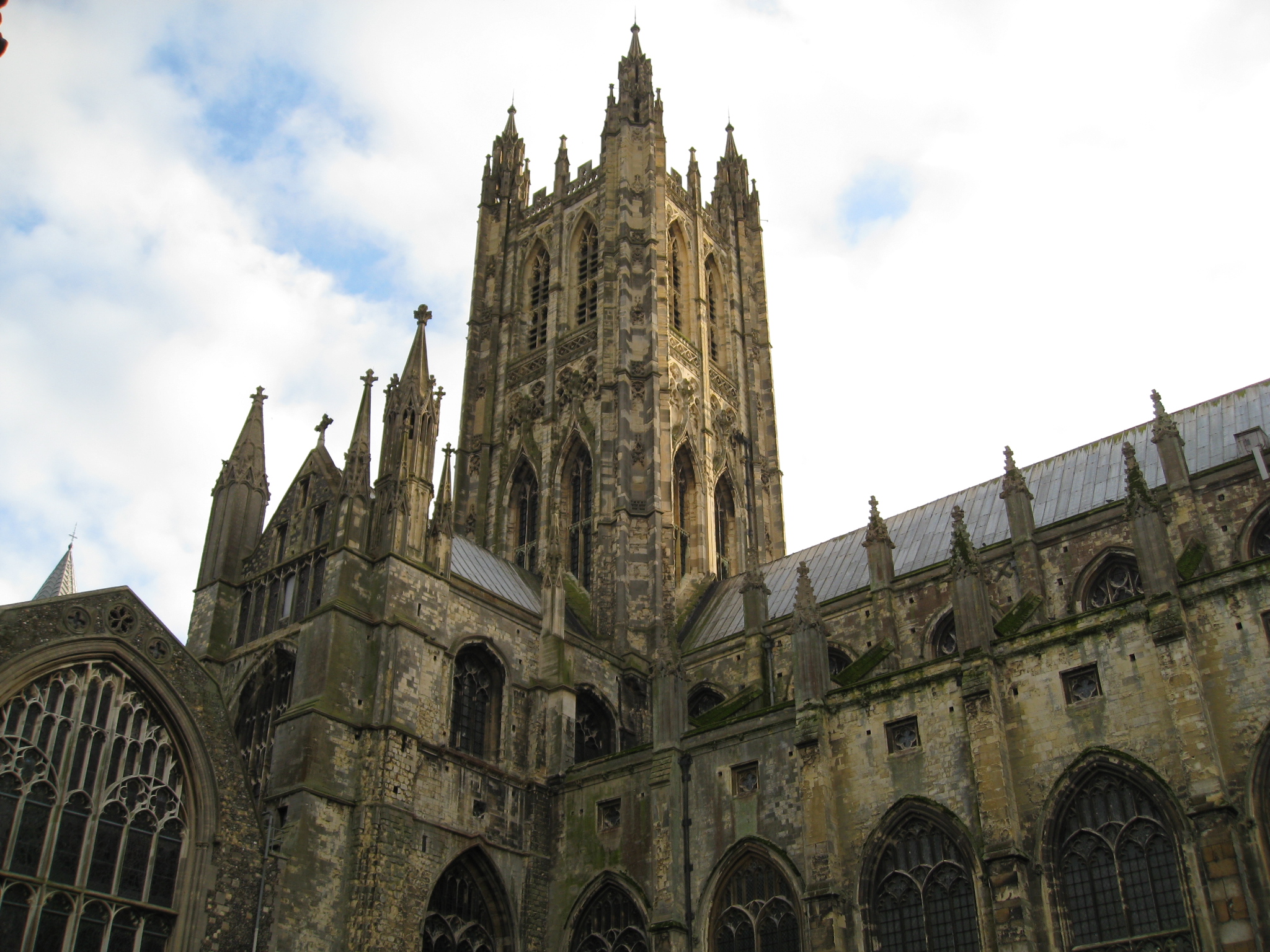
The King's School, Canterbury
The King's School is a public school (English independent day and boarding school for 13 to 18 year old pupils) in Canterbury, Kent, England. It is a member of the Headmasters' and Headmistresses' Conference and the Eton Group. It is Britain's oldest public school; and is arguably the oldest continuously operating school in the world, since education on the Abbey and Cathedral grounds has been uninterrupted since AD 597. History The school started as a medieval cathedral school said to have been founded during Late Antiquity in AD 597, a century after the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, by Augustine of Canterbury, considered the "Apostle to the English" and a founder of the English Church, thus making it arguably the world's oldest extant school. This is based on the fact that St Augustine founded an abbey (within the current school's grounds) where it is known that teaching took place. When the Dissolution of the Monasteries took place, the school was re-founded by royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour, Kent, River Stour. The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate (bishop), primate of the Church of England and the worldwide Anglican Communion owing to the importance of Augustine of Canterbury, St Augustine, who served as the apostle to the Anglo-Saxon paganism, pagan Kingdom of Kent around the turn of the 7th century. The city's Canterbury Cathedral, cathedral became a major focus of Christian pilgrimage, pilgrimage following the 1170 Martyr of the Faith, martyrdom of Thomas Becket, although it had already been a well-trodden pilgrim destination since the murder of Ælfheah of Canterbury, St Alphege by the men of cnut, King Canute in 1012. A journey of pilgrims to Becket's shrine served as the narrative frame, frame for Geoffrey Chaucer's 14th-century Wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Day School
A day school — as opposed to a boarding school — is an educational institution where children and adolescents are given instructions during the day, after which the students return to their homes. A day school has full-day programs when compared to after-school programs. A day school is a learning center whereby the learners usually goes back to their dwelling place daily and they do not dwell at the study center. It could be a secondary or tertiary Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago. The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start ... day school. It could also be privately or government owned. Consequently, parents and guardians are not required to pay for accommodation and feeding fees, this is due to the non residential status of a day school. Day school helps the child to receiving a dual training from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Mitchinson (bishop)
John Mitchinson (23 September 183325 September 1918) was a British teacher and Anglican priest who was Bishop of Barbados and later served as Master of Pembroke College, Oxford. Education He was born in Durham on 23 September 1833 and educated at Durham School and at Pembroke College, Oxford, where he gained first class honours in '' literae humaniores'' (classics) and natural science. Career He was an Assistant Master at Merchant Taylors' School, Northwood, then Headmaster of the King's School, Canterbury from 1859 to 1873. Ordained in 1860, he became part of the staff of St Philip's Church, Clerkenwell, under Warwick Reed Wroth. In 1873, he was appointed Bishop of Barbados, holding the post for eight years, but becoming known as Bishop of Barbados and the Windward Islands from 1877, when he created the separate Diocese of the Windward Islands but remained as bishop over that diocese too. He also served as coadjutor bishop (1879–1882) for Walrond Jackson, Bishop of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Tradescant The Younger
John Tradescant the Younger (; 4 August 1608 – 22 April 1662), son of John Tradescant the Elder, was a botanist and gardener. The standard author abbreviation Trad. is applied to species he described. Biography Son of John Tradescant the Elder, he was born in Meopham, Kent, and educated at The King's School, Canterbury. Like his father, who collected specimens and rarities on his many trips abroad, he undertook collecting expeditions to Virginia between 1628 and 1637 (and possibly two more trips by 1662, though Potter and other authors doubt this). Among the seeds he brought back, to introduce to English gardens were great American trees, including magnolias, bald cypress and tulip tree, and garden plants such as phlox and asters. John Tradescant the Younger added his American acquisitions to the family's cabinet of curiosities, known as The Ark. These included the ceremonial cloak of Chief Powhatan, an important Native American relic. South Lambeth Road in Vauxhall wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Harvey
William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician who made influential contributions in anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, the systemic circulation and properties of blood being pumped to the brain and the rest of the body by the heart, though earlier writers, such as Realdo Colombo, Michael Servetus, and Jacques Dubois, had provided precursors of the theory. Family William's father, Thomas Harvey, was a jurat of Folkestone where he served as mayor in 1600. Records and personal descriptions delineate him as an overall calm, diligent, and intelligent man whose "sons... revered, consulted and implicitly trusted in him... (they) made their father the treasurer of their wealth when they acquired great estates...(He) kept, employed, and improved their gainings to their great advantage." Thomas Harvey's portrait can still be seen in the central panel of a wall of the dining room at Rolls Park, Chig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Marlowe
Christopher Marlowe, also known as Kit Marlowe (; baptised 26 February 156430 May 1593), was an English playwright, poet and translator of the Elizabethan era. Marlowe is among the most famous of the Elizabethan playwrights. Based upon the "many imitations" of his play ''Tamburlaine,'' modern scholars consider him to have been the foremost dramatist in London in the years just before his mysterious early death. Some scholars also believe that he greatly influenced William Shakespeare, who was baptised in the same year as Marlowe and later succeeded him as the pre-eminent Elizabethan playwright. Marlowe was the first to achieve critical reputation for his use of blank verse, which became the standard for the era. His plays are distinguished by their overreaching protagonists. Themes found within Marlowe's literary works have been noted as humanistic with realistic emotions, which some scholars find difficult to reconcile with Marlowe's "anti-intellectualism" and his caterin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Twyne
John Twyne (c.1505–1581) was an English schoolmaster, scholar and author, and also Member of Parliament for Canterbury. Life He was born about 1501 at Bullington, Hampshire, the son of William Twyne. He was educated, according to Anthony Wood, at New Inn, Oxford, but the matter is uncertain and he seems to have frequented Corpus Christi College; he says he saw there Richard Foxe, Juan Luis Vives, and others. He graduated B.C.L. on 31 January 1525, and then married and became master of the free grammar school at Canterbury. Twyne's school was a success, and he grew rich, purchasing land. He took an active part in the municipal affairs of Canterbury: he was a common councilman from 1539 to 1547 and 1548 to 1550, Sheriff of Canterbury for 1544–45, an alderman from 1550 to 1562 and mayor of the city for 1553–4. In 1553 he represented the city in parliament. He gave offence to the Duke of Northumberland, and on 18 May the mayor of Canterbury was directed to send him up to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reginald Pole
Reginald Pole (12 March 1500 – 17 November 1558) was an English cardinal of the Catholic Church and the last Catholic archbishop of Canterbury, holding the office from 1556 to 1558, during the Counter-Reformation. Early life Pole was born at Stourton Castle, Staffordshire, on 12 March 1500, the third son of Sir Richard Pole and Margaret Pole, 8th Countess of Salisbury. He was named after the now Blessed Reginald of Orleans, O.P. His maternal grandparents were George Plantagenet, 1st Duke of Clarence, and Isabella Neville, Duchess of Clarence; thus he was a great-nephew of kings Edward IV and Richard III and a great-grandson of Richard Neville, 16th Earl of Warwick. Pole received his early education at Sheen Priory. He matriculated at Magdalen College, Oxford, in 1512, and at Oxford was taught by William Latimer and Thomas Linacre, graduating with a BA on 27 June 1515. In February 1518, King Henry VIII granted him the deanery of Wimborne Minster, Dorset; after which he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry VIII Of England
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disagreement with Pope Clement VII about such an annulment led Henry to initiate the English Reformation, separating the Church of England from papal authority. He appointed himself Supreme Head of the Church of England and dissolved convents and monasteries, for which he was excommunicated by the pope. Henry is also known as "the father of the Royal Navy" as he invested heavily in the navy and increased its size from a few to more than 50 ships, and established the Navy Board. Domestically, Henry is known for his radical changes to the English Constitution, ushering in the theory of the divine right of kings in opposition to papal supremacy. He also greatly expanded royal power during his reign. He frequently used charges of treason and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but since the 14th century have only been used in place of private acts to grant a right or power to an individual or a body corporate. They were, and are still, used to establish significant organisations such as boroughs (with municipal charters), universities and learned societies. Charters should be distinguished from royal warrants of appointment, grants of arms and other forms of letters patent, such as those granting an organisation the right to use the word "royal" in their name or granting city status, which do not have legislative effect. The British monarchy has issued over 1,000 royal charters. Of these about 750 remain in existence. The earliest charter recorded on the UK government's list was granted to the University of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
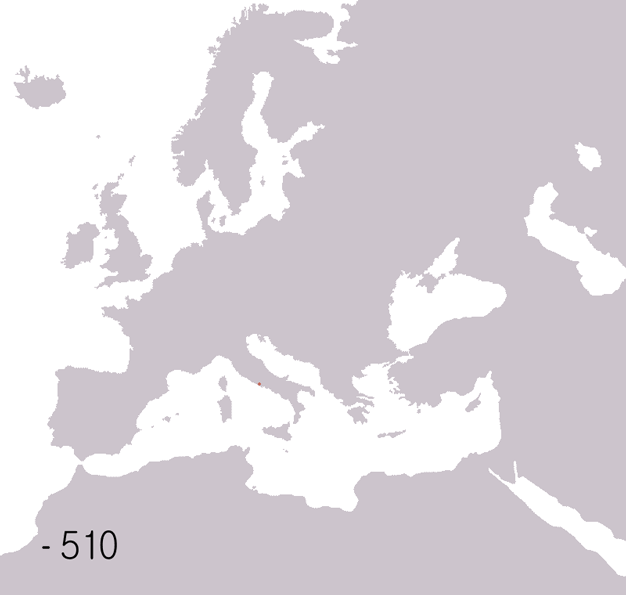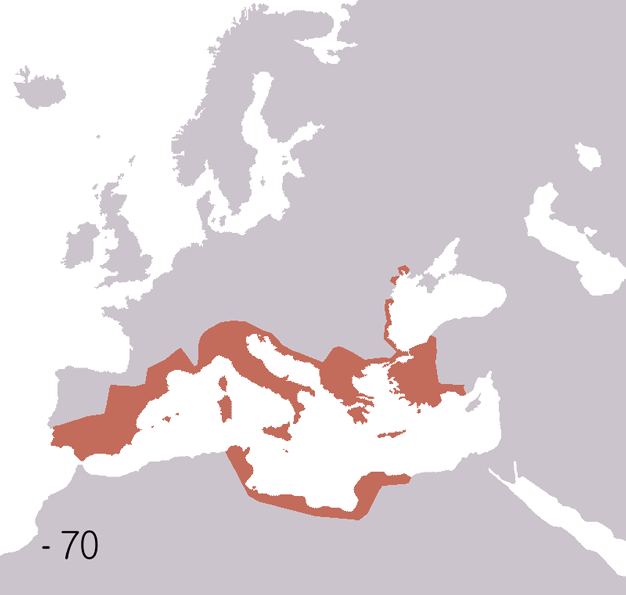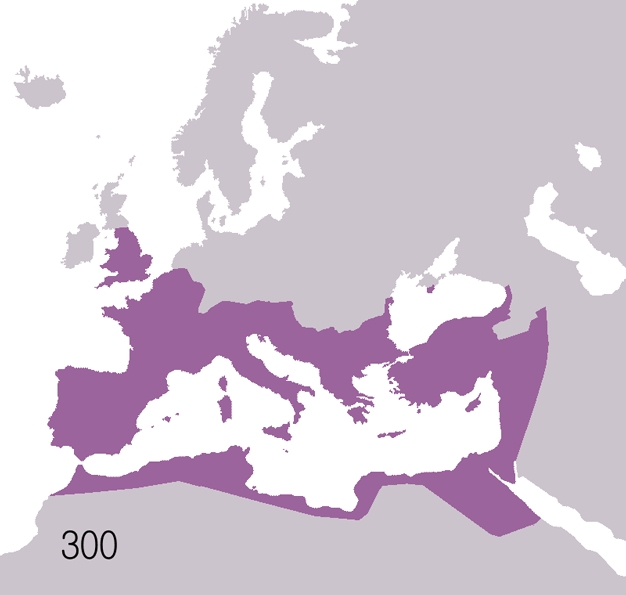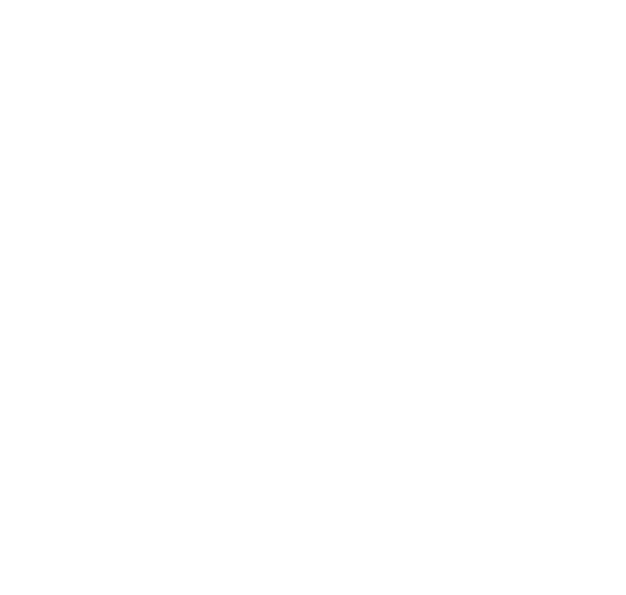
Fall Of The Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Ancient Rome, Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided into several successor Polity, polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control over its Western Roman province, provinces; modern historians posit factors including the effectiveness and numbers of the Late Roman army, army, the health and numbers of the Roman population, the strength of the Roman economy, economy, the competence of the Roman emperor, emperors, the internal struggles for power, the religious changes of the period, and the efficiency of the civil administration. Increasing pressure from invading barbarians outside Roman culture also contributed greatly to the collapse. Climate variability and change, Climatic changes and both Endemic (epide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Venenbild.jpg)