|
Tetrapodomorph
The Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) are a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as ''Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodamorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the Stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a humerus with convex he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapodomorpha
The Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) are a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as ''Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodamorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the Stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a humerus with convex he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcopterygii
Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass including amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (with mammals being the only extant group), evolved from certain sarcopterygians; under a cladistic view, tetrapods are themselves considered a subgroup within Sarcopterygii. The known extant non-tetrapod sarcopterygians include two species of coelacanths and six species of lungfishes. Characteristics Early lobe-finned fishes are bony fish with fleshy, lobed, paired fins, which are joined to the body by a single bone. The fins of lobe-finned fishes differ from those of all other fish in that each is borne on a fleshy, lobelike, scaly stalk extending from the body. The scales of sarcopterygians are true scaloids, consisting of lamellar bone sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcopterygii
Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass including amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (with mammals being the only extant group), evolved from certain sarcopterygians; under a cladistic view, tetrapods are themselves considered a subgroup within Sarcopterygii. The known extant non-tetrapod sarcopterygians include two species of coelacanths and six species of lungfishes. Characteristics Early lobe-finned fishes are bony fish with fleshy, lobed, paired fins, which are joined to the body by a single bone. The fins of lobe-finned fishes differ from those of all other fish in that each is borne on a fleshy, lobelike, scaly stalk extending from the body. The scales of sarcopterygians are true scaloids, consisting of lamellar bone sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Carboniferous, 350 million years ago. The specific aquatic ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Carboniferous, 350 million years ago. The specific aquatic ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
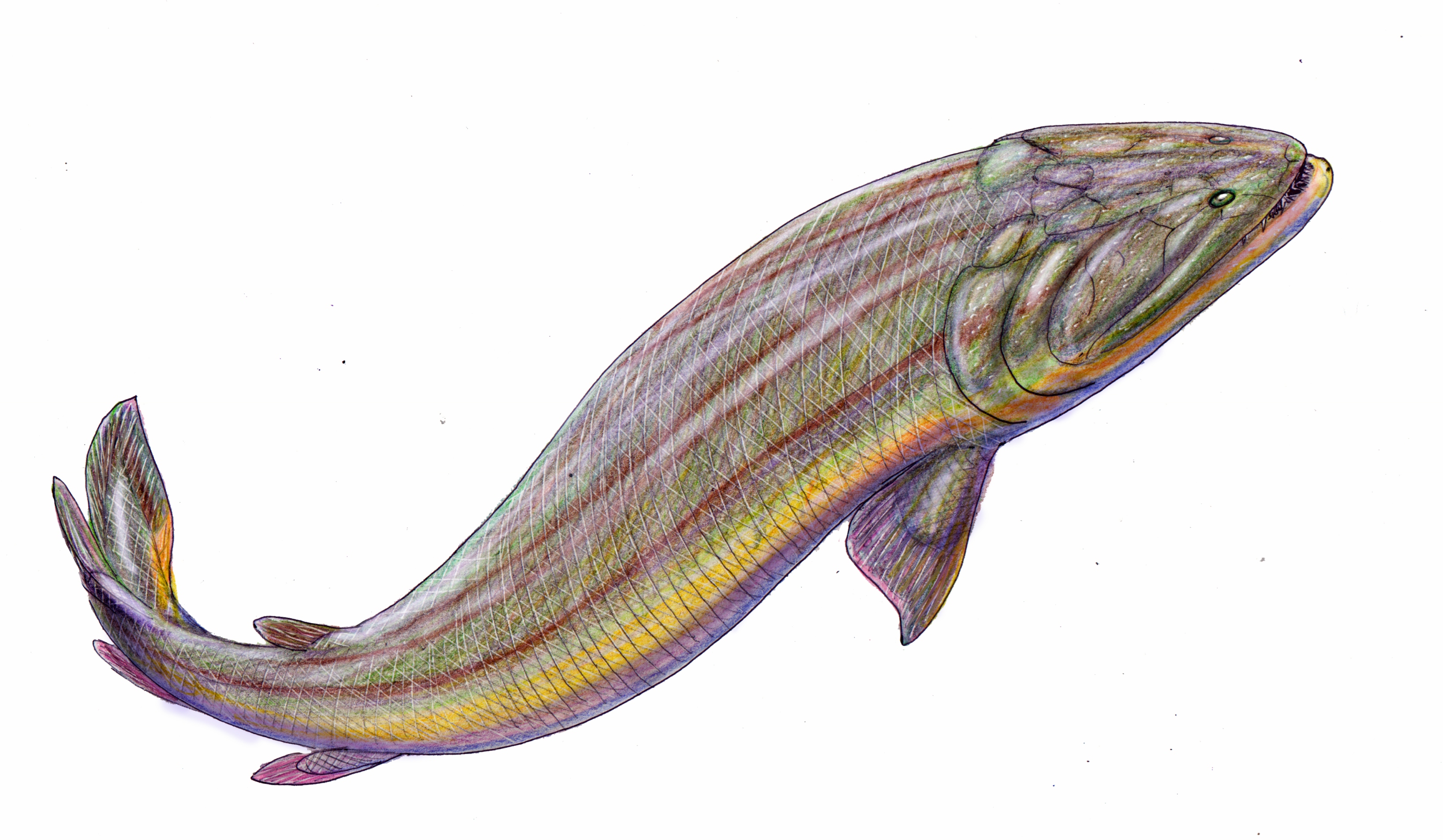
Kenichthys
''Kenichthys'' is a genus of sarcopterygian fish from the Devonian period, and a member of the clade tetrapodomorpha. The only known species of the genus is ''Kenichthys campbelli'' (named for the Australian palaeontologist Ken Campbell), the first remains of which were found in China in 1993.Chang, M. and Zhu, M. (1993) A new Middle Devonian osteolepidid from Qujing, Yunnan. ''Mem. Assoc. Australas. Palaeontol.'' 15 183-198 The genus is important to the study of the evolution of tetrapods due to the unique nature of its nostrils, which provide vital evidence regarding the evolutionary transition of fish-like nostrils to the tetrapod choanae.Zhu, M. and Ahlberg, P. (2004) The origin of the internal nostril of tetrapods. ''Nature'' 432 94-97 Description ''Kenichthys'' was a small tetrapodomorph, with a skull about long. While only areas of the front of the body are known, it seems likely that ''Kenichthys'' would have been similar in general body form to other basal sarcoptery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteolepidida
Osteolepiformes, also known as Osteolepidida, is a group of prehistoric lobe-finned fishes which first appeared during the Devonian period. The order contains the families Canowindridae, Megalichthyidae, Osteolepididae and Tristichopteridae. The order is generally considered to be paraphyletic because the characters that define it are mainly attributes of stem tetrapodomorphs. Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... showing the paraphyly of Osteolepiformes compiled and modified from Ahlberg and Johanson (1998). See also Swartz (2012). Osteolepiformes is marked by the green bracket. References External linksTree of Life Tetrapodomorphs Prehistoric fish orders Paraphyletic groups {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizodontidae
Rhizodontida is an extinct group of predatory tetrapodomorphs known from many areas of the world from the Givetian through to the Pennsylvanian - the earliest known species is about 377 million years ago (Mya), the latest around 310 Mya. Rhizodonts lived in tropical rivers and freshwater lakes and were the dominant predators of their age. They reached huge sizes - the largest known species, '' Rhizodus hibberti'' from Europe and North America, was an estimated 7 m in length, making it the largest freshwater fish known. Description The upper jaw had a marginal row of small teeth on the maxilla and premaxilla, medium-sized fangs on the ectopterygoid and dermopalatine bones, and large tusks on the vomers and premaxillae. On the lower jaw were marginal teeth on the dentary, with fangs on the three coronoids and a huge tusk at the symphysial tip of the dentary. Apparently, the left and right mandibles rotated inwards towards each other on biting. This may have been a kinetic mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauripteridae
Rhizodontida is an extinct group of predatory tetrapodomorphs known from many areas of the world from the Givetian through to the Pennsylvanian - the earliest known species is about 377 million years ago (Mya), the latest around 310 Mya. Rhizodonts lived in tropical rivers and freshwater lakes and were the dominant predators of their age. They reached huge sizes - the largest known species, '' Rhizodus hibberti'' from Europe and North America, was an estimated 7 m in length, making it the largest freshwater fish known. Description The upper jaw had a marginal row of small teeth on the maxilla and premaxilla, medium-sized fangs on the ectopterygoid and dermopalatine bones, and large tusks on the vomers and premaxillae. On the lower jaw were marginal teeth on the dentary, with fangs on the three coronoids and a huge tusk at the symphysial tip of the dentary. Apparently, the left and right mandibles rotated inwards towards each other on biting. This may have been a kinetic mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizodontida
Rhizodontida is an extinct group of predatory tetrapodomorphs known from many areas of the world from the Givetian through to the Pennsylvanian - the earliest known species is about 377 million years ago (Mya), the latest around 310 Mya. Rhizodonts lived in tropical rivers and freshwater lakes and were the dominant predators of their age. They reached huge sizes - the largest known species, '' Rhizodus hibberti'' from Europe and North America, was an estimated 7 m in length, making it the largest freshwater fish known. Description The upper jaw had a marginal row of small teeth on the maxilla and premaxilla, medium-sized fangs on the ectopterygoid and dermopalatine bones, and large tusks on the vomers and premaxillae. On the lower jaw were marginal teeth on the dentary, with fangs on the three coronoids and a huge tusk at the symphysial tip of the dentary. Apparently, the left and right mandibles rotated inwards towards each other on biting. This may have been a kinetic mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteolepiform
Osteolepiformes, also known as Osteolepidida, is a group of prehistoric lobe-finned fishes which first appeared during the Devonian period. The order contains the families Canowindridae, Megalichthyidae, Osteolepididae and Tristichopteridae. The order is generally considered to be paraphyletic because the characters that define it are mainly attributes of stem tetrapodomorphs. Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... showing the paraphyly of Osteolepiformes compiled and modified from Ahlberg and Johanson (1998). See also Swartz (2012). Osteolepiformes is marked by the green bracket. References External linksTree of Life Tetrapodomorphs Prehistoric fish orders Paraphyletic groups {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsenia
''Tungsenia'' is an extinct genus of basal tetrapodomorph bony fish known from the ~409 mya (Early Devonian) of northeastern Yunnan Province, China. Its remains were discovered in the Posongchong Formation. It is the basalmost In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to th ... known tetrapodomorph. References Tetrapodomorphs Fossil taxa described in 2012 {{Paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |