|
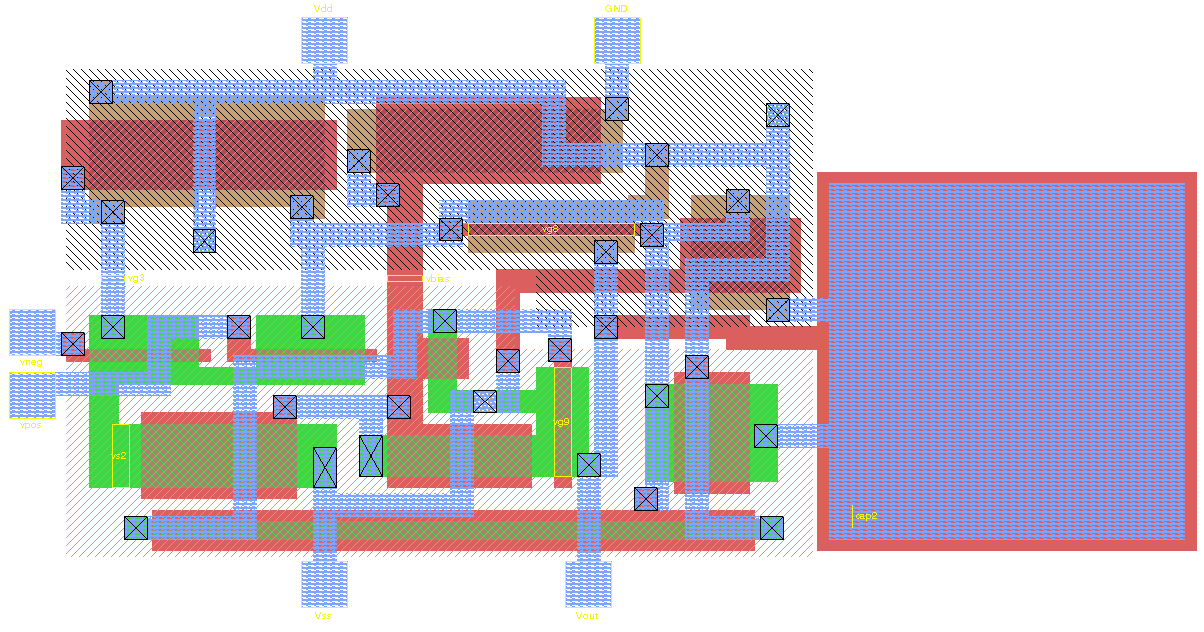
Tape Out
In electronics and photonics design, tape-out or tapeout is the final stage of the design process for integrated circuits or printed circuit boards before they are sent for manufacturing. The tapeout is specifically the point at which the graphic for the photomask of the circuit is sent to the fabrication facility. The name originates from the use of magnetic tape to send the data to the manufacturing facility. Procedures involved The term ''tapeout'' currently is used to describe the creation of the photomask itself from the final approved electronic CAD file. Designers may use this term to refer to the writing of the final file to disk or CD and its subsequent transmission to the semiconductor foundry; however, in current practice, the foundry will perform checks and make modifications to the mask design specific to the manufacturing process before actual tapeout. These modifications of the mask data include: * ''Chip finishing'' which includes custom designations and stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronics Design
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together in a design flow that chip designers use to design and analyze entire semiconductor chips. Since a modern semiconductor chip can have billions of components, EDA tools are essential for their design; this article in particular describes EDA specifically with respect to integrated circuits (ICs). History Early days The earliest electronic design automation is attributed to IBM with the documentation of its 700 series computers in the 1950s. Prior to the development of EDA, integrated circuits were designed by hand and manually laid out. Some advanced shops used geometric software to generate tapes for a Gerber photoplotter, responsible for generating a monochromatic exposure image, but even those copied digital recordings of mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resolution Enhancement Technologies
Resolution enhancement technologies are methods used to modify the photomasks in the lithographic processes used to make integrated circuits (ICs or "chips") to compensate for limitations in the optical resolution of the projection systems. These processes allow the creation of features well beyond the limit that would normally apply due to the Rayleigh criterion. Modern technologies allow the creation of features on the order of 5 nanometers (nm), far below the normal resolution possible using deep ultraviolet (DUV) light. Background Integrated circuits are created in a multi-step process known as photolithography. This process starts with the design of the IC circuitry as a series of layers than will be patterned onto the surface of a sheet of silicon or other semiconductor material known as a wafer. Each layer of the ultimate design is patterned onto a photomask, which in modern systems is made of fine lines of chromium deposited on highly purified quartz glass. Chromium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
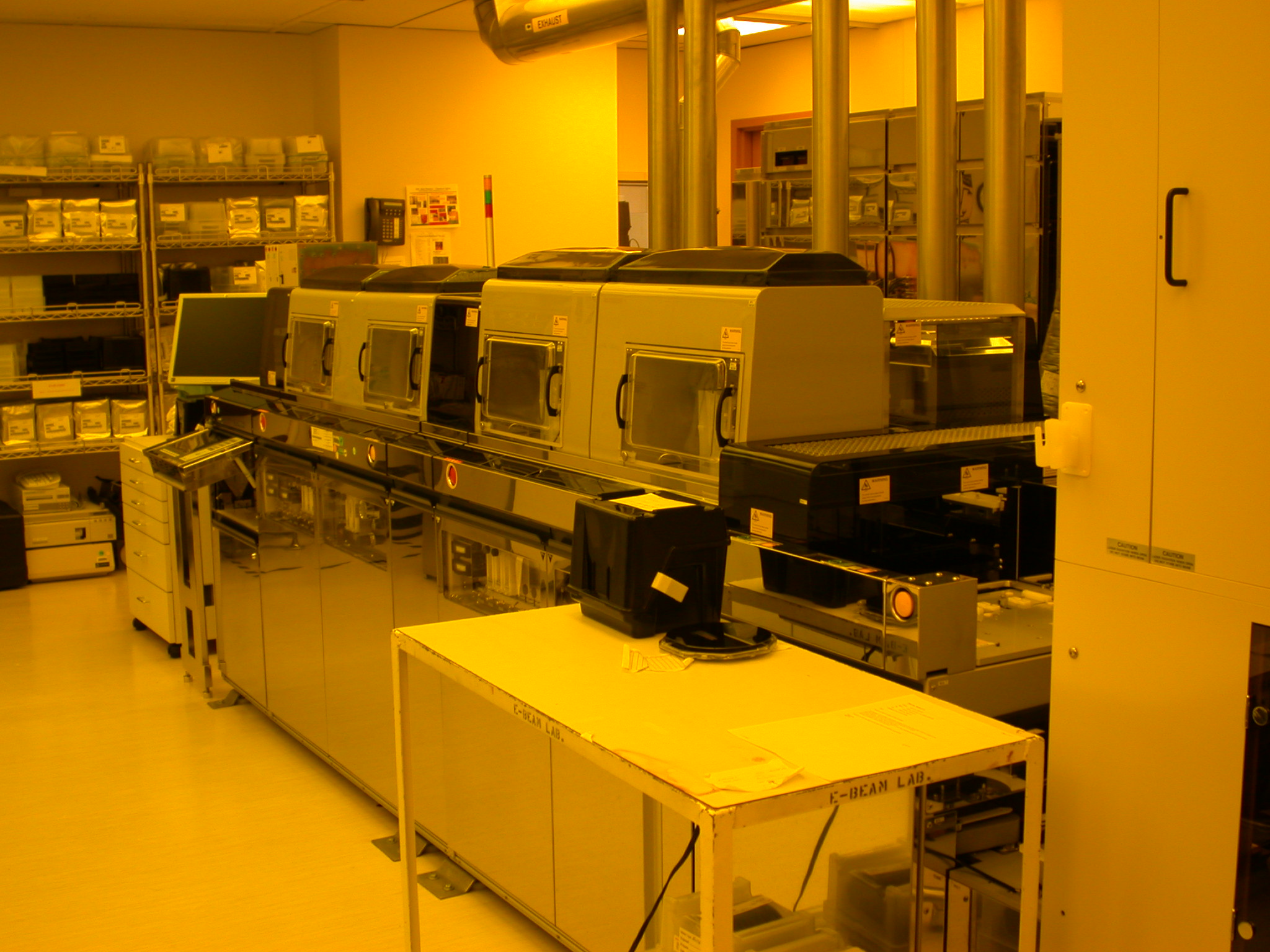
Semiconductor Fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuits (ICs) such as microprocessors, microcontrollers, and memories (such as RAM and flash memory). It is a multiple-step photolithographic and physico-chemical process (with steps such as thermal oxidation, thin-film deposition, ion-implantation, etching) during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer, typically made of pure single-crystal semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications. This article focuses on the manufacture of integrated circuits, however steps such as etching and photolithography can be used to manufacture other devices such as LCD and OLED displays. The fabrication process is performed in highly specialized semiconductor fabrication plants, also called foundries or "fabs", with the central part being the " clean room". In more advanced semi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American multinational semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog chips and embedded processors, which account for more than 80% of its revenue. TI also produces digital light processing (DLP) technology and education technology products including calculators, microcontrollers, and multi-core processors. Texas Instruments emerged in 1951 after a reorganization of Geophysical Service Incorporated, a company founded in 1930 that manufactured equipment for use in the seismic industry, as well as defense electronics. TI produced the world's first commercial silicon transistor in 1954, and the same year designed and manufactured the first transistor radio. Jack Kilby invented the integrated circuit in 1958 while working at TI's Central Research Labs. TI also invented the hand-held calculator in 1967, and intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototype is generally used to evaluate a new design to enhance precision by system analysts and users. Prototyping serves to provide specifications for a real, working system rather than a theoretical one. Physical prototyping has a long history, and paper prototyping and virtual prototyping now extensively complement it. In some design workflow models, creating a prototype (a process sometimes called materialization) is the step between the Formal specification, formalization and the evaluation of an idea. A prototype can also mean a typical example of something such as in the use of the derivation prototypical. This is a useful term in identifying objects, behaviours and concepts which are considered the accepted norm and is analogous with terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signoff (electronic Design Automation)
In the automated design of integrated circuits, signoff (also written as sign-off) checks is the collective name given to a series of verification steps that the design must pass before it can be taped out. This implies an iterative process involving incremental fixes across the board using one or more check types, and then retesting the design. There are two types of sign-off's: front-end sign-off and back-end sign-off. After back-end sign-off, the chip goes to fabrication. After listing out all the features in the specification, the verification engineer will write coverage for those features to identify bugs, and send back the RTL design to the designer. Bugs, or defects, can include issues like missing features (comparing the layout to the specification), errors in design (typo and functional errors), etc. When the coverage reaches a maximum percentage then the verification team will sign it off. By using a methodology like UVM, OVM, or VMM, the verification team develops a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Design Automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing Electronics, electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together in a Design flow (EDA), design flow that chip designers use to design and analyze entire semiconductor chips. Since a modern semiconductor chip can have billions of components, EDA tools are essential for their design; this article in particular describes EDA specifically with respect to integrated circuits (ICs). History Early days The earliest electronic design automation is attributed to IBM with the documentation of its IBM 700/7000 series, 700 series computers in the 1950s. Prior to the development of EDA, integrated circuits were designed by hand and manually laid out. Some advanced shops used geometric software to generate tapes for a Gerber format, Gerber photoplotter, responsible for generating a monochromatic ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Proximity Correction
Optical proximity correction (OPC) is a photolithography enhancement technique commonly used to compensate for image errors due to diffraction or process effects. The need for OPC is seen mainly in the making of semiconductor devices and is due to the limitations of light to maintain the edge placement integrity of the original design, after processing, into the etched image on the silicon wafer. These projected images appear with irregularities such as line widths that are narrower or wider than designed, these are amenable to compensation by changing the pattern on the photomask used for imaging. Other distortions such as rounded corners are driven by the resolution of the optical imaging tool and are harder to compensate for. Such distortions, if not corrected for, may significantly alter the electrical properties of what was being fabricated. Optical proximity correction corrects these errors by moving edges or adding extra polygons to the pattern written on the photomask. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design For Manufacturability (IC)
Design for manufacturability (also sometimes known as design for manufacturing or DFM) is the general engineering practice of designing products in such a way that they are easy to manufacture. The concept exists in almost all engineering disciplines, but the implementation differs widely depending on the manufacturing technology. DFM describes the process of designing or engineering a product in order to facilitate the manufacturing process in order to reduce its manufacturing costs. DFM will allow potential problems to be fixed in the design phase which is the least expensive place to address them. Other factors may affect the manufacturability such as the type of raw material, the form of the raw material, dimensional tolerances, and secondary processing such as finishing. Depending on various types of manufacturing processes there are set guidelines for DFM practices. These DFM guidelines help to precisely define various tolerances, rules and common manufacturing checks relate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit Design
Integrated circuit design, semiconductor design, chip design or IC design, is a sub-field of electronics engineering, encompassing the particular Boolean logic, logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits (ICs). An IC consists of miniaturized electronic components built into an electrical network on a monolithic semiconductor substrate by photolithography. IC design can be divided into the broad categories of Digital data, digital and analog electronics, analog IC design. Digital IC design is to produce components such as microprocessors, FPGAs, memories (Random-access memory, RAM, Read-only memory, ROM, and flash memory, flash) and digital Application-specific integrated circuit, ASICs. Digital design focuses on logical correctness, maximizing circuit density, and placing circuits so that clock and timing signals are routed efficiently. Analog IC design also has specializations in power IC design and Radio frequency, RF IC design. Analog IC design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mask Data Preparation
A mask is an object normally worn on the face, typically for protection, disguise, performance, or entertainment, and often employed for rituals and rites. Masks have been used since antiquity for both ceremonial and practical purposes, as well as in the performing arts and for entertainment. They are usually worn on the face, although they may also be positioned for effect elsewhere on the wearer's body. In art history, especially sculpture, "mask" is the term for a face without a body that is not modelled in the round (which would make it a "head"), but for example appears in low relief. Etymology The word "mask" appeared in English in the 1530s, from Middle French ''masque'' "covering to hide or guard the face", derived in turn from Italian ''maschera'', from Medieval Latin ''masca'' "mask, specter, nightmare". This word is of uncertain origin, perhaps from Arabic ''maskharah'' مَسْخَرَۃٌ "buffoon", from the verb ''sakhira'' "to ridicule". However, it may a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Foundry
In the microelectronics industry, a semiconductor fabrication plant, also called a ''fab'' or a ''foundry'', is a factory where integrated circuits (ICs) are manufactured. The ''cleanroom'' is where all fabrication takes place and contains the machinery for integrated circuit production such as steppers and/or scanners for photolithography, etching, cleaning, and doping. All these devices are extremely precise and thus extremely expensive. Prices for pieces of equipment for the processing of 300 mm wafers range to upwards of $4,000,000 each with a few pieces of equipment reaching as high as $340,000,000 (e.g. EUV scanners). A typical fab will have several hundred equipment items. Semiconductor fabrication requires many expensive devices. Estimates put the cost of building a new fab at over one billion U.S. dollars with values as high as $3–4 billion not being uncommon. For example, TSMC invested $9.3 billion in its ''Fab15'' in Taiwan. The same company estimations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |