|
Tail-sitter
A tail-sitter, or tailsitter, is a type of VTOL aircraft that takes off and lands on its tail, then tilts horizontally for forward flight. Originating in the 1920s with the inventor Nikola Tesla, the first aircraft to adopt a tail-sitter configuration were developed by Nazi Germany during the Second World War. Development of such aircraft spiked during the late 1940s and 1950s, as aircraft designers and defence planners alike recognised the potential value of fixed-wing aircraft that could perform both a vertical take-off and vertical landing while also transitioning into and out of conventional flight. Inherent problems with tail-sitter aircraft were poor pilot visibility and control difficulties, especially during vertical descent and landing. Programmes to develop manned tail-sitters were typically terminated in the form of the more practical thrust vectoring approach, as used by aircraft such as the Hawker Siddeley Harrier and Yakovlev Yak-38. Description A tail-sitter sits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
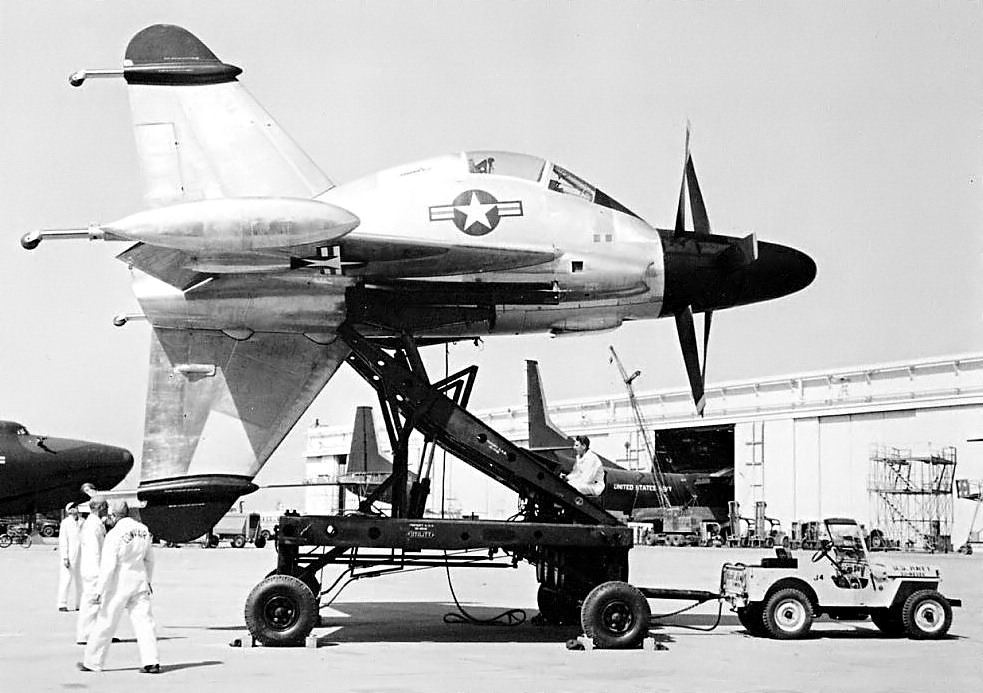 |
Convair XFY
The Convair XFY Pogo was an experiment in vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) tail-sitter. The Pogo had delta wings and three-bladed contra-rotating propellers powered by a turboprop engine. It was intended to be a high-performance fighter aircraft capable of operating from small warships. Landing the XFY-1 was difficult, as the pilot had to look over his shoulder while carefully working the throttle to land. Design and development After World War II, the Cold War prompted the United States Army and Navy to study VTOL operations. It was envisaged to protect task forces, convoys or any fleet, even without aircraft carriers, by placing VTOL aircraft on any ship. These fighters would be housed within a conical protective housing, saving limited deck space available aboard ships. They would provide first line of airborne defense and reconnaissance capability, before more aircraft could be scrambled to help, with flight performance that helicopters could not provide. In May 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
VTOL
A vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft is one that can take off and land vertically without relying on a runway. This classification can include a variety of types of aircraft including helicopters as well as thrust-vectoring fixed-wing aircraft and other hybrid aircraft with powered rotors such as cyclogyros/cyclocopters and gyrodynes. Some VTOL aircraft can operate in other modes as well, such as CTOL (conventional take-off & landing), STOL (short take-off & landing), or STOVL (short take-off & vertical landing). Others, such as some helicopters, can only operate as VTOL, due to the aircraft lacking landing gear that can handle taxiing. VTOL is a subset of V/STOL (vertical or short take-off & landing). Some lighter-than-air aircraft also qualify as VTOL aircraft, as they can hover, takeoff and land with vertical approach/departure profiles. Electric vertical takeoff and landing aircraft, or eVTOLs, are being developed along with more autonomous flight con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), Glider (aircraft), gliders, Powered paragliding, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Aircrew, Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard Aircraft pilot, pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, Powered aircraft#Methods of propulsion, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
SNECMA Coléoptère
The SNECMA C.450 Coléoptère (meaning "beetle" in French, descended from Greek for "sheathed wing") was a vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft that was designed by the French company SNECMA and manufactured by Nord Aviation. While work on the aircraft proceeded to the test flying phase, the project never progressed beyond experimental purposes. The Coléoptère was one of multiple efforts to produce a viable VTOL aircraft being conducted around the world throughout the 1950s. SNECMA had previously experimented with several wingless test rigs, known as the Atar Volant, which influenced the design. In terms of its general configuration, the Coléoptère was a single-person aircraft with an unusual annular wing; the aircraft was designed to take-off and land vertically, therefore requiring no runway and very little space. Performing its maiden flight during December 1958, the sole prototype was destroyed on its ninth flight on 25 July 1959. While there were intentions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Contra-rotating Propeller
Aircraft equipped with contra-rotating propellers, also referred to as CRP, coaxial contra-rotating propellers, or high-speed propellers, apply the maximum power of usually a single piston or turboprop engine to drive a pair of coaxial propellers in contra-rotation. Two propellers are arranged one behind the other, and power is transferred from the engine via a planetary gear or spur gear transmission. Contra-rotating propellers are also known as counter-rotating propellers, although counter-rotating propellers is much more widely used when referring to airscrews on separate non-coaxial shafts turning in opposite directions. Operation When airspeed is low, the mass of the air flowing through the propeller disk (thrust) causes a significant amount of tangential or rotational air flow to be created by the spinning blades. The energy of this tangential air flow is wasted in a single-propeller design, and causes handling problems at low speed as the air strikes the vertical sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Kaman Aircraft
Kaman Corporation is an American aerospace company, with headquarters in Bloomfield, Connecticut. It was founded in 1945 by Charles Kaman. During the first ten years the company operated exclusively as a designer and manufacturer of several helicopters that set world records and achieved many aviation firsts. In 1956, Kaman began to diversify as an aerospace subcontractor of McDonnell Douglas, Grumman, and others. In the mid-1960s Kaman diversified outside of the aerospace industry, using the expertise Kaman had gained in composite materials and the end of the need for skilled woodworkers to craft wooden rotor blades. Charles Kaman, a guitarist as well as an aerospace pioneer, worked with his engineers and other musicians to create the round-backed, composite-body Ovation guitar, which led to the eventual creation of Kaman Music (now KMCMusicorp). Kaman Music was an independent distributor of musical instruments and accessories, and a major producer of guitars and guitar par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg) |
Interceptor Aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are capable of being or are employed as both ‘standard’ air superiority fighters and as interceptors are sometimes known as fighter-interceptors. There are two general classes of interceptor: light fighters, designed for high performance over short range; and heavy fighters, which are intended to operate over longer ranges, in contested airspace and adverse meteorological conditions. While the second type was exemplified historically by specialized night fighter and all-weather interceptor designs, the integration of mid-air refueling, satellite navigation, on-board radar and beyond visual range (BVR) missile systems since the 1960s has allowed most frontline fighter designs to fill the roles once reserved for specialised night/all-we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Supersonic
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound (Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times the speed of sound (Mach 5) are often referred to as hypersonic. Flights during which only some parts of the air surrounding an object, such as the ends of rotor blades, reach supersonic speeds are called transonic. This occurs typically somewhere between Mach 0.8 and Mach 1.2. Sounds are traveling vibrations in the form of pressure waves in an elastic medium. Objects move at supersonic speed when the objects move faster than the speed at which sound propagates through the medium. In gases, sound travels longitudinally at different speeds, mostly depending on the molecular mass and temperature of the gas, and pressure has little effect. Since air temperature and composition varies significantly with altitude, the speed of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Ramjet
A ramjet, or athodyd (aero thermodynamic duct), is a form of airbreathing jet engine that uses the forward motion of the engine to produce thrust. Since it produces no thrust when stationary (no ram air) ramjet-powered vehicles require an assisted take-off like a rocket assist to accelerate it to a speed where it begins to produce thrust. Ramjets work most efficiently at supersonic speeds around and can operate up to speeds of . Ramjets can be particularly useful in applications requiring a small and simple mechanism for high-speed use, such as missiles. The US, Canada, and UK had widespread ramjet powered missile defenses during the 1960s onward, such as the CIM-10 Bomarc and Bloodhound. Weapon designers are looking to use ramjet technology in artillery shells to give added range; a 120 mm mortar shell, if assisted by a ramjet, is thought to be able to attain a range of . They have also been used successfully, though not efficiently, as tip jets on the ends of hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Annular Wing
A closed wing is a wing that effectively has two main planes which merge at their ends so that there are no conventional wing tips. Closed wing designs include the annular wing (commonly known as the cylindrical or ring wing), the joined wing, the box wing and spiroid tip devices. Like many wingtip devices, the closed wing aims to reduce the wasteful effects associated with wingtip vortices which occur at the tips of conventional wings. Although the closed wing has no unique claim on such benefits, many closed wing designs do offer structural advantages over a conventional cantilever monoplane. Characteristics Wingtip vortices form a major component of wake turbulence and are associated with induced drag, which is a significant contributor to total drag in most regimes. A closed wing avoids the need for wingtips and thus might be expected to reduce wingtip drag effects. In addition to potential structural advantages over open cantilevered wings, closed wing surfaces have som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Helmut Zborowski
Helmut Graf von Zborowski (21 August 1905 in Theresienstadt, Bohemia – 16 November 1969 in Brunoy, France) was an Austrian aircraft designer for VTOL. In rocket technology, he was involved in the development of the Fieseler Fi 103 and the A4 with Wernher von Braun Wernher Magnus Maximilian Freiherr von Braun ( , ; 23 March 191216 June 1977) was a German and American aerospace engineer and space architect. He was a member of the Nazi Party and Allgemeine SS, as well as the leading figure in the develop .... References 1905 births 1969 deaths Austrian designers Aircraft designers People from Terezín {{engineer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |