|
Systems Neuroscience
Systems neuroscience is a subdiscipline of neuroscience and systems biology that studies the structure and function of neural circuits and systems. Systems neuroscience encompasses a number of areas of study concerned with how nerve cells behave when connected together to form neural pathways, neural circuits, and larger brain networks. At this level of analysis, neuroscientists study how different neural circuits analyze sensory information, form perceptions of the external world, make decisions, and execute movements. Researchers in systems neuroscience are concerned with the relation between molecular and cellular approaches to understanding brain structure and function, as well as with the study of high-level mental functions such as language, memory, and self-awareness (which are the purview of behavioral and cognitive neuroscience). Systems neuroscientists typically employ techniques for understanding networks of neurons as they are seen to function, by way of electroph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the science, scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders. It is a Multidisciplinary approach, multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and Mathematical Modeling, mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the Biology, biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular biology, molecular and cell biology, cellular studies of indivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example: * Fluorodeoxyglucose ( 18F">sup>18FDG or FDG) is commonly used to detect cancer; * 18Fodium fluoride">sup>18Fodium fluoride (Na18F) is widely used for detecting bone formation; * Oxygen-15 (15O) is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common imaging technique, a medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical – a radioisotope attached to a drug – is injected into the body as a radioactive tracer, tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is emitted, and when the positron interacts with an or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Substrate
A neural substrate is a term used in neuroscience to indicate the part of the central nervous system (i.e., brain and spinal cord) that underlies a specific behavior, cognitive process, or psychological state. ''Neural'' is an adjective relating to "a nerve or the nervous system", while a ''substrate'' is an "underlying substance or layer". Some examples are the neural substrates of language acquisition, memory, prediction and reward, pleasure, facial recognition Facial recognition or face recognition may refer to: * Face detection, often a step done before facial recognition * Face perception, the process by which the human brain understands and interprets the face * Pareidolia, which involves, in part, se ..., envisioning the future, intentional empathy, religious experience, spontaneous musical performance, and anxiety. See also * Neural correlate References Neuroscience {{neuroscience-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
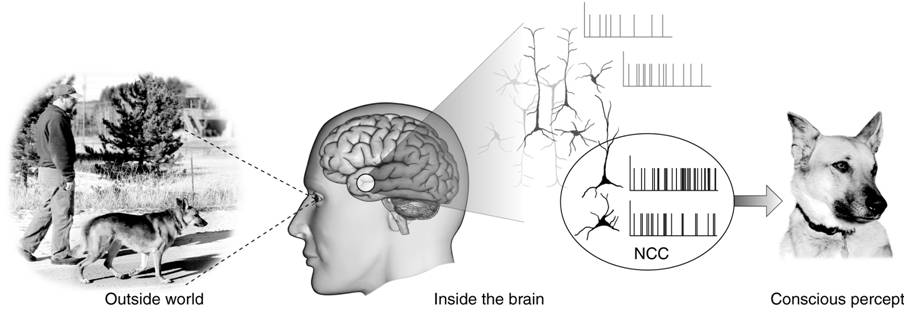
Neural Correlate
The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) refer to the relationships between mental states and neural states and constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena; that is, neural changes which necessarily and regularly correlate with a specific experience. The set should be ''minimal'' because, under the materialist assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it. Neurobiological approach to consciousness A science of consciousness must explain the exact relationship between subjective mental states and brain states, the nature of the relationship between the conscious mind and the electro-chemical interactions in the body (mind–body problem). Progress in neuropsychology and neurophilosophy has come from focusing on the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Oscillation
Neural oscillations, or brainwaves, are rhythmic or repetitive patterns of neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in an electroencephalogram. Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Neuroscience
Sensory neuroscience is a subfield of neuroscience which explores the anatomy and physiology of neurons that are part of sensory systems such as vision, hearing, and olfaction. Neurons in sensory regions of the brain respond to stimuli by firing one or more nerve impulses (action potentials) following stimulus presentation. How is information about the outside world encoded by the rate, timing, and pattern of action potentials? This so-called neural code is currently poorly understood and sensory neuroscience plays an important role in the attempt to decipher it. Looking at early sensory processing is advantageous since brain regions that are "higher up" (e.g. those involved in memory or emotion) contain neurons which encode more abstract representations. However, the hope is that there are unifying principles which govern how the brain encodes and processes information. Studying sensory systems is an important stepping stone in our understanding of brain function in general. Typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual System
The visual system comprises the sensory organ (the eye) and parts of the central nervous system (the retina containing photoreceptor cells, the optic nerve, the optic tract and the visual cortex) which gives organisms the sense of sight (the ability to detect and process visible light) as well as enabling the formation of several non-image photo response functions. It detects and interprets information from the optical spectrum perceptible to that species to "build a representation" of the surrounding environment. The visual system carries out a number of complex tasks, including the reception of light and the formation of monocular neural representations, colour vision, the neural mechanisms underlying stereopsis and assessment of distances to and between objects, the identification of a particular object of interest, motion perception, the analysis and integration of visual information, pattern recognition, accurate motor coordination under visual guidance, and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatosensory System
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch ( haptic perception), as well as temperature ( thermoception), body position ( proprioception), and pain. It is a subset of the sensory nervous system, which also represents visual, auditory, olfactory, and gustatory stimuli. Somatosensation begins when mechano- and thermosensitive structures in the skin or internal organs sense physical stimuli such as pressure on the skin (see mechanotransduction, nociception). Activation of these structures, or receptors, leads to activation of peripheral sensory neurons that convey signals to the spinal cord as patterns of action potentials. Sensory information is then processed locally in the spinal cord to drive reflexes, and is also conveyed to the brain for conscious perception of touch and proprioception. Note, somatosensory information from the face and head enters the brain through periph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory System
The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing sensory information. A sensory system consists of sensory neurons (including the sensory receptor cells), neural pathways, and parts of the brain involved in sensory perception. Commonly recognized sensory systems are those for vision, hearing, touch, taste, smell, and balance. Senses are transducers from the physical world to the realm of the mind where people interpret the information, creating their perception of the world around them. The receptive field is the area of the body or environment to which a receptor organ and receptor cells respond. For instance, the part of the world an eye can see, is its receptive field; the light that each rod or cone can see, is its receptive field. Receptive fields have been identified for the visual system, auditory system and somatosensory system. Stimulus :Organisms need information to solve at least three kinds of problems: (a) to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reward System
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and classical conditioning), and positively-valenced emotions, particularly ones involving pleasure as a core component (e.g., joy, euphoria and ecstasy). Reward is the attractive and motivational property of a stimulus that induces appetitive behavior, also known as approach behavior, and consummatory behavior. A rewarding stimulus has been described as "any stimulus, object, event, activity, or situation that has the potential to make us approach and consume it is by definition a reward". In operant conditioning, rewarding stimuli function as positive reinforcers; however, the converse statement also holds true: positive reinforcers are rewarding. The reward system motivates animals to approach stimuli or engage in behaviour that incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory System
The olfactory system, or sense of smell, is the sensory system used for smelling (olfaction). Olfaction is one of the special senses, that have directly associated specific organs. Most mammals and reptiles have a main olfactory system and an accessory olfactory system. The main olfactory system detects airborne substances, while the accessory system senses fluid-phase stimuli. The senses of smell and taste (gustatory system) are often referred to together as the chemosensory system, because they both give the brain information about the chemical composition of objects through a process called transduction. Structure Peripheral The peripheral olfactory system consists mainly of the nostrils, ethmoid bone, nasal cavity, and the olfactory epithelium (layers of thin tissue covered in mucus that line the nasal cavity). The primary components of the layers of epithelial tissue are the mucous membranes, olfactory glands, olfactory neurons, and nerve fibers of the olfactory nerves. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor System
The motor system is the set of central and peripheral structures in the nervous system that support motor functions, i.e. movement. Peripheral structures may include skeletal muscles and neural connections with muscle tissues. Central structures include cerebral cortex, brainstem, spinal cord, pyramidal system including the upper motor neurons, extrapyramidal system, cerebellum, and the lower motor neurons in the brainstem and the spinal cord. Pyramidal motor system The pyramidal motor system, also called the pyramidal tract or the corticospinal tract, start in the motor center of the cerebral cortex.Rizzolatti G, Luppino G (2001) The Cortical Motor System. ''Neuron'' 31: 889-90SD/ref> There are upper and lower motor neurons in the corticospinal tract. The motor impulses originate in the giant pyramidal cells or Betz cells of the motor area; i.e., precentral gyrus of cerebral cortex. These are the upper motor neurons (UMN) of the corticospinal tract. The axons of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |