|
Symmetry-protected Topological Order
Symmetry-protected topological (SPT) order is a kind of order in zero-temperature quantum-mechanical states of matter that have a symmetry and a finite energy gap. To derive the results in a most-invariant way, renormalization group methods are used (leading to equivalence classes corresponding to certain fixed points). The SPT order has the following defining properties: (a) ''distinct SPT states with a given symmetry cannot be smoothly deformed into each other without a phase transition, if the deformation preserves the symmetry''. (b) ''however, they all can be smoothly deformed into the same trivial product state without a phase transition, if the symmetry is broken during the deformation''. The above definition works for both bosonic systems and fermionic systems, which leads to the notions of bosonic SPT order and fermionic SPT order. Using the notion of quantum entanglement, we can say that SPT states are short-range entangled states ''with a symmetry'' (by contrast: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Absolute Zero
Absolute zero is the lowest limit of the thermodynamic temperature scale, a state at which the enthalpy and entropy of a cooled ideal gas reach their minimum value, taken as zero kelvin. The fundamental particles of nature have minimum vibrational motion, retaining only quantum mechanical, zero-point energy-induced particle motion. The theoretical temperature is determined by extrapolating the ideal gas law; by international agreement, absolute zero is taken as −273.15 degrees on the Celsius scale ( International System of Units), Note: The triple point of water is 0.01 °C, not 0 °C; thus 0 K is −2890.15 °C, not −273.16 °C. which equals −459.67 degrees on the Fahrenheit scale ( United States customary units or Imperial units). The corresponding Kelvin and Rankine temperature scales set their zero points at absolute zero by definition. It is commonly thought of as the lowest temperature possible, but it is not the lowest ''enthalpy'' stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
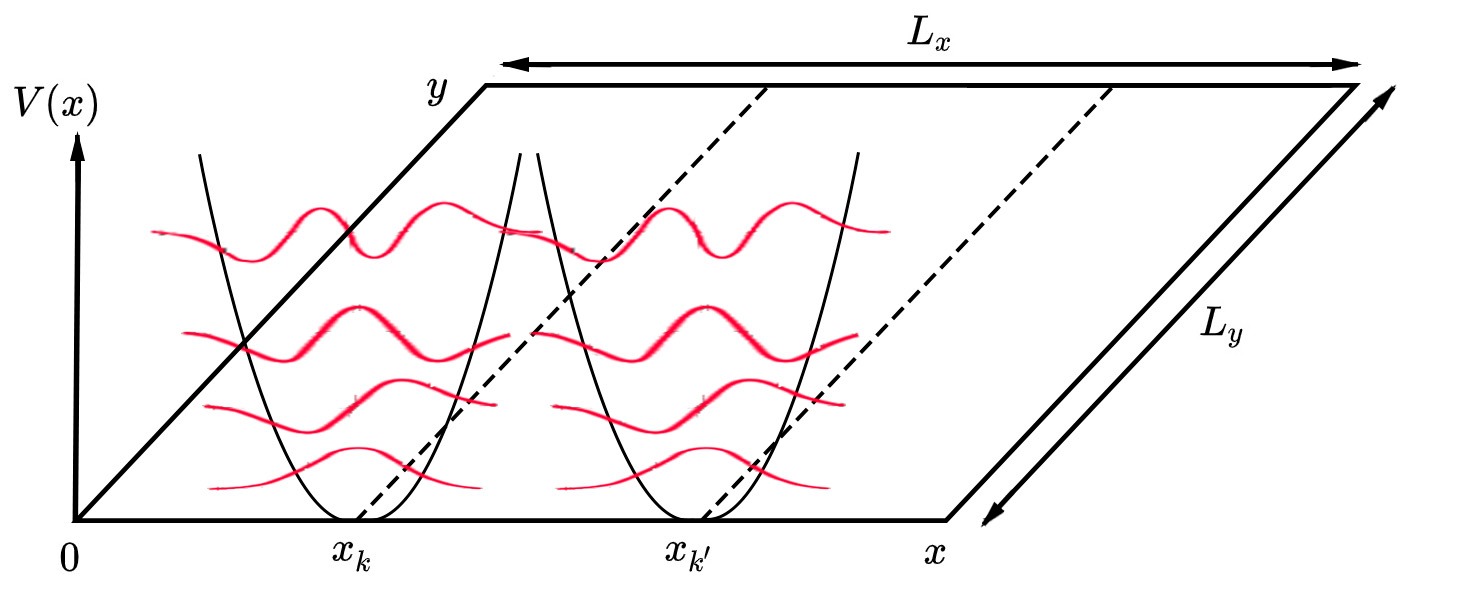 |
Quantum Hall Effect
The quantum Hall effect (or integer quantum Hall effect) is a quantized version of the Hall effect which is observed in two-dimensional electron systems subjected to low temperatures and strong magnetic fields, in which the Hall resistance exhibits steps that take on the quantized values : R_ = \frac = \frac , where is the Hall voltage, is the channel current, is the elementary charge and is Planck's constant. The divisor can take on either integer () or fractional () values. Here, is roughly but not exactly equal to the filling factor of Landau levels. The quantum Hall effect is referred to as the integer or fractional quantum Hall effect depending on whether is an integer or fraction, respectively. The striking feature of the integer quantum Hall effect is the persistence of the quantization (i.e. the Hall plateau) as the electron density is varied. Since the electron density remains constant when the Fermi level is in a clean spectral gap, this situation correspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Mathematical Physics
Mathematical physics refers to the development of mathematics, mathematical methods for application to problems in physics. The ''Journal of Mathematical Physics'' defines the field as "the application of mathematics to problems in physics and the development of mathematical methods suitable for such applications and for the formulation of physical theories". An alternative definition would also include those mathematics that are inspired by physics (also known as physical mathematics). Scope There are several distinct branches of mathematical physics, and these roughly correspond to particular historical periods. Classical mechanics The rigorous, abstract and advanced reformulation of Newtonian mechanics adopting the Lagrangian mechanics and the Hamiltonian mechanics even in the presence of constraints. Both formulations are embodied in analytical mechanics and lead to understanding the deep interplay of the notions of symmetry (physics), symmetry and conservation law, con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Condensed Matter Physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid phases which arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms. More generally, the subject deals with "condensed" phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions between them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on crystal lattices of atoms, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in ultracold atomic systems. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other theories to develop mathematical models. The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Quantum Phases
Quantum phases are quantum states of matter at zero temperature. Even at zero temperature a quantum-mechanical system has quantum fluctuations and therefore can still support phase transitions. As a physical parameter is varied, quantum fluctuations can drive a phase transition into a different phase of matter. An example of a canonical quantum phase transition is the well-studied Superconductor Insulator Transition in disordered thin films which separates two quantum phases having different symmetries. Quantum magnets provide another example of QPT. The discovery of new quantum phases is a pursuit of many scientists. These phases of matter exhibit properties and symmetries which can potentially be exploited for technological purposes and the benefit of mankind. The difference between these states and classical states of matter is that classically, materials exhibit different phases which ultimately depends on the change in temperature and/or density or some other macroscopic proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Topological Order
In physics, topological order is a kind of order in the zero-temperature phase of matter (also known as quantum matter). Macroscopically, topological order is defined and described by robust ground state degeneracy and quantized non-Abelian geometric phases of degenerate ground states. Microscopically, topological orders correspond to patterns of long-range quantum entanglement. States with different topological orders (or different patterns of long range entanglements) cannot change into each other without a phase transition. Various topologically ordered states have interesting properties, such as (1) topological degeneracy and fractional statistics or non-abelian statistics that can be used to realize a topological quantum computer; (2) perfect conducting edge states that may have important device applications; (3) emergent gauge field and Fermi statistics that suggest a quantum information origin of elementary particles; See also (4) topological entanglement entropy tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Quantum Spin Hall Effect
The quantum spin Hall state is a state of matter proposed to exist in special, two-dimensional semiconductors that have a quantized spin-Hall conductance and a vanishing charge-Hall conductance. The quantum spin Hall state of matter is the cousin of the integer quantum Hall state, and that does not require the application of a large magnetic field. The quantum spin Hall state does not break charge conservation symmetry and spin-S_z conservation symmetry (in order to have well defined Hall conductances). Description The first proposal for the existence of a quantum spin Hall state was developed by Charles Kane and Gene Mele who adapted an earlier model for graphene by F. Duncan M. Haldane which exhibits an integer quantum Hall effect. The Kane and Mele model is two copies of the Haldane model such that the spin up electron exhibits a chiral integer quantum Hall Effect while the spin down electron exhibits an anti-chiral integer quantum Hall effect. A relativistic version of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Periodic Table Of Topological Invariants
The periodic table of topological invariants is an application of topology to physics. It indicates the group of topological invariant for topological insulators and superconductors in each dimension and in each discrete symmetry class. Discrete symmetry classes There are ten discrete symmetry classes of topological insulators and superconductors, corresponding to the ten Altland–Zirnbauer classes of random matrices. They are defined by three symmetries of the Hamiltonian \hat = \sum_ H_ c_i^ c_j, (where c_i, and c_i^, are the annihilation and creation operators of mode i, in some arbitrary spatial basis) : time reversal symmetry, particle hole (or charge conjugation) symmetry, and chiral (or sublattice) symmetry. Chiral symmetry is a unitary operator S, that acts on c_i, as a unitary rotation (S c_i S^ = (U_S)_ c_j,) and satisfies S^2 = 1. A Hamiltonian H possesses chiral symmetry when S\hatS^=-\hat, for some choice of S (on the level of first-quantised Hamiltonians, this m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
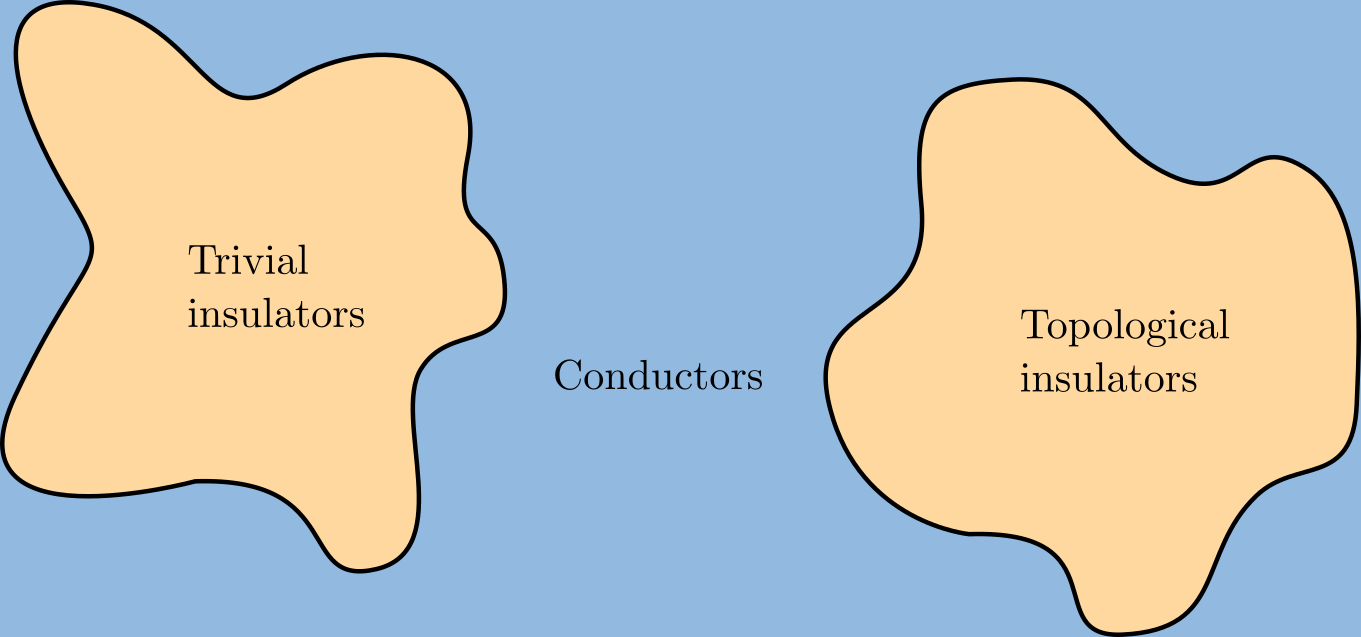 |
Topological Insulator
A topological insulator is a material whose interior behaves as an electrical insulator while its surface behaves as an electrical conductor, meaning that electrons can only move along the surface of the material. A topological insulator is an insulator for the same reason a " trivial" (ordinary) insulator is: there exists an energy gap between the valence and conduction bands of the material. But in a topological insulator, these bands are, in an informal sense, "twisted", relative to a trivial insulator. The topological insulator cannot be continuously transformed into a trivial one without untwisting the bands, which closes the band gap and creates a conducting state. Thus, due to the continuity of the underlying field, the border of a topological insulator with a trivial insulator (including vacuum, which is topologically trivial) is forced to support a conducting state. Since this results from a global property of the topological insulator's band structure, local (sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
AKLT Model
The AKLT model is an extension of the one-dimensional quantum Heisenberg spin model. The proposal and exact solution of this model by Ian Affleck, Elliott H. Lieb, Tom Kennedy and provided crucial insight into the physics of the spin-1 Heisenberg chain. It has also served as a useful example for such concepts as valence bond solid order, symmetry-protected topological order and matrix product state wavefunctions. Background A major motivation for the AKLT model was the Majumdar–Ghosh chain. Because two out of every set of three neighboring spins in a Majumdar–Ghosh ground state are paired into a singlet, or valence bond, the three spins together can never be found to be in a spin 3/2 state. In fact, the Majumdar–Ghosh Hamiltonian is nothing but the sum of all projectors of three neighboring spins onto a 3/2 state. The main insight of the AKLT paper was that this construction could be generalized to obtain exactly solvable models for spin sizes other than 1/2. Just a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Group Super-cohomology
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together. Groups of people * Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity * Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic identity * Religious group (other), a group whose members share the same religious identity * Social group, a group whose members share the same social identity * Tribal group, a group whose members share the same tribal identity * Organization, an entity that has a collective goal and is linked to an external environment * Peer group, an entity of three or more people with similar age, ability, experience, and interest Social science * In-group and out-group * Primary, secondary, and reference groups * Social group * Collectives Science and technology Mathematics * Group (mathematics), a set together with a binary operation satisfying certain algebraic conditions Chemistry * Functional group, a group of atoms whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Group Cohomology
In mathematics (more specifically, in homological algebra), group cohomology is a set of mathematical tools used to study groups using cohomology theory, a technique from algebraic topology. Analogous to group representations, group cohomology looks at the group actions of a group ''G'' in an associated ''G''-module ''M'' to elucidate the properties of the group. By treating the ''G''-module as a kind of topological space with elements of G^n representing ''n''- simplices, topological properties of the space may be computed, such as the set of cohomology groups H^n(G,M). The cohomology groups in turn provide insight into the structure of the group ''G'' and ''G''-module ''M'' themselves. Group cohomology plays a role in the investigation of fixed points of a group action in a module or space and the quotient module or space with respect to a group action. Group cohomology is used in the fields of abstract algebra, homological algebra, algebraic topology and algebraic numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |